10-K: Annual report pursuant to Section 13 and 15(d)
Published on February 21, 2024
UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
FORM
(Mark One)
ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the fiscal year ended
OR
TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the transition period from to
Commission file number
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter)
|
||
(State or Other Jurisdiction of Incorporation or Organization) |
(I.R.S. Employer Identification No.) |
|
|
|
||
(Address of Principal Executive Offices) |
(Zip Code) |
Registrant’s telephone number, including area code (
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act:
Title of each class |
Trading Symbol(s) |
|
Name of each exchange on which registered |
|
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act:
NONE
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act.
No ☐ |
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Act.
Yes ☐ |
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports) and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days.
No ☐ |
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically every Interactive Data File required to be submitted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit such files).
No ☐ |
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, a smaller reporting company or an emerging growth company. See the definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer,” “smaller reporting company” and “emerging growth company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act.
☑ |
Accelerated Filer |
☐ |
|
Non-accelerated Filer |
☐ |
Smaller reporting company |
|
Emerging growth company |
If an emerging growth company, indicate by check mark if the registrant has elected not to use the extended transition period for complying with any new or revised financial accounting standards provided pursuant to Section 13(a) of the Exchange Act. ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has filed a report on and attestation to its management’s assessment of the effectiveness of its internal control over financial
reporting under Section 404(b) of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act (15 U.S.C. 7262(b)) by the registered public accounting firm that prepared or issued its audit report.
If securities are registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act, indicate by check mark whether the financial statements of the registrant included in the filing reflect the correction of an error to previously issued financial statements.
Indicate by check mark whether any of those error corrections are restatements that required a recovery analysis of incentive-based compensation received by any of the registrant’s executive officers during the relevant recovery period pursuant to §240.10D-1(b). ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined by Rule 12b-2 of the Act).
Yes |
No ☑ |
The aggregate market value of the voting and non-voting common stock held by non-affiliates of the registrant computed as of June 30, 2023 (the last business day of the registrant’s most recent completed second fiscal quarter) based on the closing price of the Class A common stock on the New York Stock Exchange was $
Documents Incorporated by Reference:
Portions of the registrant’s definitive proxy statement for the 2024 annual meeting of stockholders, to be filed no later than 120 days after the end of the fiscal year, are incorporated by reference into Part III of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Table of Contents
1
PART I
CAUTIONARY NOTE REGARDING FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENTS
The information in this Annual Report on Form 10-K includes “forward-looking statements” within the meaning of Section 27A of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended (the “Securities Act”), and Section 21E of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the “Exchange Act”). All statements, other than statements of historical fact, included in this Annual Report regarding our strategy, future operations, financial position, estimated revenues and losses, projected costs, prospects, plans and objectives of management are forward-looking statements. When used in this Annual Report, the words “could,” “believe,” “anticipate,” “intend,” “estimate,” “expect,” “project,” “preliminary,” “forecast,” and similar expressions or variations are intended to identify forward-looking statements, although not all forward-looking statements contain such identifying words. These forward-looking statements are based on our current expectations and assumptions about future events and are based on currently available information as to the outcome and timing of future events. When considering forward-looking statements, you should keep in mind the risk factors and other cautionary statements described under the heading “Risk Factors” included elsewhere in this Annual Report on Form 10-K, as well as those set forth from time to time in our other filings with the Securities and Exchange Commission (the “SEC”). These forward-looking statements are based on management’s current belief, based on currently available information, as to the outcome and timing of future events.
Important factors that could cause actual results to differ materially from those in the forward-looking statements include, but are not limited to, those summarized below:
| ● | global economic distress, including that resulting from the sustained Russia-Ukraine war and related economic sanctions, the conflict in the Israel-Gaza region and continued hostilities in the Middle East, inflation and high interest rates, and potential energy insecurity in Europe, each of which may decrease demand for oil and natural gas or contribute to volatility in the prices for oil and natural gas, which may decrease demand for our services; |
| ● | actions taken by the members of the Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (“OPEC”) and Russia (together with OPEC and other allied producing countries, “OPEC+”) with respect to oil production levels and announcements of potential changes in such levels, including the ability of the OPEC+ countries to agree on and comply with announced supply limitations, which may be exacerbated by an increase in hostilities in the Middle East; |
| ● | the level of capital spending and access to capital markets by oil and gas companies in response to changes in commodity prices or reduced demand; |
| ● | the ability to source certain raw materials and other critical components or manufactured products globally on a timely basis from economically advantaged sources, including any delays and/or supply chain disruptions due to increased hostilities in the Middle East; |
| ● | the impact of central bank policy actions, such as sustained interest rate increases in response to high rates of inflation, and disruptions in the bank and capital markets; |
| ● | the severity and duration of world health events, including the coronavirus (“COVID-19”) pandemic and associated repercussions, and any resulting impact on commodity prices and supply and demand considerations; |
| ● | the potential deterioration of our customers’ financial condition, including defaults resulting from actual or potential insolvencies; |
| ● | the degree to which consolidation among our customers may affect spending on U.S. drilling and completions, including the recent consolidation in the Permian Basin; |
2
| ● | trends and volatility in oil and gas prices, and our ability to manage through such volatility; |
| ● | the impact of current and future laws, rulings and governmental regulations, including those related to hydraulic fracturing, accessing water, disposing of wastewater, transferring produced water, interstate freshwater transfer, chemicals, carbon pricing, pipeline construction, taxation or emissions, leasing, permitting or drilling on federal lands and various other environmental matters; |
| ● | regional impacts to our business, including our key infrastructure assets within the Bakken, the Northern Delaware and Midland Basin portions of the Permian Basin, and the Haynesville; |
| ● | capacity constraints on regional oil, natural gas and water gathering, processing and pipeline systems that result in a slowdown or delay in drilling and completion activity, and thus a decrease in the demand for our services in our core markets; |
| ● | regulatory and related policy actions intended by federal, state and/or local governments to reduce fossil fuel use and associated carbon emissions, or to drive the substitution of renewable forms of energy for oil and gas, may over time reduce demand for oil and gas and therefore the demand for our services, including as a result of the Inflation Reduction Act of 2022 (“IRA 2022”) or otherwise; |
| ● | actions taken by the Biden Administration or state governments, such as executive orders or new or expanded regulations, that may negatively impact the future production of oil and natural gas in the U.S. or our customers’ access to federal and state lands for oil and gas development operations, thereby reducing demand for our services in the affected areas; |
| ● | changes in global political or economic conditions, generally, and in the markets we serve, including the rate of inflation and potential economic recession; |
| ● | growing demand for electric vehicles that may result in reduced demand for refined products deriving from crude oil such as gasoline and diesel fuel, and therefore the demand for our services; |
| ● | our ability to hire and retain key management and employees, including skilled labor; |
| ● | our access to capital to fund expansions, acquisitions and our working capital needs and our ability to obtain debt or equity financing on satisfactory terms, including as a result of sustained increases in cost of capital resulting from Federal Reserve policies and otherwise; |
| ● | our health, safety and environmental performance; |
| ● | the impact of competition on our operations; |
| ● | the degree to which our E&P customers may elect to operate their water-management services in-house rather than source these services from companies like us; |
| ● | our level of indebtedness and our ability to comply with covenants contained in our Sustainability-Linked Credit Facility (as defined herein) or future debt instruments; |
| ● | delays or restrictions in obtaining permits by us or our customers; |
| ● | constraints in supply or availability of equipment used in our business; |
| ● | the impact of advances or changes in well-completion technologies or practices that result in reduced demand for our services, either on a volumetric or time basis; |
3
| ● | acts of terrorism, war or political or civil unrest in the U.S. or elsewhere, such as the Russia-Ukraine war, the conflict in the Israel-Gaza region and/or other instability and hostilities in the Middle East; |
| ● | accidents, weather, natural disasters or other events affecting our business; and |
| ● | the other risks identified in this Annual Report on Form 10-K, including, without limitation, those under the headings “Item 1A. Risk Factors,” “Item 1. Business,” “Item 7. Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” and “Item 13. Certain Relationships and Related Transactions, and Director Independence.” |
These factors are not necessarily all of the important factors that could cause actual results to differ materially from those expressed in any of our forward-looking statements. Other unknown or unpredictable factors also could have material adverse effects on our future results. Our future results will depend upon various other risks and uncertainties, including those described elsewhere in this Annual Report. Readers are cautioned not to place undue reliance on forward-looking statements, which speak only as of the date hereof. We undertake no obligation to update or revise any forward-looking statements after the date they are made, whether as a result of new information, future events or otherwise. All forward-looking statements attributable to us are qualified in their entirety by this cautionary note.
4
Risk Factor Summary
Risks Related to Our Business Operations
| ● | Our business depends on capital spending by the oil and gas industry in the U.S. and reductions in capital spending could have a material adverse effect on our liquidity, results of operations and financial condition. |
| ● | Continuing or worsening inflationary issues and associated changes in monetary policy have resulted in and may result in additional increases to the costs of our goods, services and personnel, which in turn could cause our capital expenditures and operating costs to rise. |
| ● | The failure to successfully integrate acquired assets or operations on a timely basis. |
| ● | Continued volatility in oil and/or natural gas prices may adversely affect the demand for our services. |
| ● | The IRA 2022 could accelerate the transition to new energy sources and could impose new costs on our customers’ operations. |
| ● | Our key infrastructure assets in Louisiana, North Dakota, New Mexico and Texas are immobile and thus vulnerable to risks associated with conducting business in these regions. |
| ● | Restrictions on the ability to procure water or changes in sourcing or disposal requirements could add costs or decrease demand for some of our services. |
| ● | Regulatory and societal efforts to reduce fossil fuel use and associated carbon emissions could reduce demand for oil and natural gas, and thereby the demand for our services, including as a result of the IRA 2022 or otherwise. |
| ● | We may be subject to claims for personal injury and property damage. |
| ● | We may be subject to cybersecurity risks. |
| ● | We may be adversely affected by uncertainty in the global financial markets and a worldwide economic downturn. |
| ● | A significant increase in fuel prices may adversely affect our transportation costs. |
Risks Related to Customers and Suppliers
| ● | Significant price volatility or interruptions in supply of our raw materials for our chemicals business may result in increased costs and negatively impact our financial results. |
Risks Related to Compliance with Regulations
| ● | Legislative and regulatory initiatives in the U.S. relating to hydraulic fracturing or water management could result in operating restrictions, delays or cancellations in our customers’ operations, reducing demand for our services. |
| ● | Our and our customers' operations are subject to a number of regulatory risks as a result of climate change initiatives. |
| ● | Our chemical products are subject to regulations that tend to become more onerous over time, that could result in increased costs. |
| ● | State and federal legislation and regulatory initiatives relating to our disposal operations and seismicity could harm our business. |
Risks Related to Personnel and Related Parties
| ● | Our industry typically experiences a high rate of employee turnover. |
| ● | Transactions with related parties present possible conflicts of interest. |
Risks Related to Our Capital Structure
| ● | If we fail to maintain and enhance an effective system of internal controls, we may not be able to accurately report our financial results or prevent fraud. |
| ● | We may incur indebtedness or issue additional equity securities to execute our long-term growth strategy. |
5
| ● | Our Sustainability-Linked Credit Facility subjects us to various financial and other restrictive covenants. |
| ● | Future sales or issuances of our equity securities may depress our share price or dilute your ownership. |
| ● | Provisions in our governing documents and Delaware law may discourage takeover attempts. |
| ● | SES Legacy Holdings, LLC (“Legacy Owner Holdco”) controls a significant percentage of our voting power. |
| ● | Our amended and restated certificate of incorporation may limit certain corporate opportunities. |
| ● | Our amended and restated certificate of incorporation designates the Court of Chancery of the State of Delaware as the sole and exclusive forum for certain types of actions and proceedings. |
Risks Related to Our Organizational Structure
| ● | We are a holding company and our sole material asset consists of common units (“SES Holdings LLC Units”) in SES Holdings, LLC (“SES Holdings”), which we are dependent upon for distributions and payments. |
| ● | We are party to two tax receivable agreements (the “Tax Receivable Agreements”) that require payments for certain tax benefits, and such payment amounts could be significant. |
| ● | In certain cases, payments under the Tax Receivable Agreements may be accelerated and/or significantly exceed the actual benefits. |
| ● | If SES Holdings were to become a publicly-traded partnership taxable as a corporation for U.S. federal income tax purposes, we could experience tax inefficiencies. |
| ● | Crestview Partners II GP, L.P. (“Crestview GP”) may have interests that conflict with the interests of holders of the Class A common stock. |
| ● | Our ability to use certain of our current and future net operating loss carryforwards (“NOLs”) may be limited and could adversely affect our operating results and cash flows. |
General Risks
| ● | We may not be able to finance future growth of our operations or future acquisitions. |
| ● | The growth of our business through acquisitions may expose us to various risks. |
| ● | Our success depends on key members of our management. |
| ● | We may be required to take write-downs of the carrying values of our long-lived assets and finite-lived intangible assets. |
ITEM 1. BUSINESS
Select Water Solutions, Inc. and its consolidated subsidiaries (collectively referred to as “Select,” the “Company,” “we,” “us,” or “our”) is a leading provider of sustainable water-management and chemical solutions to the energy industry in the U.S. As a leader in the water solutions industry, we place the utmost importance on safe, environmentally responsible management of oilfield water throughout the lifecycle of a well. Additionally, we believe that responsibly managing water resources through our operations to help conserve and protect the environment in the communities in which we operate is paramount to our continued success.
With a footprint across every major unconventional basin in the U.S., we operate through three primary segments: Water Services, Water Infrastructure and Chemical Technologies.
Our Water Services segment, which contributed approximately 65% of our 2023 revenue and 68% of our 2022 revenue, provides the complex services needed to support new well completions as well as ongoing production over the life of the well, including water transfer, water sourcing, flowback and well testing, water containment, fluids hauling, water monitoring and water network automation, as well as various on-site rental equipment and accommodation offerings. Through our patented WaterONE™ automation services and our proprietary AquaView® software platform, our Water Services segment provides extensive technology solutions that enable 24/7 monitoring and visibility for our customers into all of their water-related operations, including hydrographic mapping, water volume and quality monitoring, remote pit and tank monitoring, leak detection, asset and fuel tracking and automated-equipment services. We believe these technologies help our customers lower their operating costs, improve well productivity, increase safety, reduce the risk of spills and reduce the environmental footprint of their operations.
6
Our Water Infrastructure segment, which contributed approximately 15% of our 2023 revenue and 9% of our 2022 revenue, develops, builds, and operates semi-permanent and permanent infrastructure solutions to support full life cycle water solutions. These solutions incorporate both new oil and gas well development as well as ongoing production activity, including recycling and disposal of flowback and produced water as well as the associated logistics. As our customers transition from appraisal to full-field development, our fixed infrastructure networks can provide environmental benefits by reducing the demand for water disposal volumes and water hauling by truck as well as economies of scale that help reduce their capital expenditures and lease operating expenses over the life of the field. These networks can also help balance water supply across regions and customers to promote greater water reuse.
Our Water Infrastructure operations, which include long-term contracted agreements and accompanying customer infrastructure investments, deliver not only water but also solutions that focus more prominently on produced water management over the life of the well compared to our other segments. These agreements, which commonly entail higher margins over a longer contractual term, underscore our commitment to environmental stewardship through the sustainable treatment, management and disposal of wastewater over the life of its production. Our operations facilitate both the delivery of, and the takeaway and reuse of water enabled by permanent pipeline infrastructure, semi-permanent pipeline infrastructure, fixed and mobile treatment and recycling facilities, earthen pits, and saltwater disposal wells (“SWDs”). These agreements often involve dedicated acreage commitments from customers that facilitate further infrastructure network expansion.
In line with our strategic vision, we are actively expanding our portfolio of water recycling facilities across multiple regions, emphasizing water recycling opportunities as a cornerstone of our operations. We recognize produced water as an invaluable, sustainable non-potable water source, naturally generated from sources below the water table during oil and/or gas production. Through our dedicated efforts in recycling, we aim to progressively reduce the proportion of produced water being reinjected into SWDs over time, thereby diminishing the industry’s reliance on fresh water and reinforcing our commitment to responsible resource management. We believe there is substantial opportunity to advance our recycling solutions to include the potential to recycle water for alternative beneficial reuse outside the energy industry over the long-term.
Specifically, we are pursuing solutions that could enable the beneficial reuse of produced water for non-energy applications. This could enable substitution of treated produced water in agriculture, carbon capture, or drought mitigation, among other opportunities. Further advancements could preserve substantial fresh water sources and enable the industry to become a contributor to the water lifecycle.
Our Chemical Technologies segment, which contributed approximately 20% of our 2023 revenue and 23% of our 2022 revenue, develops, manufactures, manages logistics and provides a full suite of chemicals used in hydraulic fracturing, stimulation, cementing, pipelines and well completions. Our completion chemicals are sold primarily to leading integrated and independent E&P companies and pressure-pumping service companies in the U.S. to support well stimulation and completion. We also provide customized water treatment and flow assurance solutions across the completion and production lifecycle. Additionally, through our FluidMatch™ solutions, we provide comprehensive testing and analysis of our customers’ application conditions, product chemistry and key performance requirements for oil and gas well completion fluid-system design. This process may include water profiling, application and fluid assessment, treatment assessment, product selection, optimization and customization.
Industry and Company Overview
Over the past two decades, advancements in horizontal drilling and completions technologies have led to significant and sustained growth in oil and natural gas production in the U.S. Advances in drilling and completion technology have propelled U.S. shale-oil production from about 500,000 barrels per day in 2010 to more than nine million barrels per day currently, accounting for approximately 10% of the total global oil supply. Additionally, U.S. shale gas production has increased from about 15 billion cubic feet per day in 2010 to about 80 billion cubic feet per day as of November 2023, or nearly 80% of U.S. natural gas production and nearly 20% of global natural gas supply. This growth has dramatically impacted fundamental global supply and demand dynamics and has resulted in a generally balanced to over-supplied market in recent years. While demand for oil and natural gas has generally increased over the last thirteen years, demand is cyclical and subject to many factors. For example in 2020, the market was significantly impacted by demand declines driven by the economic disruption resulting from the COVID-19 pandemic; however, this
7
impact was greatly abated over the last three years and demand has largely recovered to pre-pandemic levels. Demand in the energy industry has been further impacted by the sustained Russia-Ukraine war and related economic sanctions and the conflict in the Israel-Gaza region and increased hostilities in the Middle East. Demand for our services is largely influenced by the level of drilling and completion activity by E&P companies, which in turn depends largely on the current and anticipated profitability of developing oil and natural gas reserves, as well as the ongoing production of existing wells.
Water is essential to the development and completion of unconventional oil and gas wells, where producers rely on hydraulic fracturing to stimulate the production of oil and gas from subsurface rock formations with low permeability. The modern hydraulic fracturing process involves the high-pressure injection of large volumes of water and proppant, together with chemicals, through a cased and cemented wellbore into targeted subsurface formations thousands of feet below ground to fracture the surrounding rock. Modern hydraulic fracturing involves complex, engineered solutions to produce oil and gas from tight geological formations in a cost-effective manner.
The volume of water required to economically produce tight oil and gas reserves in the U.S. has grown in recent years and water and water-related services comprise a meaningful portion of our customers’ drilling and completion budgets. For example, in 2010, the completion of a typical horizontal well could require roughly 75,000 barrels of water, but today, current horizontal well completion designs can call for in excess of 750,000 barrels for a single well. Our customers’ current multi-well pad development plans can require in excess of five million barrels to complete all of the wells on the pad. Furthermore, in recent years and in the pursuit of further efficiencies, operators have advanced the development of “zipper fracturing” and “simul-fracturing” operations. Zipper fracturing results in two wells being stimulated on the same pad at the same time. This significantly reduces the amount of time needed to complete operations on a single pad. With simul-fracturing operations, operators can even further eliminate idle time on the remaining wells on a single pad by making forward progress across all the wells on a pad. For example, on a four-well, with simul-fracturing operations, the operator can pump down two wells, while perforating the other two, allowing you to complete more lateral footage in the same amount of time compared to current zipper-fracturing operations where two of the wells would remain idle during the stimulation phase of the first two wells. While this does not increase the overall water consumption on a per-site basis, this does significantly increase the volumetric flow rates required to the wellsite and the sophistication of the logistics required for delivery, while concurrently decreasing the overall number of days spent on a single location. Significant mechanical, logistical, environmental and safety issues related to the sourcing, transfer, storage and treatment of such large volumes of water and the rate of delivery have increased both the total cost of water and related services and the complexity and importance of the services required. This trend has shifted many of our customers’ operational focus away from legacy small, local water service providers, to larger regional and national players like us, who have the expertise, technology and scale to provide high-quality, reliable, comprehensive and environmentally responsible water-management solutions for the full extent of the water lifecycle.
Delivering these comprehensive and environmentally responsible water management solutions requires significant logistical expertise to overcome the challenges of gathering, treating, blending, and delivering significant volumes of produced water. These logistical challenges are typically met through a combination of temporary and permanent solutions utilizing pipe and hose infrastructure to deliver water across the broad geographic areas in which we operate. These logistical solutions significantly reduce the cost and environmental footprint compared to legacy solutions such as tank truck and frac tank operations. For a single representative multi-well pad that requires five million barrels of water, we can utilize our pipe and hose infrastructure solutions and eliminate the approximate equivalent of 38,500 tank truck loads from the roads. This significantly reduces the capital and operating expenditure costs for our customers while dramatically improving the safety of our operations. Importantly, these solutions also reduce the environmental impact and carbon footprint of our customers’ operations by limiting spills and diesel exhaust emissions, as well as reducing the social impact of heavy vehicle traffic in the communities in which we operate.
We also develop and source completion chemicals that are a key part of the U.S. energy industry. Completion chemicals are blended with water to improve the transport and placement of proppant in targeted zones within the producing geological formations. The induced fractures near the wellbore allow hydrocarbons to flow into the wellbore for extraction. Our team of chemists and research and development personnel work directly with our customers to support the optimization of their fracturing fluid systems through our FluidMatch™ solutions. Through laboratory and
8
application experience, we apply our expertise in chemistry to develop, manufacture and supply a wide range of specialized and customizable products to our customers for their well completion fluid systems.
Up to fifty percent of the water pumped into the well during the hydraulic fracturing process returns as “flowback” during the first several weeks following the well completion process, and a large percentage of the remainder, plus naturally occurring water in the producing formation, is recovered as produced water over the life of the well. The total volumes of flowback and produced water are significantly greater than the volumes used for new well completions. By some estimates, the U.S. oil and gas industry today produces over 24 billion barrels of water per year and this volume is likely to grow, relative to the demand for volumes for new well completions of approximately six billion barrels per year. This flowback and produced water must be captured, contained and then either treated and recycled for reuse in subsequent fracturing jobs or disposed of in an environmentally-responsible manner. We provide services that support the operator’s management of flowback and produced water for either reuse or disposal. Additionally, our customized chemical treatment programs help improve well productivity and reduce production costs, thereby extending the economic life of our customers’ oil and gas wells.
As produced water volumes have significantly grown in recent years, logistical advancements similar to those seen in the delivery of source water volumes for new well completions have been developed for managing these produced water volumes. Increasingly, the transportation of these produced water volumes has shifted away from traditional tank truck operations and onto gathering pipeline infrastructure for disposal or recycling and reuse. Recycling produced water through dedicated infrastructure for reuse significantly reduces the lease operating costs for our customers over the life of a well, while also reducing the environmental impact and carbon footprint of our customers’ operations by limiting diesel exhaust emissions and reducing truck traffic in our local communities.
We believe that sustainable water and chemical solutions are critical to the ongoing energy transition and will lead to a new era of growth for Select. As water is vital to the health, economic, and social well-being of our communities, our goal is to develop sustainable water solutions with a shared commitment to conservation. We have a dedicated team of specialists developing and deploying innovative water treatment and reuse solutions for our customers. We believe the opportunity to repurpose produced water for reuse in new well completions instead of using fresh water creates new sustainable water sources from previously inaccessible underground water resources. This also includes, over the long-term, the potential for repurposing produced water for new beneficial uses outside of the oil and gas industry instead of disposing of it, ultimately contributing positively back to the total water cycle. Select is actively partnering with industry leading oil and gas operators, universities and government agencies to develop and pilot technologies and processes to treat produced water for potential beneficial reuse opportunities with a goal to develop scalable and economic methods of treating produced water to create alternative water sources for commercial, non-consumptive agricultural or other industrial purposes. While the industry is still in the early stages of developing these solutions and the regulatory environment will require certain advancements to allow for these solutions to be provided at commercial scale, we believe that Select is well positioned to play a leadership role in the ultimate development and deployment of beneficial reuse technologies in the coming years.
Ultimately, our customers are required to manage more than 24 billion barrels of produced water annually, and we are focused on how we can create the most beneficial resource out of what has historically been viewed solely as a waste stream. We believe the industry will increasingly turn to specialized water solutions companies like us to help cost-effectively manage produced water in an environmentally responsible manner. Select intends to play an important role in the advancement of water and chemical solutions that are designed to meet the sustainability goals of all stakeholders.
Recent Developments
Effective June 1, 2023, our chief operating decision maker began to strategically view and manage certain water sourcing and transfer operations, previously included in our Water Infrastructure segment, as part of our Water Services segment. These changes were driven by a number of factors, including the preponderance of our water sourcing business that integrates with our water transfer operations, the continued transition of completions water demand from fresh and brackish water to recycled water, as well as the diversifying demand for these water transfer services beyond the immediate vicinity of our pipeline infrastructure. Due to these changes, we believe the Water Services segment
9
management is best suited to manage these operations. As a result of these changes, we anticipate more efficient sharing and utilization of resources and to realize potential synergies. Prior periods have been recast to include the water sourcing and transfer operations within the Water Services segment and remove the results of those operations from the Water Infrastructure segment.
Concurrently, we also decided to rename our Oilfield Chemicals segment as Chemical Technologies. This change was based on a number of factors, including the continued success of our chemicals business in delivering customized, specialty chemicals products developed through our own research and development efforts and the de-emphasis of certain traditional commoditized chemistry products within the oil and gas industry, as well as the continued investments in time and resources we make to manufacture and sell our specialty chemical products into non-oilfield industrial-related applications. We believe these segment changes better align the business with the current and future state of the Company’s operations and capital allocation and strategic objectives. This change was a naming convention only change that did not impact any Current Period or Prior Period numbers.
On May 8, 2023, we announced that our stockholders approved the Company’s Fifth Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation which, among other things, changed the name of the Company from Select Energy Services, Inc. to Select Water Solutions, Inc. to reflect our strategic focus as a water-first company focused on full life cycle water management. We retained our current stock ticker “WTTR” trading on the New York Stock Exchange.
The armed conflict between Ukraine and Russia continued throughout 2023, and additional conflicts arose in Israel and elsewhere in the Middle East. As a result of the Russian invasion of the Ukraine, the U.S., the United Kingdom, the member states of the European Union and other public and private actors have sustained severe sanctions on Russian financial institutions, businesses and individuals. In October 2023, Hamas militants conducted attacks in Israel and an armed conflict has ensued between Israel and Hamas. The ensuing conflict has resulted in increased hostilities and instability in oil and gas producing regions in the Middle East as well as in key adjacent shipping lanes. In tandem with such conflict, the Houthi movement, which controls parts of Yemen, has targeted and launched numerous attacks on Israeli, American and international commercial marine vessels in the Red Sea, resulting in many shipping companies re-routing to avoid the region altogether and worsening existing supply chain issues, including delays in supplier deliveries, extended lead times and increased cost of freight, insurance and materials. The potential for an international conflict with Iran, a major oil producer, the Houthi movement in Yemen or the Hezbollah movement in Lebanon has been perceived by many to have increased due to continued increasing hostilities in the Middle East. The Russia-Ukraine conflict, and the resulting sanctions and concerns regarding global energy security, has contributed to, and the conflict in the Israel-Gaza region and any heightened hostilities in the Middle East may contribute to, increases and volatility in the prices for oil and natural gas. Such volatility, coupled with an increased cost of capital, due, in part to higher rates of inflation and interest rates, may lead to a more difficult investing and planning environment for us and our customers. The ultimate geopolitical and macroeconomic consequences of these conflicts and associated sanctions and/or international responses cannot be predicted, and such events, or any further hostilities elsewhere, could severely impact the world economy and may adversely affect our financial condition. An end to these conflicts and an easing or elimination of the related sanctions and/or international response could result in a significant fall in commodity prices as hydrocarbons become more readily accessible in global markets, which could have an adverse effect on our customers, and therefore adversely affect our customers’ demand for our services. An intensification of that conflict could also have an adverse effect on our customers and their demand for our services.
Sustainability
Select is committed to a corporate strategy that supports the long-term viability of our business model in a manner that focuses on all stakeholders, including our people, our customers, the environment, and the communities in which we operate. We believe this focus will help us and our customers achieve their short-term and long-term environmental, social and governance (“ESG”) goals, help us attract and retain top talent, and further our efforts to generate investor returns. We believe our commitment to foster a culture of corporate responsibility is an important part of being a company with operations spanning the contiguous U.S. Further, we believe being a good corporate steward is strategic to our growth in the energy industry and will better allow us to develop solutions that both address the needs of our customers and contribute to sustainable business practices. As a service company, we compete with other service providers based on various factors, including safety and operational performance, technological innovation, process
10
efficiencies and reputational awareness. We have identified the following four priorities as part of our comprehensive corporate responsibility initiative: Environmental Consciousness, Health and Safety, Human Capital Management and Community Outreach. We believe there is a strong link between these corporate responsibility initiatives and our ability to provide value to our stakeholders.
We are one of the few public companies whose primary focus is on the management of water and water logistics in the energy industry with a focus on driving efficient, environmentally responsible, and economic solutions that lower costs throughout the lifecycle of the well. We believe water is a valuable resource and understand that the energy industry as well as other industries and the general public are competing for this resource. As a company, we continue to provide access to water as demanded by our customers and have significantly increased our focus on the recycling and reuse of produced water, as well as assessing other industrial water sources, to meet the industry’s water demand and align our operations with the goals of our customers. We have invested significantly in the development and acquisition of fixed and mobile recycling facilities that support the advancement of commercialized produced water reuse solutions. By doing so, we strive to reduce the amount of produced water being reinjected into SWDs and to reduce our usage of fresh water as well as that of our customers. We view our rather unique position as an opportunity to strategically transform water management by leveraging our Chemical Technologies business to develop produced water management solutions that increase our customers’ ability to reuse this produced water and add value to their operations. By implementing our innovative approach to water solutions, Select has become a leader in recycling produced water to be reused for energy production. See Part I, Item 1. “Business – Competitive Strengths” and “—Description of Business Segments” for more discussion on our operating capabilities and expertise around advancing sustainable water and chemical solutions.
Our strong company culture includes commitments to all stakeholders, and we aim to create a work environment that fosters a diverse and inclusive company culture. Additionally, we prioritize safety in our operations through rigorous training, structured protocols and ongoing automation of our operations. Our prioritization of safety includes a commitment to safeguarding the communities in which we operate. See Part I, Item 1. “Business—Human Capital” and Part I, Item 1. “Business—Environmental and Occupational Safety and Health Matters” for more discussion on our efforts on safety, training, employee culture and other stakeholder engagement.
We believe that proper alignment of our management and our board of directors with our shareholders is critical to creating long-term value, including the alignment of management compensation and incentive structures and the continued leadership of an experienced, diverse and independent board of directors. See Part III, Item 10. “Directors, Executive Officers and Corporate Governance” and Part III, Item 11 “Executive Compensation” for additional discussion on our governance and compensation structures.
Human Capital
We consider our employees vital to our success and are focused on attracting, developing and retaining the most qualified employees at all levels of our business. In particular, the quality of our customer service depends significantly on employee engagement and retention. We strive to create a productive and collaborative work environment for our employees.
As of December 31, 2023, we had more than 4,200 employees, and we believe we have good relations with our employees.
To attract talent and meet the needs of our employees, we offer a competitive benefits package for regular, full-time employees, including health benefits such as medical, dental and vision, welfare benefits such as life and accident insurance, an employee assistance program, and a qualified defined contribution plan to all eligible employees. We also provide our employees with resources for professional development, including training, feedback and performance reviews from supervisors. Our human capital measures and objectives focus on several areas including, but not limited to, the safety of our employees, human rights and social responsibility, culture, employee development and training, and operational execution.
11
Safety: Select maintains a culture of safety, committed to the protection of the health and the safety of our employees, as well as preserving the environment and our relationships with the communities in which we operate. Select works closely with federal, state, local and tribal governments and community organizations to help ensure that our operations comply with legal requirements and community standards. We place a strong emphasis on the safe execution of our operations, including safety training for our employees and the development of a variety of safety programs designed to make us a market leader in safety standards and performance. We have a comprehensive approach to formulating and managing training requirements for all of Select’s operational employees. This includes mandatory participation in monthly, quarterly, and annual environmental, health and safety meetings, a combination of live in-person training and computer-based training tailored to specific job-duties and operational activities, and comprehensive safety reference material. The investment and creation of our Safety Recognition Program in 2016 has had a profound impact on our organization. By acknowledging and rewarding employees for their commitment to safety, we have witnessed a significant improvement in overall workplace safety culture. Employees are more vigilant, proactive, and engaged in promoting a safe working environment. Incidents and accidents have seen a noticeable decline, reflecting the program's success in fostering a collective sense of responsibility for safety. Additionally, the positive reinforcement from the recognition program has boosted employee morale and teamwork, creating a ripple effect that extends beyond safety practices, contributing to a healthier and more productive workplace overall. Select also empowers operational personnel with stop-work authority (“SWA”) as a tool for helping ensure safety. Our SWA policy empowers our employees to stop work whenever they identify unsafe work conditions. When SWA is employed, operations cease until the risk is addressed and both the employee and management agree that it is safe to resume work. Lastly, when our employees identify a heightened safety risk, we respond quickly to mitigate the risk through communication, coordination and, if appropriate, a change in policy, procedures and training. We believe that our customers select their operational partners based in part on the quality of their safety and compliance records, and therefore, we will continue to make investments to be a market leader in this area.
| ● | Human Rights: Select is committed to conducting business in a manner that respects all human rights. Select is committed to promoting and encouraging respect for people and fundamental freedoms for all without distinctions of any kind, such as race, color, sex, language, religion, or political or other opinions. We are committed to partnering with personnel, business parties and other stakeholders directly linked to our operations that share our commitment to these same principles. We demonstrate this commitment in our employment practices, through our Code of Conduct, our Equal Employment Opportunity Employer Policy, and our Anti-Harassment Policy, as well as through our policies on safety and security for our employees. Additionally, our human resource department tracks and reviews metrics on the sex, age, and ethnicity of our employees to help ensure that current employees and prospective employees are treated fairly. Select provides several ways for individuals to raise concerns anonymously, including the 24-hour Employee Hotline, Whistleblower Hotline and Environmental Health & Safety Hotline, which promotes quick and confidential remediation without fear of retaliation. |
| ● | Culture: We believe company culture is an integral part of business that affects recruitment, job satisfaction, work performance and morale and begins with our mission, vision and core values. Our Company’s core values (Accountability, Continuous Improvement and Teamwork or “ACT”) are leveraged to ensure focus on how we ACT to be successful employees and build a great company that provides innovative solutions to our customers. Every day, our employees put our core values into action to improve operational excellence, safety, and the customer experience. These core values are helping to align our efforts to accomplish our vision to be the recognized leader and trusted partner in sustainable water management solutions. Through a series of employee-centric videos called “This is How We ACT,” we demonstrate an inclusive and dynamic team all working towards the same goal. |
| ● | Employee Development: Select encourages managers and supervisors at all levels to have frequent, open and constructive dialogue with their direct reports about job performance, continuous performance improvement and development. In addition, managers and employees are directed to connect and conduct one-on-one conversations twice a year on employee well-being, performance, development and growth opportunities utilizing a formal |
12
| feedback program. Employees answer four simple questions relating to their recent performance (successes and challenges) and development. As part of this conversation, our core values play an important part in communicating expected behaviors and how we expect each of us to ACT. With these and related practices, we strive for a culture of open dialogue and commitment to development. During 2023, Select focused on the continuous improvement of our managers by offering training to better their understanding of company policies and how to better support our employees. Training sessions were led by Safety and Legal with Human Resources. We continued the use of a National Awareness Calendar and subsequent employee communication with the ongoing purpose of increasing employee awareness on important employee-related topics such as Mental Health Awareness, Military Appreciation and National Diabetes Awareness, an effort that we expect to continue going forward. |
| ● | Operational Execution: It is critical that all Select employees that serve our customers are qualified and trained for their roles, understand our policies and work procedures, and receive the work direction necessary to operate safely. Site managers create daily, weekly and monthly plans to coordinate tasks and personnel. Our employees use standard operating procedures and best practices to standardize effective and consistent execution. Further, we employ a comprehensive mentor program, where more experienced employees provide guidance and instruction to less experienced employees and use videos to train and develop our operational personnel. |
Competitive Strengths
We believe our ability to integrate the complexities of our water and chemical-related services through both temporary, customized services and longer-term solutions that include investments in sustainable water reuse infrastructure gives us a competitive advantage and is the foundation of our business. We believe our comprehensive suite of sustainable water and chemical solutions, inventory of water sources, advanced technology and recycling capabilities, networked disposal capacity and permanent and semi-permanent pipeline infrastructure position us to be a leading provider of water and chemical solutions in all of the geographic basins that we serve. We have well-established field operations in what we believe to be core areas of the most active shale plays, basins and regions in the U.S., including the Permian, Bakken, Eagle Ford, Haynesville, Marcellus, Utica, Rockies and Mid-Continent (“MidCon”) regions. Our broad geographic footprint enables us to service the majority of current domestic unconventional drilling and completion activity. We estimate that approximately 85% of all currently active U.S. onshore horizontal rigs are operating in our primary service areas. We believe that the vast majority of rigs that will be deployed in the near- to medium-term will be situated in these areas. In particular, we have established a strong position in the Permian Basin, which accounts for approximately 50% of the industry activity in the U.S., and is presently our largest operating region, accounting for approximately 48% of our revenue in 2023 and 47% of our revenue in 2022.
Our Water Services segment focuses on supplying the services and customized, job-specific solutions needed as our customers’ activities move from location to location across the geographic footprint of their acreage over time. These services include the transportation, logistics and storage solutions needed to support the delivery of water to the wellsite for new well completions, the flowback and well testing services needed to manage the initial production phases of the well, the sourcing of water volumes and the logistics services needed to manage the long-term produced water volumes associated with oil and gas production over the life of the well. We believe we are a market leader in providing comprehensive water-related services to the industry and we have dedicated significant resources to developing technology solutions to manage the increasingly complex needs of our customers throughout the water lifecycle.
To meet the water demands of our customers, we have secured access to significant volumes of water in key unconventional development areas. Water sources are often difficult to locate, acquire and permit, particularly in the quantities and at the locations needed for multi-well pad development programs. We have secured permits or long-term access rights to approximately two billion barrels of water annually from hundreds of sources, including surface, subsurface, municipal and industrial sources, including brackish water, produced water and effluent.
We have invested significantly in our patented WaterONE™ and AquaView® suite of proprietary hardware and software applications for measuring, monitoring and automating our water services throughout the well lifecycle. Our
13
suite of automated solutions include automated water transfer pumps, automated manifolds, automated proportioning systems and telemetry meter trailers. WaterONE™ provides true automation to gather, analyze and act on data in real-time – all without human intervention – giving operators the ability to remotely set and maintain or improve the operational control of their frac and produced water-related requirements. When our monitoring systems detect that certain defined thresholds set by our customers are out of the desired range, our equipment sends out an alert and then, through dynamic machine learning, takes action to keep operations running safely and smoothly. This can include actions such as raising a pump’s RPM to maintain desired flow rates, adjusting valves in a proportioning system to maintain the desired water quality in real time while blending fresh, brackish, produced or otherwise impaired water sources or shutting down the system and valves completely in the event of a detected loss of pressure. In addition to reducing the risk of spills and injuries, our automated operations increase efficiency across the water transfer supply chain, reducing the risk of pressure spikes and increasing associated fuel efficiency, thereby significantly reducing overall fuel emissions. Our automation capabilities provide a safer, more efficient and cost-effective transfer, treatment and containment of produced or otherwise impaired water sources.
Within our AquaView® monitoring software systems, our solar-powered cellular and satellite-based remote-monitoring telemetry systems give our customers the ability to gain precise and accurate volumetric analyses of water sources and provide real-time data to our customers that is accessible 24/7 via computer, smart phone or tablet. Our Hydrographic Mapping Vessels (“HMVs”) use sonar, satellite, and compass technology to provide precise volumetric analyses of water sources. The HMVs are rapidly deployed, durable enough to handle flowback pits, and can navigate through tight spaces in natural ponds. Additionally, our AquaView® sensors give timely information about pH levels, water quality, temperature and flow rate to ensure there is sufficient water at the right quality levels required by our customers and provide alarm notifications to prevent problems during the well completion. We believe that our investments in technology provide a significant competitive advantage for us relative to our smaller, regionally-focused competitors by delivering more reliable, efficient, and environmentally responsible solutions, often at a lower overall cost.
Our Water Infrastructure segment develops networks covering the full water life cycle, recycling infrastructure and the associated semi-permanent and permanent pipeline infrastructure to both meet our customers’ needs for source water for new well completions as well as their requirements for the gathering of flowback and produced water for either recycling and reuse or ultimately for disposal. Our networks of recycling, disposal, and pipeline assets, combined with our complementary expertise in chemistry, strategic integration with customer infrastructure, and a well-coordinated network of internal and external logistics allow for optimized water resource management for our customers and the environment. We believe that investments in infrastructure such as commercialized recycling facilities or disposal wells that serve multiple customers, when underwritten by longer-term contracts, lowers the cost of production for our customers, while reducing the overall environmental footprint and impact on the local communities. Additionally, the development of water pipeline infrastructure networks to serve multiple customers covering larger blocks of acreage can improve the economics of non-potable water sourcing, including produced water recycling and therefore reduce the demand for fresh water required in oil and gas operations while also reducing required disposal volumes.
We have also invested in significant pipeline infrastructure to support the delivery of water from our water sources, consisting of approximately 3,000 miles of both above-ground and buried infrastructure, including key systems in the Permian Basin, including the Delaware Basin in New Mexico and Midland Basin in Texas, the Bakken Shale in the Williston Basin in North Dakota and the Haynesville Shale in Texas and Louisiana. We continue to focus our efforts on the development of non-potable sources as well as the infrastructure and solutions required for the treatment, recycling and reuse of produced water. We have developed and maintained extensive relationships with landowners as well as local, state, tribal and federal authorities to ensure that we can sustainably meet both the economic and operational needs of our customers while responding to the concerns of the local communities in which we operate. We believe that our extensive relationships and regulatory expertise will continue to constitute a competitive advantage in identifying and developing additional sources of water, including recycled volumes of produced water, in a responsible and sustainable manner.
Water is vital to the health, economic, and social well-being of the communities where we live and work. In support of industry-wide efforts to reduce the demand for fresh water for hydraulic fracturing, we have a dedicated team of specialists focused on developing and deploying innovative water treatment and reuse services for our customers. We
14
strive to fully understand local water issues, and to develop sustainable solutions with a commitment to conservation. Working collaboratively with our customers, we are actively operating and developing fixed recycling facilities in the Delaware and Midland Basin portions of the Permian Basin, as well as in the Rockies region, and will continue to focus on evaluating new fixed recycling facilities and deploying mobile recycling technologies in all of the areas that we operate. As customers consolidate, we believe our focus on commercialized solutions that connect multiple operators to strategic infrastructure that provides for greater use of treated produced water for new well completions will reduce the use of fresh water for hydraulic fracturing. By doing so, we also strive to both reduce the industry’s need for fresh water and reduce the portion of produced water being reinjected into SWDs, particularly in areas with active seismicity concerns.
We believe that greater use of produced water to reduce fresh water consumption will require collaboration with all stakeholders as we together develop water infrastructure networks to meet the needs of multiple operators. In addition to investing in pipelines and related infrastructure, Select offers mechanical and chemical solutions for treatment of produced water, and other non-potable water sources customized for our E&P customers’ complex fracturing fluid systems. We believe our expertise in utilizing chemical technologies in the water reclamation and conditioning process, combined with our chemical expertise in fracturing fluid system design, gives us a competitive advantage. For example, we offer a wide spectrum of bacterial control, aeration, proportioning and recycling technologies to condition source water or reuse flowback and produced water for hydraulic fracturing.
Additionally, we invest in gathering infrastructure to collect produced water, and we actively operate produced water disposal facilities in major U.S. shale plays with a permitted capacity of approximately 1.3 million barrels/day (“bbl/d”) with an additional 0.2 million bbl/d of permitted capacity available for development to support the disposal of produced water that cannot be economically recycled and reused for new well completions. This disposal capacity is critical to support recycling and reuse capabilities, as it provides an alternative outlet during times when limited completions activity in an area may not support additional water reuse demand.
In short, Select intends to play an important role in the advancement of sustainable water solutions that are designed to align the needs of the oil and gas industry with the sustainability goals of all stakeholders.
Our Chemical Technologies segment, develops, manufactures, manages logistics and delivers a full suite of completion chemical products utilized in hydraulic fracturing, stimulation, cementing and related well completion and production processes. Our Chemical Technologies product lines support the fluid systems utilized primarily in the completion and development of unconventional resources. These products include polymers that create viscosity, crosslinkers, friction reducers, surfactants, buffers, breakers and other specialty chemical technologies, and are provided to leading E&P operators and pressure pumping service companies in the U.S. The use of automated monitoring systems combined with direct-to-wellsite delivery ensures seamless product availability for our customers, while our chemical expertise enables us to deliver a customized suite of products to meet customers’ technical, economic and environmental product needs.
With our wide range of manufactured proprietary products and our expertise in completion chemistry, we believe we are well positioned to support our customers as completion chemistry evolves in the coming years in response to changes in technology and the evolution of completion water fluid systems. In addition to our chemical product offerings, we provide inventory management services, including procurement, warehousing and delivery services as well as a full suite of laboratory technologies and FluidMatch™ consultation services, including water analysis, quality control and assurance, additive compatibility analysis, solids analysis and stimulation recommendations. We have two primary manufacturing facilities, one each in west Texas and east Texas, regional distribution centers and a logistics fleet supporting geographic regions in the Permian, MidCon, Bakken, Eagle Ford, Haynesville and Rockies. We introduced the first in-basin manufacturing facility of emulsion polymers (friction reducers) in our industry, strategically located in the Permian Basin, which provides the advantage of reducing our overall transportation costs of delivering finished goods to our customers locally within the basin.
We also provide advanced water treatment solutions throughout the water lifecycle, as well as specialized stimulation flow assurance and integrity management, and post-treatment monitoring services. We deliver customized programs using proven chemical technologies and mobile equipment to treat virtually any oilfield water for reuse.
15
Following our treatment applications, fluid samples are analyzed again to ensure the treatment is optimized to reduce overall chemical investment. We provide disinfection treatment with a smaller environmental footprint, lower power costs and manpower needs than alternative solutions, resulting in a reduced emissions profile. Our expertise allows us to advise our customers on the best economic and operational solutions to optimally manage their water quality as well as chemical solutions needs across water qualities and well completion fluid systems.
As mentioned under “⸺Human Capital” above, we maintain a culture focused on safety. With more than 4,200 employees and operations spanning the U.S., we believe our commitment to foster a culture of safety and corporate responsibility is essential. Our employee base is made up of dedicated operational and technical professionals, including many with advanced degrees, professional licenses and project development experience, and diverse backgrounds in geology, geography, land management, petroleum, chemical and electrical engineering, computer science, environmental science, geographic information systems and legal and regulatory affairs. In addition, we emphasize preserving the environment and building relationships with the communities in which we operate. We work closely with federal, state, local and tribal governments and community organizations to help ensure that our operations comply with legal requirements, community standards and industry best practices. Further, we believe being a good corporate steward is strategic to our leadership in the water solutions industry and will better allow us to develop solutions that both address the needs of our customers and contribute to sustainable business practices. Our solutions significantly decrease the number of trucks on the road, thereby reducing fuel use and emissions and limiting the traffic footprint in the communities in which we operate. We believe that our customers will select their service providers based in part on the quality of their safety and compliance records and their ability to support their long-term sustainability goals and therefore, we will continue to make investments to be a market leader in these areas.
Description of Business Segments
We offer our services through the following three reportable segments: (i) Water Services, (ii) Water Infrastructure and (iii) Chemical Technologies.
Water Services Segment
Our Water Services segment consists of our services businesses, including water transfer, flowback and well testing, water sourcing, fluids hauling, water monitoring, water containment and water network automation, primarily serving E&P companies. Additionally, this segment includes the operations of our accommodations and rentals business.
Water Services Service Lines
Our Water Services segment is divided into the following service lines:
| ● | Water Transfer. We believe we are the largest provider of water transfer services to the industry. Our Water Transfer service line installs temporary above-ground pipeline systems that can be equipped with full automation to deliver water autonomously at high volumes and rates from a water source to water containment facilities (tanks and pits), or directly to the wellsite. |
We install layflat hose as part of a flexible water transfer solution that can be customized to fit a specific project. Our layflat hose allows for quick, cost-effective deployment and removal of transfer assets with limited environmental disturbance and can be quickly redeployed for new projects, including projects in different geographic regions. Layflat hose has a significantly lower risk of spills than most other types of temporary jointed pipe as a result of the strength and durability of the hose as well as the secure nature of any coupling joints used to connect multiple sections of hose. Our layflat hose consists primarily of 12-inch and 10-inch diameter segments, powered by mobile pumps. Historically, this equipment has been powered by diesel; however, we are actively developing and deploying electric pumping units, which should decrease emissions and further reduce the environmental impact of our operations. Depending on the requirements of a project, layflat hose may run from a water source directly to a containment area, such as an above-ground pit or storage tank, or to a wellsite. Water can also be transferred from one containment
16
area to another as part of managing a larger supply network. Our customers generally prefer layflat hose to alternative temporary piping options due to the cost-effectiveness, limited environmental impact, customizability and reduced risk of spills.
| o | Water Network Automation. Our proprietary and industry-leading automation technologies provide integrated water transfer solutions with automated pump operation, automated valve control, automated blending and proportioning capabilities, automated manifolds, level monitoring and data collection with analytics. We are able to provide our customers with increased visibility into their water inventories and usage, improving their efficiency and decreasing their costs. Our technology also provides us with the unique ability to detect potential issues and prevent them from occurring, as well as to reduce manpower and equipment on certain jobs, in turn mitigating safety and environmental risks while reducing overall fuel emissions. |
| ● | Flowback and Well Testing. Our flowback and well testing services, covering a dynamic range of temperature, pressure, volume and H2S concentrations, adds value for our customers by providing well productivity data associated with our services, including fracturing support, fracturing plug drill out, flaring operations, ventless flowback operations, sand management and production testing. Our specialized well testing equipment is outfitted with advanced metering and telemetry, bringing remote visibility to our customers. Services are provided by highly-trained personnel that specialize in delivering performance optimization, or our high demand equipment is available for rental without personnel. We believe we are one of the largest flowback and well testing providers both in service and rental equipment inventory to the U.S. land industry. Additionally, certain of our services utilize specialized, closed-loop vapor tanks that prevent the release of methane and vapors to the atmosphere during drill out and flowback operations. |
We are a seasoned operator within Environmental Protection Agency (“EPA”) emissions regulations, offering green completions through our mobile production facilities. This collaborative process safely contains and combusts flare gas, reducing emissions at the wellsite, providing our customers with enhanced emissions reduction solutions to help meet their sustainability targets and initiatives without the need for an external power supply, further reducing the environmental impact.
| ● | Fluids Hauling. We currently operate over 900 tractor trailers and body load trucks and believe we are one of the largest providers of fluids hauling to the oil and gas industry. Our Fluids Hauling group, provides transportation for water and various drilling, completion, and production fluids, utilizing our fleet of vacuum, winch and kill trucks, hot oilers, and hydrovacs, along with other related assets, such as mobile storage tanks. Our operations span the Permian, MidCon, Bakken, Eagle Ford, Marcellus/Utica, Haynesville, and Rockies regions. |
| ● | Water Monitoring. Our Water Monitoring services support the full scope of our Water Services offerings and include hydrographic mapping services, remote pit and tank monitoring, generator monitoring, leak detection and automation-equipment monitoring services, including automated transfer pumps, automated manifolds, automated blending and proportioning systems and telemetry meter trailers. These services securely track water assets and measure information such as flow rates, temperature, pressure and water qualities such as pH and salinity, providing real-time data through our customized portals and alert systems, which are accessible 24/7 via computer, smartphone or tablet. |
| ● | Water Containment. We provide a diverse set of primary and secondary containment solutions for the temporary storage and containment of water and fluids. We believe we are the largest provider of high-capacity aboveground water storage tanks (“ASTs”) in the U.S. We offer ASTs ranging in size from 4,500 to 80,000 barrels (or 189,000 to 3.4 million gallons) per tank, with remote monitoring capability in every major U.S. basin. Our ASTs provide a high-volume, low-cost containment alternative to traditional mobile storage tanks, which typically hold 500 barrels (or 21,000 gallons). ASTs can also be set up as part of our Water Treatment & Recycling service offerings, which can be bundled with our Water Sourcing and Water Transfer services. A 40,000 barrel AST can be delivered by three trucks and installed in a single day, replacing the equivalent of 80 trucks delivering individual 500-barrel mobile storage tanks. This reduction |
17
| in truck traffic provides a significant reduction in traffic congestion in local communities as well as the associated emissions from the transportation of mobile storage tanks. Our modular tank design allows for twenty different tank configurations to meet each customer’s individual needs. We also offer assorted secondary containment solutions, from drive-over to raised barriers and multi-ringed nested AST solutions, that are designed to reduce the risk and environmental impact of potential spills. |
| ● | Water Sourcing. Our Water Sourcing service line provides water, permitting and, in some instances, necessary logistics required by our E&P customers to support their drilling and completion operations. Our sourcing efforts include identifying, developing and obtaining the right to use water from a variety of sources, including surface, subsurface, industrial, municipal and produced water. Through a portfolio of contracts with and permits from regulatory bodies, corporations and individual landowners, we have secured rights of approximately two billion barrels of water annually from hundreds of strategically located sources across the U.S. |
| ● | Accommodations and Rentals. Our accommodations and rentals service line provides workforce accommodations and surface rental equipment supporting drilling, completion and production operations in the U.S. onshore energy industry. The services provided include fully furnished office and living quarters, freshwater supply and wastewater treatment and removal, portable power generation and light plants, internet, phone, intercom, surveillance and monitoring services and other long-term rentals supporting field personnel. Further, our 2021 acquisition of assets from H.B. Rentals, L.C. (“HB Rentals”) bolstered our presence in multiple regions and added thousands of fixed asset units, including skid-mounted housing units and trailer housing units giving us a market-leading position in this service line. |
Water Services Geographic Areas of Operation
We provide our Water Services offerings in most of the major unconventional shale plays in the continental U.S., as illustrated by a “✓” in the chart below.
Geographic Region |
|||||||
Marcellus / |
|||||||
Services Provided |
Permian |
MidCon |
Bakken |
Eagle Ford |
Utica |
Haynesville |
Rockies |
Water Transfer |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
Flowback and Well Testing |
✓ |
✓ |
— |
✓ |
✓ |
— |
✓ |
Fluids Hauling |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
Water Monitoring |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
Water Containment |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
Water Sourcing |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
— |
✓ |
✓ |
Accommodations and Rentals |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
— |
✓ |
Water Services Customers
Our Water Services customers primarily include major integrated and independent U.S. and international oil and gas producers.
Water Services Competition
Our industry is highly competitive. Our customers typically award contracts after a competitive bidding process. Operational track record, the skill and competency of our people, pricing, safety, technology and environmental performance are key factors in the bid evaluation. Equipment availability, location, service breadth and technical specifications can also be significant considerations.
18
Certain large domestic and international oilfield services companies offer some water-oriented and environmental services, though these are generally ancillary to their core businesses. As a result, the water solutions industry is highly fragmented and our main competitors are typically smaller and often private service providers that focus on water solutions and logistical services across a narrow geographic area or service offering. We seek to differentiate ourselves from our competitors by delivering comprehensive, high-quality services and equipment supported in many regions by fixed infrastructure networks, coupled with well-trained people and a commitment to sustainability, superior execution and a safe working environment.
Water Infrastructure Segment
Our Water Infrastructure segment provides recycling, gathering, transferring and disposal of water. Water Infrastructure operations are provided through or enabled by a network of permanent pipeline infrastructure, semi-permanent pipeline infrastructure, water recycling facilities, earthen pits, water sources and SWDs.
Water Infrastructure Service Lines
Our Water Infrastructure segment is divided into the following service lines:
| ● | Water Recycling & Reuse. We believe we are one of the largest providers of water treatment and recycling to the energy industry. Our Water Recycling & Reuse business provides tailored solutions to fit specific customer water quality and delivery needs. We utilize both standard and proprietary processes and technology, including mechanical and chemical technologies, that provide high-quality, large volume throughput and cost-optimized recycling and reuse solutions for our E&P customers. These solutions are largely designed for the recycling and reuse of flowback and produced water from existing operations to meet a customer’s well completion water needs. We provide our customers with high-quality completion water volumes while reducing the need to source fresh water as well as reducing the need for disposal into SWDs. Our recycling operations consist of temporary, semi-permanent and permanent infrastructure, including above-ground and in-ground containment along with treatment processing assets and facilities capable of recycling large volumes of produced water for reuse in the hydraulic fracturing process. |
We have invested substantially in the development of produced water recycling infrastructure since 2022, commencing operations in the Delaware and Midland Basin portions of the Permian Basin and DJ Basin portion of the Rockies Region backed by long-term contracts with mobile operations commencing in the Haynesville during 2023. Our combined mobile and fixed recycling operations include a consolidated daily throughput capacity of approximately three million barrels per day of active produced water recycling capacity and 15 million barrels of produced water storage.
| ● | Pipelines & Logistics. We have developed some of our larger, strategic water sources into comprehensive, permanent pipeline systems designed to provide water used for drilling, completion and production activity across a wide geography or to collect and redistribute produced water into our recycling and disposal facilities. In many instances, we also provide the associated storage and logistics needed to deliver the water directly to our customers’ wellsites. We have developed or acquired pipeline systems in the Permian Basin, including the Northern Delaware Basin of New Mexico and the Midland Basin in Texas, the Bakken Shale in North Dakota, the Haynesville Shale in Louisiana and the DJ Basin in Colorado within the Rockies region. These pipeline networks encompass more than 1,000 miles of temporary and permanent pipeline infrastructure and related storage facilities and pumps throughout the Permian Basin, more than 90 miles of gathering and distribution pipelines in the Bakken Shale, a 60-mile dual lined buried gathering and distribution pipeline system in the Haynesville Shale and other long-term contracted gathering pipeline and distribution systems in the MidCon and Rockies regions. These pipelines utilize a combination of industrial, surface and produced water sources and include a number of long-term contracts, including take-or-pay agreements and minimum volume commitments supporting the operations. |
| ● | Fluid Disposal. Our strategic acquisitions of Nuverra Environmental Solutions, Inc. (“Nuverra”) in 2022, as well as Cypress, Agua Libre Midstream, LLC (“Agua Libre”), and Complete Energy Services, Inc. (“Complete”) in 2021 ushered in a phase of growth and operational expansion to our disposals business. |
19
| These acquisitions significantly augmented the number of active SWDs under our ownership and operation. Presently, we manage an extensive portfolio of active SWDs spanning across the Permian, MidCon, Bakken, South Texas, Rockies, Marcellus/Utica, and Haynesville regions, establishing a formidable presence in key energy basins. We also have substantial additional permitted, undeveloped disposal capacity and permits currently in process that provide growth opportunities for us. In aggregate, we command a daily permitted disposal capacity of more than 1.5 million barrels per day across our operational basins. Our disposal services cater to both flowback water generated during well completion operations and naturally-occurring produced water extracted during the oil and natural gas production process. These volumes are transported to our SWDs through a well-orchestrated network of owned and third-party gathering pipelines, as well as a fleet of owned and third-party fluid hauling trucks, ensuring the efficient management of this critical aspect of our operations. |
| ● | Solids Management. We operate one special waste landfill facility in North Dakota located on a 50-acre site with more than five million cubic yards of permitted capacity. The facility, acquired in the Nuverra acquisition, primarily disposes of solid waste from the E&P industry and provides a unique opportunity for Select to expand its logistics capabilities into a new service offering. Additionally, we operate a solids treatment facility in Ohio within the Marcellus/Utica basin capable of treating contaminated and residual solids with 3,000 barrels per day of liquids equivalent processing capacity. The facility also provides tank cleanout and lab services and is connected via pipeline to a Select wastewater disposal facility. |
Water Infrastructure Geographic Areas of Operation
We provide our Water Infrastructure offerings in most of the major unconventional shale plays in the continental U.S., as illustrated by a “✓” in the chart below.
Geographic Region |
|||||||
Marcellus / |
|||||||
Services Provided |
Permian |
MidCon |
Bakken |
Eagle Ford |
Utica |
Haynesville |
Rockies |
Water Recycling & Reuse |
✓ |
— |
— |
— |
— |
✓ |
✓ |
Pipelines & Logistics |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
— |
— |
✓ |
✓ |
Fluid Disposal |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
Solids Management |
— |
— |
✓ |
— |
✓ |
— |
— |
Water Infrastructure Customers
Our Water Infrastructure customers primarily include major integrated and independent U.S. and international oil and gas producers.
Water Infrastructure Competition
While our customers typically award contracts after a competitive bidding process, the presence of existing infrastructure in an acreage position can be critical in realizing economic value. In addition to the reach and capacity of existing area networks, track record, the skill and competency of our people, pricing, safety, the ability to move sufficient volumes at scale and environmental performance are key factors in the bid evaluation. Equipment availability, location, and technical specifications can also be significant considerations. We have a successful track record of utilizing our infrastructure to obtain various long-term contracts such as areas-of-mutual-interest, acreage dedications, well bore dedications, minimum volume commitments and take-or-pay agreements, while maintaining operational capacity for short-term work that may emerge.
Certain large midstream companies offer some water-oriented and infrastructure services, though these are generally ancillary to their core businesses of gathering and transporting oil and gas volumes. There are also public water-midstream-focused competitors. Additionally, certain of our E&P customers have invested in water infrastructure
20
for their own operations. As a result, the water infrastructure competitive landscape is highly fragmented and our main competitors, aside from E&P companies, can often be private water midstream companies that focus on a more limited geographic area or service offering. We seek to differentiate ourselves from our competitors through our expansive scale and by delivering high-quality solutions throughout the sourcing, recycling and disposal elements of the water lifecycle, coupled with extensive regulatory expertise, well-trained people and a commitment to superior execution and a safe working environment. Additionally, we believe our ability to couple our water infrastructure with our water services and oilfield chemicals expertise provides an advantage relative to our competition.
Chemical Technologies Segment
Within our Chemical Technologies segment, we develop, manufacture, manage logistics and provide a full suite of completion chemical products utilized in hydraulic fracturing, stimulation, cementing and related well completion processes. We sell chemicals and provide services primarily to leading E&P operators and pressure-pumping service companies in the U.S. We also provide customized water treatment and flow assurance solutions to our customers throughout the lifecycle of a well.
Chemical Technologies Service Lines
Our Chemical Technologies segment is made up of the following service lines:
| ● | Chemical Manufacturing. We are a specialty manufacturer of polyacrylamides, surfactants, crosslinkers and other custom chemistries. Polyacrylamides, or friction reducers, are water-soluble polymers that reduce friction and boost viscosity of the hydraulic fluid during application in energy production. We manufacture this reactive chemistry in Midland, Texas and Tyler, Texas with regional distribution facilities across the United States. Our in-basin manufacturing provides reduced lead times to decrease non-productive time on location for our customers with fully automated processes from raw materials to finished goods. We are among the largest manufacturers of friction reducers to the energy industry, producing both anionic and viscosifying friction reducers. Our manufacturing is supported by in-house logistics and comprehensive lab services. |
| ● | Completion Chemicals. Our Completion Chemicals service line provides technical solutions, products and expertise related to chemical applications in the energy industry. We develop solutions, manage logistics and provide a full suite of chemicals used in hydraulic fracturing, stimulation, cementing, pipelines and well completions for customers ranging from major integrated and independent oil and gas producers to pressure pumpers. This service line also utilizes its chemical experience and lab testing capabilities to customize tailored water treatment solutions designed to optimize the fracturing fluid system in conjunction with the quality of water used in well completions. Through our Completion Chemicals service line, we develop and provide a full suite of chemicals utilized in hydraulic fracturing, stimulation and cementing, including polymers that create viscosity, crosslinkers, friction reducers, surfactants, buffers, breakers and other chemical technologies. We source our products through our own manufacturing operations as well as through third-party producers and distributors. We provide 24/7/365 time-critical logistical support to our customers and our warehousing and service includes inventory management with computerized tracking and monthly reporting. We use automated communications systems combined with direct-to-wellsite delivery to ensure seamless product availability for our customers. With our expertise in fracturing chemistry, we can develop customized products to meet customers’ frac-fluid system requirements. |
| ● | Water Treatment. Through our Water Treatment service line, we provide advanced water treatment solutions throughout the well lifecycle, as well as specialized stimulation flow assurance and integrity management, and post-treatment monitoring services in the U.S. land market. Our specialty chemicals are used in applications such as water conditioning, water recycling, on-the-fly treatment and water reuse and mining. Our chemical experts provide pre-treatment water sampling, analysis and testing to determine a water’s chemistry, then design the most effective fracturing fluid system. The team delivers customized programs using proven chemical technologies and mobile equipment to treat almost any oilfield water for reuse. Following our treatment applications, fluid samples are analyzed again to ensure the treatment is |
21
| optimized to reduce overall chemical investment. Water Treatment provides disinfection solutions to neutralize microorganisms, hydrogen sulfide (H2S), iron sulfide, phenols, mercaptans, and polymers in the surface water. Our Water Treatment team works closely with our Chemical Technologies service line as well as our water monitoring, reuse and recycling teams within our Water Services and Water Infrastructure segments to advise our customers on the best economic and operational solutions to manage their water quality and chemical solutions needs. |
Chemical Technologies Geographic Areas of Operation
We provide Chemical Technologies services in most of the major unconventional shale plays in the continental U.S. In the chart below, a “✓” indicates that we offer the service line in the indicated geographic region.
Geographic Region |
|||||||
Marcellus / |
|||||||
Services Provided |
Permian |
MidCon |
Bakken |
Eagle Ford |
Utica |
Haynesville |
Rockies |
Chemical Manufacturing |
✓ |
— |
— |
— |
— |
✓ |
— |
Completion Chemicals |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
Water Treatment |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
— |
✓ |
✓ |
Chemical Technologies Customers
Our Chemical Technologies customers primarily include pressure pumpers, and major integrated and independent U.S. and international oil and gas producers.
Chemical Technologies Competition
The Chemical Technologies business is highly competitive. Our competitors include both large manufacturers and companies that are pure distributors of commodities and specialty chemicals. We believe that the principal competitive factors in the markets we serve are technical expertise, manufacturing capacity, workforce competency, efficiency, safety record, reputation, experience and price. Additionally, projects are often awarded on a bid basis, which tends to create a highly competitive environment. We seek to differentiate ourselves from our competitors by delivering high-quality services and solutions paired with water treatment expertise through our FluidMatch™ design solutions, coupled with superior execution and operating efficiency in a safe working environment. Additionally, many of our competitors focus on serving multiple industries outside of oil and gas, and therefore we believe our dedicated focus on the oil and gas industry and in-basin manufacturing capabilities provides a competitive advantage. We also believe our expertise in water management provides a competitive advantage that allows us to assess and optimize our chemical solutions in a unique manner.
Significant Customers
There were no customers that accounted for 10% or more of our consolidated revenues for the year ended December 31, 2023.
Sales and Marketing
We direct our sales activities through a network of sales representatives and business development personnel, which allows us to support our customers at both the field and corporate level. Our sales representatives work closely with local operations managers to target potential opportunities through strategic focus and regular customer interaction. We track the drilling and completion activities of our current and potential new customers. Our operations managers meet with our sales team several times a week, and monitor sales activity via daily reporting. To support our sales strategy, we have developed a proprietary database that integrates market information such as current rig, completion crew and permit activity and the location of our strategic water sources and networks.
22
Our marketing activities are performed by an internal marketing group with input from key executives. We intend to build and maintain a well-recognized brand in the oil and gas industry through multiple media outlets, including our website and social media accounts, print and billboard advertisements, presenting at and participating in various industry-specific conferences, case studies, publications and lectures.
Environmental and Occupational Safety and Health Matters
Our water-related operations in support of energy development and production activities pursued by our customers are subject to stringent and comprehensive federal, tribal, state and local laws and regulations in the U.S. governing occupational safety and health, the discharge of materials into the environment and environmental protection. Numerous governmental entities, including the EPA, the U.S. Occupational Safety and Health Administration (“OSHA”) and analogous state agencies, have the power to enforce compliance with these laws and regulations and the permits issued under them, often requiring difficult and costly actions. These laws and regulations may, among other things (i) require the acquisition of permits or other approvals to take fresh water from surface water and groundwater, construct pipelines or containment facilities, drill wells and other regulated activities; (ii) restrict the types, quantities and concentration of various substances that can be released into the environment or injected into non-producing belowground formations; (iii) limit or prohibit our operations on certain lands lying within wilderness, wetlands and other protected areas; (iv) require remedial measures to mitigate pollution from former and ongoing operations; (v) impose specific safety and health criteria addressing worker protection; and (vi) impose substantial liabilities for pollution resulting from our operations. Any failure to comply with these laws and regulations may result in the assessment of sanctions, including administrative, civil and criminal penalties, the imposition of investigatory, remedial or corrective action obligations or the incurrence of capital expenditures; the occurrence of restrictions, delays or cancellations in the permitting, performance or expansion of projects; and the issuance of orders enjoining performance of some or all of our operations in a particular area.
Our business activities present risks of incurring significant environmental costs and liabilities, including costs and liabilities resulting from our handling of oilfield and other wastes, because of potential air emissions and wastewater discharges related to our operations, and due to historical oilfield industry operations and waste disposal practices. Our businesses include the operation of oilfield waste disposal injection wells that pose risks of environmental liability, including leakage from the wells to surface or subsurface soils, surface water or groundwater. In addition, private parties, including the owners of properties upon which we perform services and facilities where our wastes are taken for reclamation or disposal, also may have the right to pursue legal actions to enforce compliance as well as to seek damages for non-compliance with environmental laws and regulations or for personal injury or property or natural resource damages. Some environmental laws and regulations may impose strict liability, which means that in some situations we could be exposed to liability as a result of our conduct that was lawful at the time it occurred or the conduct of, or conditions caused by, prior operators or other third parties.
The trend in U.S. environmental regulation is typically to place more restrictions and limitations on activities that may affect the environment. In particular, President Biden has issued several executive orders since taking office, and has made combating climate change a priority under his administration. Moreover, accidental releases or spills may occur in the course of our operations, and we cannot assure you that we will not incur significant costs and liabilities as a result of such releases or spills, including any third-party claims for damage to property, natural resources or persons. Historically, our environmental compliance costs in the U.S. have not had a material adverse effect on our results of operations; however, there can be no assurance that such costs will not be material in the future or that such future compliance will not have a material adverse effect on our business and operational results. Our customers may also incur increased costs or restrictions, delays or cancellations in permitting or operating activities as a result of more stringent environmental laws and regulations, which may result in curtailment of exploration, development or production activities that would reduce the demand for our services. Any new laws and regulations, amendment of existing laws and regulations, reinterpretation of legal requirements or increased governmental enforcement that result in more stringent and costly construction, completion or water-management activities, waste handling, storage transport, disposal, or remediation requirements or increased climate-related restrictions on our customers’ operations could have a material adverse effect on our financial position and results of operations. We may be unable to pass on such increased compliance costs to our customers.
23
The following is a summary of the more significant existing environmental and occupational safety and health laws in the U.S., as amended from time to time, to which our operations are subject and for which compliance may have a material adverse impact on our capital expenditures, results of operations or financial position.
Hazardous substances and wastes. The federal Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (“RCRA”), and comparable state statutes regulate the generation, transportation, treatment, storage, disposal and cleanup of hazardous and non-hazardous wastes. Pursuant to rules issued by the EPA, the individual states administer some or all of the provisions of RCRA, sometimes in conjunction with their own, more stringent requirements. Drilling fluids, produced waters, and most of the other wastes associated with the exploration, development, and production of oil or gas, if properly handled, are currently exempt from regulation as hazardous waste under RCRA, and instead are regulated under RCRA’s less stringent non-hazardous waste provisions, state laws or other federal laws. However, it is possible that certain oil and gas drilling and production wastes now classified as non-hazardous could be classified as hazardous wastes in the future. Any loss of the RCRA exclusion for drilling fluids, produced waters and related wastes could result in an increase in our and our oil and gas producing customers’ costs to manage and dispose of generated wastes, which could have a material adverse effect on our and our customers’ results of operations and financial position. In the course of our operations, we generate some amounts of ordinary industrial wastes, such as paint wastes, waste solvents and waste oils that may be regulated as hazardous wastes.
Wastes containing naturally occurring radioactive materials (“NORM”) may also be generated in connection with our operations. Certain processes used to produce oil and gas may enhance the radioactivity of NORM, which may be present in oilfield wastes. NORM is subject primarily to individual state radiation control regulations. In addition, NORM handling and management activities are governed by regulations promulgated by the OSHA. These state and OSHA regulations impose certain requirements concerning worker protection, the treatment, storage and disposal of NORM waste, the management of waste piles, containers and tanks containing NORM, as well as restrictions on the uses of land with NORM contamination.
The federal Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation and Liability Act (“CERCLA”), also known as the Superfund law, and comparable state laws impose liability, without regard to fault or legality of conduct, on classes of persons considered to be responsible for the release of a “hazardous substance” into the environment. These persons include the current and past owner or operator of the site where the hazardous substance release occurred and anyone who disposed or arranged for the disposal of a hazardous substance released at the site. Under CERCLA, such persons may be subject to joint and several, strict liability for the costs of cleaning up the hazardous substances that have been released into the environment, for damages to natural resources and for the costs of certain health studies. CERCLA also authorizes the EPA and, in some instances, third parties to act in response to threats to the public health or the environment and to seek to recover from the responsible classes of persons the costs they incur. In addition, neighboring landowners and other third parties may file claims for personal injury and property damage allegedly caused by the hazardous substances released into the environment. We generate materials in the course of our operations that may be regulated as hazardous substances.
We currently own, lease, or operate numerous properties that have been used for activities supporting oil and gas exploration, development and production for a number of years. Although we believe that we have utilized operating and waste disposal practices that were standard in the industry at the time, hazardous substances, wastes, or petroleum hydrocarbons may have been released on, under or from the properties owned or leased by us, or on, under or from other locations, including off-site locations, where we conduct services for our customers or where such substances have been taken for treatment or disposal. In addition, some of our properties have been operated by third parties or by previous owners or operators whose treatment and disposal of hazardous substances, wastes, or petroleum hydrocarbons was not under our control. These properties and the substances disposed or released on, under or from them may be subject to CERCLA, RCRA and analogous state laws. Under such laws, we could be required to undertake response actions or corrective measures, which could include removal of previously disposed substances and wastes, cleanup of contaminated property or performance of remedial operations to prevent future contamination, the costs of which could be material.
Water discharges and use. The Federal Water Pollution Control Act, also known as the Clean Water Act (“CWA”), and analogous state laws, impose restrictions and strict controls with respect to the discharge of pollutants,
24
including spills and leaks of oil and hazardous substances, into state waters and waters of the U.S. The discharge of pollutants into regulated waters is prohibited, except in accordance with the terms of a permit issued by the EPA or an analogous state agency. Spill prevention, control and countermeasure plan requirements imposed under the CWA require appropriate containment berms and similar structures to help prevent the contamination of navigable waters in the event of a petroleum hydrocarbon tank spill, rupture or leak. In addition, the CWA and analogous state laws require individual permits or coverage under general permits for discharges of stormwater runoff from certain types of facilities.
The CWA also prohibits the discharge of dredge and fill material in regulated waters, including wetlands, unless authorized by permit. There continues to be uncertainty on the federal government’s applicable jurisdictional reach under the CWA over waters of the U.S., including wetlands, as the EPA and the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers (“Corps”) under the Obama, Trump and Biden Administrations have pursued multiple rulemakings since 2015 in an attempt to determine the scope of such reach. Most recently, following legal action on a January 2023 final rule, the U.S. Supreme Court’s decision in Sackett v. EPA, and the enactment of a subsequent September 2023 rule, the implementation of the definition “waters of the United States” (“WOTUS”) is split based on jurisdiction. In 27 states, the January 2023 rule is enjoined subject to litigation, and EPA and the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers are implementing the definition of WOTUS consistent with the pre-2015 regulatory regime and the changes made by the Sackett decision, which utilizes the “continuous surface connection” test to determine if wetlands qualify as WOTUS. In the remaining 23 states, the agencies are implementing the September 2023 rule, which amended the January 2023 rule to incorporate the Sackett decision. However, the September 2023 rule does not define the term “continuous surface connection,” and it is currently unclear how broadly the September 2023 rule and the Sackett decision will be interpreted by the agencies. To the extent that any new final rule or rules issued by the EPA and Corps under the Biden Administration expands the scope of the CWA’s jurisdiction in areas where we or our customers conduct operations, such developments could increase compliance expenditures or mitigation costs, contribute to delays, restrictions, or cessation of the development of projects, and also reduce the rate of production of natural gas or crude oil from operators with whom we have a business relationship and, in turn, have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations and cash flows. Federal and state regulatory agencies can impose administrative, civil and criminal penalties for non-compliance with discharge permits or other requirements of the CWA and analogous state laws and regulations.
The Oil Pollution Act of 1990 (“OPA”) amends the CWA and sets minimum standards for prevention, containment and cleanup of oil spills in waters of the U.S. The OPA applies to vessels, offshore facilities, and onshore facilities, including E&P facilities that may affect waters of the U.S. Under OPA, responsible parties including owners and operators of onshore facilities may be held strictly liable for oil cleanup costs and natural resource damages as well as a variety of public and private damages that may result from oil spills. The OPA also currently limits the liability of a responsible party for economic damages, excluding all oil spill response costs, to $137.7 million; although this limit does not apply if the spill was caused by gross negligence or willful misconduct, resulted from a violation of a federal safety, construction or operating regulation, or if the party failed to report a spill or cooperate fully in the cleanup. The OPA also requires owners or operators of certain onshore facilities to prepare Facility Response Plans for responding to a worst-case discharge of oil into waters of the U.S.
Saltwater disposal wells and induced seismicity. Saltwater disposal via underground injection is regulated pursuant to the Underground Injection Control (“UIC”) program established under the federal Safe Drinking Water Act (the “SDWA”) and analogous state and local laws and regulations. The UIC program includes requirements for permitting, testing, monitoring, recordkeeping and reporting of injection well activities, as well as a prohibition against the migration of fluid containing any contaminant into underground sources of drinking water. State regulations require a permit from the applicable regulatory agencies to operate underground injection wells. Although we monitor the injection process of our wells, any leakage from the subsurface portions of the injection wells could cause degradation of fresh groundwater resources, potentially resulting in suspension of our UIC permit, issuance of fines and penalties from governmental agencies, incurrence of expenditures for remediation of the affected resource and imposition of liability by third parties claiming damages for alternative water supplies, property and personal injuries. A change in UIC disposal well regulations or the inability to obtain permits for new disposal wells in the future may affect our ability to dispose of produced waters and other substances, which could affect our business.
Furthermore, in response to seismic events in the past several years near underground disposal wells used for the disposal by injection of produced water resulting from oil and gas activities, federal and some state agencies are
25
investigating whether such wells have caused increased seismic activity, and some states have restricted, suspended or shut down the use of such disposal wells in certain areas prone to increased seismic activity. Developing research suggests that the link between seismic activity and wastewater disposal may vary by region and that only a very small fraction of the tens of thousands of injection wells have been suspected to be, or have been, the likely cause of induced seismicity. In 2016, the U.S. Geological Survey identified six states with the most significant hazards from induced seismicity, including Oklahoma, Kansas, Texas, Colorado, New Mexico and Arkansas. As a result of these concerns, regulators in some states have imposed, or are considering imposing, additional requirements in the permitting of produced water disposal wells or otherwise to assess any relationship between seismicity and the use of such wells. For example, Oklahoma has issued rules for wastewater disposal wells that imposed certain permitting and operating restrictions and reporting requirements on disposal wells in proximity to faults. The Texas Railroad Commission adopted similar rules in Texas.
States also may issue orders to temporarily shut down or to curtail the injection depth of existing wells in the vicinity of seismic events. For example, in Texas, the Texas Railroad Commission has pursued several regulatory initiatives during the latter half of 2021 as a result of recent seismic activity in an area of the Midland Basin from northeast Ector County to southwest Martin County known as the Gardendale Seismic Response Area (“SRA”), including: (i) directing wells operators in September 2021 to pursue voluntary reductions in produced water disposals from scores of produced water well facilities in response to six earthquakes of magnitude 3.5 or greater that occurred in the Gardendale SRA between February 2020 and September 2021; (ii) suspending injection operations of seven deep disposal wells within the Gardendale SRA effective December 15, 2021 in response to a 3.6 magnitude earthquake that occurred on October 26, 2021 and a 3.5 magnitude earthquake that occurred on November 16, 2021: and (iii) suspending all disposal well permits to inject oil and gas waste into deep strata within the boundaries of the Gardendale SRA (affecting some 33 wells) effective December 31, 2021. The Gardendale SRA was expanded following a magnitude 5.4 earthquake on December 16, 2022, adding 17 wells to the SRA. On December 31, 2020, a magnitude 4.2 earthquake occurred about 11 miles north of Stanton, Texas, about five miles east of the unincorporated community of Lenorah and 25 miles northeast of Midland. In response to this earthquake and some eight other earthquakes with magnitudes greater than 3.9, the Texas Railroad Commission established the Stanton SRA in January 2022, and operators in the SRA initiated an operator-led response plan beginning May 15, 2022. The Northern Culberson-Reeves SRA was established in March 2022 with an operator-led response plan; however, in December 2023 the Texas Railroad Commission suspended all deep disposal well permits in that SRA, affecting 23 deep disposal wells. In Oklahoma, the Oklahoma Corporation Commission released well completions seismicity guidelines in late 2016 for operators in the SCOOP and STACK that call for hydraulic fracturing operations to be suspended following earthquakes of certain magnitudes in the vicinity and, furthermore, has, from time to time, issued orders limiting future increases in the volume of oil and gas wastewater injected below ground into the Arbuckle formation in an effort to reduce the number of earthquakes in the state.
An additional consequence of this seismic activity is lawsuits alleging that disposal well operations have caused damage to neighboring properties or otherwise violated state and federal rules regulating waste disposal. The adoption and implementation of any new laws, regulations or directives that restrict our ability to dispose of wastewater gathered from our customers by limiting volumes, disposal rates, disposal well locations or otherwise, or requiring us to shut down disposal wells, could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, and results of operations.
Hydraulic fracturing activities. Hydraulic fracturing involves the injection of water, sand or other proppants and chemical additives under pressure into targeted geological formations to fracture the surrounding rock and stimulate production. Hydraulic fracturing is an important and common practice that is typically regulated by state oil and natural gas commissions or similar agencies. However, the practice continues to be controversial in certain parts of the country, resulting in increased scrutiny and regulation of the hydraulic fracturing process, including by federal agencies that have asserted regulatory authority or pursued investigations over certain aspects of the hydraulic fracturing process. For example, the EPA has asserted regulatory authority pursuant to the SDWA UIC program over hydraulic fracturing activities involving the use of diesel and issued guidance covering such activities, as well as published an Advanced Notice of Proposed Rulemaking regarding Toxic Substances Control Act (“TSCA”) reporting of the chemical substances and mixtures used in hydraulic fracturing. While this notice was subsequently withdrawn, certain chemical disclosures are required on the state level in some states, and the EPA could seek further rulemaking under TSCA in the future.
26
In late 2016, the EPA released its final report on the potential impacts of hydraulic fracturing on drinking water resources, concluding that “water cycle” activities associated with hydraulic fracturing may impact drinking water resources under some circumstances. The Biden Administration has also called for revisions and restrictions to the leasing and permitting programs for oil and gas development on federal lands and, for a time, suspended federal oil and gas leasing activities. Further administrative and regulatory restrictions may be adopted by the Biden Administration that could restrict hydraulic fracturing activities on federal lands and waters. For example, in November 2022 the Bureau of Land Management (“BLM”) proposed a rule that would limit flaring from well sites on federal lands, as well as allow the delay or denial of permits if BLM finds that an operator’s methane waste minimization plan is insufficient, and to increase the costs associated with federal oil and gas leasing. Additionally, in July 2023 the BLM proposed a rule to update the fiscal terms of federal oil and gas leases, increasing fees, rents, royalties, and bonding requirements. The rule would also add new criteria for BLM to consider when determining whether to lease nominated land, including the presence of important habitats or wetlands, the presence of historical properties or sacred sites, and recreational use of the land. BLM anticipates a final action on this proposal in Spring 2024.
Moreover, some state and local governments have adopted, and other governmental entities are considering adopting, regulations that could impose more stringent permitting, disclosure and well-construction requirements on hydraulic fracturing operations, including states where we or our customers operate. For example, Texas, Oklahoma, California, Ohio, Pennsylvania and North Dakota, among others, have adopted regulations that impose stringent permitting, disclosure, disposal and well-construction requirements on hydraulic fracturing operations. States could also elect to place certain prohibitions on hydraulic fracturing. In addition to state laws, local land use restrictions, such as city ordinances, may restrict drilling in general and/or hydraulic fracturing in particular, as certain local governments in California have done. Other states, such as Texas, Oklahoma and Ohio have taken steps to limit the authority of local governments to regulate oil and gas development.
In the event that new federal, state or local restrictions or bans on the hydraulic fracturing process are adopted in areas where we or our customers conduct business, we or our customers may incur additional costs or permitting requirements to comply with such requirements that may be significant in nature and our customers could experience added costs, restrictions, delays or cancellations in their exploration, development, or production activities, which would in turn reduce the demand for our services and have a material adverse effect on our liquidity, consolidated results of operations, and consolidated financial condition.
Air Emissions. The U.S. Clean Air Act (“CAA”) and comparable state laws restrict the emission of air pollutants from many sources through air emissions standards, construction and operating permit programs and the imposition of other compliance standards. These laws and regulations may require us to obtain pre-approval for the construction or modification of certain projects or facilities expected to produce or significantly increase air emissions, obtain and strictly comply with stringent air permit requirements or utilize specific equipment or technologies to control emissions of certain pollutants. The need to obtain permits has the potential to delay our projects as well as our customers’ development of oil and gas projects. Over the next several years, we or our customers may incur certain capital expenditures for air pollution control equipment or other air emissions-related issues. For example, in 2015, the EPA issued a final rule under the CAA, making the National Ambient Air Quality Standard (“NAAQS”) for ground-level ozone more stringent. Since that time, the EPA has issued attainment/nonattainment designations with respect to ground-level ozone and in December 2020, the EPA under the Trump Administration published a final action that, upon conducting a periodic review of the ozone standard in accord with CAA requirements, elected to retain the 2015 ozone NAAQS without revision on a going-forward basis. However, several groups have filed litigation over this December 2020 decision, and the Biden Administration has announced plans to reconsider the December 2020 final action in favor of a more stringent ground-level ozone NAAQS, a decision on which remains pending. State implementation of the revised NAAQS could also result in the imposition of more stringent requirements. Compliance with the NAAQS requirements or other air pollution control and permitting requirements has the potential to delay the development of oil and gas projects and increase our or our customers’ costs of development and production, which costs could reduce demand for our services and have a material adverse impact on our business and results of operations.
Climate Change. The issue of climate change continues to attract considerable attention from the public and policymakers in the U.S. and around the world. As a result, numerous proposals have been made, and more are likely forthcoming at the international, national, regional and state levels of government to monitor and limit existing emissions of greenhouse gases (“GHGs”) as well as to restrict or eliminate such future emissions. As a result, our
27
operations as well as the operations of our oil and natural gas exploration and production customers are subject to a series of regulatory, political, litigation, and financial risks associated with the production and processing of fossil fuels and emission of GHGs.
In the U.S., no comprehensive climate change legislation has been implemented at the federal level, though the IRA 2022, passed in August 2022, advances numerous climate-related objectives. Federal regulatory initiatives have focused on, among other things, establishing construction and operating permit reviews for GHG emissions from certain large stationary sources, requiring the monitoring and annual reporting of GHG emissions from certain petroleum and natural gas system sources, and reducing methane emissions from oil and gas production and natural gas processing and transmission operations through limitations on venting and flaring and the implementation of enhanced emission leak detection and repair requirements. In recent years, there has been considerable uncertainty surrounding regulation of methane emissions. During 2020, the Trump Administration revised performance standards for methane established in 2016 to lessen the impact of those standards and remove the transmission and storage segments from the source category for certain regulations. However, shortly after taking office in 2021, President Biden issued an executive order calling on the EPA to revisit federal regulations regarding methane and establish new or more stringent standards for existing or new sources in the oil and gas sector, including the transmission and storage segments. The U.S. Congress also passed, and President Biden signed into law, a revocation of the 2020 rulemaking, effectively reinstating the 2016 standards. In response to President Biden’s executive order, in December 2023, the EPA finalized a rule that established more stringent Quad Ob new source and Quad Oc first-time existing source standards of performance for methane and volatile organic compound (“VOC”) emissions in the crude oil and natural gas source category. Under the final rule, states will have two years to prepare and submit their plans to impose methane emission controls on existing sources. The presumptive standards under the final rule are generally the same for both new and existing sources, including enhanced leak detection using optical gas imaging and subsequent repair requirements, reduction of emissions by 95% through capture and control systems, zero-emission requirements, operations and maintenance requirements, and so-called green well completion requirements. The rule also revises requirements for fugitive emissions monitoring and repair as well as equipment leaks and the frequency of monitoring surveys, establishes a “super-emitter” response program to timely mitigate emissions events as detected by governmental agencies or qualified third parties, triggering certain investigation and repair requirements, and provides additional options for the use of advanced monitoring to encourage the deployment of innovative technologies to detect and reduce methane emissions. However, it is likely that these requirements will be subject to legal challenge.
In August 2022, the IRA 2022 was signed into law. This law, among other provisions, amends the CAA to establish the first federal fee on methane emissions from sources required to report their GHG emissions to the EPA, including certain oil and gas operations. The methane emissions charge will start in calendar year 2024 at $900 per ton of methane, increase to $1,200 in 2025, and be set at $1,500 for 2026 and subsequent years. Calculation of the methane fee is based on certain thresholds established in the IRA 2022. The IRA 2022 additionally appropriates significant federal funding for renewable energy initiatives. The methane emissions fee could increase our and our customers’ operating costs, and the funding and incentives established for renewable energy sources could accelerate the transition away from fossil fuels, which could in turn reduce demand for our products and services and adversely affect our business and results of operations.
Separately, various states and groups of states have adopted or are considering adopting legislation, regulations or other regulatory initiatives that are focused on such areas as GHG cap and trade programs, carbon taxes, reporting and tracking programs, and restriction of emissions. For example, Colorado has begun to increasingly regulate oil and gas
operations with consideration towards GHG emissions and cumulative impacts of oil and gas development. In January
2024, the Colorado Energy and Carbon Management Commission (formerly the Colorado Oil and Gas Conservation
Commission) released draft rules that would apply increased scrutiny to the cumulative impacts of GHG emissions of oil
and gas development and set GHG emissions intensity targets for oil and gas operators. At the international level, there exists a non-binding agreement, the United Nations-sponsored “Paris Agreement,” which is a non-binding agreement among participating nations to limit their GHG emissions through individually-determined reduction goals every five years after 2020. President Biden announced in April 2021 a new, more rigorous nationally determined emissions reduction level of 50-52% reduction from 2005 levels in economy-wide net GHG emissions by 2030. Moreover, the international community gathered again in Glasgow in November 2021 at the 26th Conference of the Parties (“COP26”), during which multiple announcements (not having the effect of law) were made, including a call for parties to eliminate certain fossil fuel subsidies and pursue further action on non-CO2 GHGs. Relatedly, the U.S. and European Union
28
jointly announced at COP26 the launch of a Global Methane Pledge, an initiative which over 100 counties joined, committing to a collective goal of reducing global methane emissions by at least 30 percent from 2020 levels by 2030, including “all feasible reductions” in the energy sector. At COP27 in November 2022, countries reiterated the agreements from COP26 and were called upon to accelerate efforts toward the phase out of inefficient fossil fuel subsidies. The U.S. also announced, in conjunction with the European Union and other partner countries, that it would develop standards for monitoring and reporting methane emissions to help create a market for low methane-intensity natural gas. At the 28th Conference of the Parties (“COP28”) in December 2023, the parties signed onto an agreement to transition away from fossil fuels in energy systems and increase renewable energy capacity, though no timeline for doing so was set. While non-binding, the agreements coming out of COP28 could result in increased pressure among financial institutions and various stakeholders to reduce or otherwise impose more stringent limitations on funding for and increase potential opposition to the production and use of fossil fuels. Although no firm commitment or timeline to phase out or phase down all fossil fuels was made at these conferences, there can be no guarantees that countries will not seek to implement such a phase out in the future. The impacts of these orders, pledges, agreements and any legislation or regulation promulgated to fulfill the U.S. commitments under the Paris Agreement, COP28, or other international conventions cannot be predicted at this time.
Since taking office, President Biden has issued several executive orders calling for more expansive action to address climate change to suspend new oil and gas operations on federal lands and waters, and most recently, to pause certain decisions relating to authorizations for liquefied natural gas exports. Litigation risks are also increasing, as a number of states, municipalities and other plaintiffs have sought to bring suit against the largest oil and natural gas exploration and production companies in state or federal court, alleging, among other things, that such companies created public nuisances by producing fuels that contributed to global warming effects, such as rising sea levels, and therefore are responsible for roadway and infrastructure damages as a result, or alleging that the companies have been aware of the adverse effects of climate change for some time but defrauded their investors by failing to adequately disclose those impacts.
Moreover, access to capital by fossil fuel producers as well as other companies supporting the oil and gas industry may be impacted by climate change policies. Stockholders and bondholders currently invested in fossil fuel energy companies but concerned about the potential effects of climate change may elect in the future to shift some or all of their investments into non-fossil fuel energy related sectors. Institutional investors who provide financing to fossil fuel energy companies have also focused on sustainability lending practices that favor “clean” power sources such as wind and solar and some of these investors may elect not to provide funding for carbon-intensive energy companies. Many of the largest U.S. banks have made “net zero” carbon emission commitments and have announced that they will be assessing financed emissions across their portfolios and taking steps to quantify and reduce those emissions. At COP26, the Glasgow Financial Alliance for Net Zero (“GFANZ”) announced that commitments from over 450 firms across 45 countries had resulted in over $130 trillion in capital committed to net zero goals. The various sub-alliances of GFANZ generally require participants to set short-term, sector-specific targets to transition their financing, investing, and/or underwriting activities to net zero emissions by 2050. These and other developments in the financial sector could lead to some lenders restricting access to capital for or divesting from certain industries or companies, including the oil and natural gas sector, or requiring that borrowers take additional steps to reduce their GHG emissions. Additionally, there is the possibility that financial institutions will be required to adopt policies that limit funding to the fossil fuel sector. In late 2020, the Federal Reserve announced that it had joined the Network for Greening the Financial System (“NGFS”), a consortium of financial regulators focused on addressing climate-related risks in the financial sector. More recently, in November 2021, the Federal Reserve issued a statement in support of the efforts of the NGFS to identify key issues and potential solutions for the climate-related challenges most relevant to central banks and supervisory authorities. In September 2022, the Federal Reserve announced that six of the U.S.’ largest banks will participate in a pilot climate scenario analysis exercise, which took place throughout 2023, to enhance the ability of firms and supervisors to measure and manage climate-related financial risk. While we cannot predict what policies may result from this, a material reduction in the capital available to the fossil fuel industry could make it more difficult to secure funding for exploration, development, production, transportation, and processing activities, which could reduce demand for our services.
In addition, the SEC has proposed a rule that would require registrants to make certain climate-related disclosures in registration statements and annual reports, including their governance of climate-related risks, material climate-related impacts on strategy, outlook and business model, climate risk management, Scope 1 and 2 GHG emissions and Scope 3 GHG emissions under certain circumstances, and if the registrant has set them, climate-related
29
targets and goals. The final rule is expected in 2024. Some states have enacted or are otherwise considering disclosure requirements for certain climate-related risks. Enhanced climate-related disclosure requirements could increase our operating costs and lead to reputational or other harm with customers, regulators, or other stakeholders to the extent our disclosures do not meet their own standards or expectations. Consequently, we are also exposed to increased litigation risks relating to alleged climate-related damages resulting from our operations, statements alleged to have been made by us or others in our industry regarding climate change risks, or in connection with any future disclosures we may make regarding reported emissions, particularly given the inherent uncertainties and estimations with respect to calculating and reporting GHG emissions. Separately, the SEC has from time to time applied additional scrutiny to existing climate-change related disclosures in public filings, increasing the potential for enforcement if the SEC were to allege that an issuer’s existing climate disclosures were misleading or deficient.
Finally, increasing concentrations of GHGs in the Earth's atmosphere may produce climate changes that have significant physical effects, such as increased frequency and severity of storms, droughts, floods, rising sea levels and other climatic events, as well as chronic shifts in temperature and precipitation patterns. These climatic developments have the potential to cause physical damage to our assets and thus could have an adverse effect on our operations. Additionally, changing meteorological conditions, particularly temperature, may result in changes to the amount, timing, or location of demand for energy or our solutions. While our consideration of changing climatic conditions and inclusion of safety factors in design is intended to reduce the uncertainties that climate change and other events may potentially introduce, our ability to mitigate the adverse impacts of these events depends in part on the effectiveness of our facilities and our disaster preparedness and response and business continuity planning, which we may not have considered or be prepared for every eventuality.
Endangered Species. The federal Endangered Species Act (the “ESA”) restricts activities that may affect endangered or threatened species or their habitats. Similar protections are offered to migratory birds under the federal Migratory Bird Treaty Act (the “MBTA”). The U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service ("FWS") under the Trump Administration issued a final rule in January 2021 clarifying that criminal liability under the MBTA would apply only to actions "directed at" migratory birds, their nests, or their eggs; however, the FWS under the Biden Administration has since published a final rule in October 2021 revoking the January 2021 rule and affirmatively stating that the MBTA prohibits incidental takes of migratory birds. To the degree that species listed under the ESA or similar state laws, or are protected under the MBTA, live in the areas where we or our oil and gas producing customers operate, our and our customers’ abilities to conduct or expand operations and construct facilities could be limited or be forced to incur material additional costs. Moreover, our customers’ drilling activities may be delayed, restricted, or cancelled in protected habitat areas or during certain seasons, such as breeding and nesting seasons. Some of our operations and the operations of our customers are located in areas that are designated as habitats for protected species. In addition, the FWS may make determinations on the listing of unlisted species as endangered or threatened under the ESA. The dunes sagebrush lizard and the lesser prairie chicken are examples of species that, if listed as endangered or threatened under the ESA in the future, could impact our or our customers’ operations. For example, in November 2022, the FWS listed two distinct population segments of the lesser prairie chicken under the ESA, one as threatened and one as endangered. The designation of previously unidentified endangered or threatened species could indirectly cause us to incur additional costs, cause our or our oil and gas producing customers’ operations to become subject to operating restrictions or bans and limit future development activity in affected areas. The FWS and similar state agencies may designate critical or suitable habitat areas that they believe are necessary for the survival of threatened or endangered species. Such a designation could materially restrict use of or access to federal, state, and private lands.
Chemical Safety. We are subject to a wide array of laws and regulations governing chemicals, including the regulation of chemical substances and inventories, such as TSCA in the U.S. These laws and regulations change frequently and have the potential to limit or ban altogether the types of chemicals we may use in our products, as well as result in increased costs related to testing, storing, and transporting our products prior to providing them to our customers. For example, in 2016, President Obama signed into law the Frank R. Lautenberg Chemical Safety for the 21st Century Act (the “Lautenberg Act”), which substantially revised TSCA. Amongst other items, the Lautenberg Act eliminated the cost-benefit approach to analyzing chemical safety concerns with a health-based safety standard and requires all chemicals in commerce, including those “grandfathered” under TSCA, to undergo a safety review. The Lautenberg Act also requires safety findings before a new chemical can enter the market. Any new restrictions on the development of new products, increases in regulation, or disclosure of confidential, competitive information could have an adverse effect on our operations and our cost of doing business.
30
Furthermore, governmental, regulatory and societal demands for increasing levels of product safety and environmental protection could result in increased pressure for more stringent regulatory control with respect to the chemical industry. These concerns could influence public perceptions regarding our products and operations, the viability of certain products, our reputation, the cost to comply with regulations, and the ability to attract and retain employees. Moreover, changes in environmental, health and safety regulations could inhibit or interrupt our operations, or require us to modify our facilities or operations. Accordingly, environmental or regulatory matters may cause us to incur significant unanticipated losses, costs or liabilities, which could reduce our profitability.
Occupational Safety and Health and other legal requirements. We are subject to the requirements of the federal Occupational Safety and Health Act and comparable state statutes whose purpose is to protect the health and safety of workers. In addition, the OSHA’s hazard communication standard, the EPA’s Emergency Planning and Community Right-to-Know Act and comparable state regulations and any implementing regulations require that we organize and/or disclose information about hazardous materials used or produced in our operations and that this information be provided to employees, state and local governmental authorities and citizens. We have an internal program of inspection designed to monitor and enforce compliance with worker safety requirements.
In addition, as part of the services we provide, we operate as a motor carrier and therefore are subject to regulation by the U.S. Department of Transportation (“U.S. DOT”) and analogous state agencies. These regulatory authorities exercise broad powers, governing activities such as the authorization to engage in motor carrier operations, regulatory safety, and hazardous materials labeling, placarding and marking. There are additional regulations specifically relating to the trucking industry, including testing and specification of equipment and product handling requirements. The trucking industry is subject to possible regulatory and legislative changes that may affect the economics of the industry by requiring changes in operating practices or by changing the demand for common or contract carrier services or the cost of providing truckload services. From time to time, various legislative proposals are introduced, including proposals to increase federal, state or local taxes on motor fuels, among other things, which may increase our costs or adversely impact the recruitment of drivers. We cannot predict whether, or in what form, any increase in such taxes applicable to us will be enacted.
Seasonality
Our results of operations have historically been adversely affected by seasonal declines in the activity levels of our customers, typically in the fourth quarter, related to holidays, inclement winter weather and in some years the exhaustion of our customers’ annual drilling and completions capital expenditure budgets.
Intellectual Property
Protection of our products and processes is important to our businesses. We own numerous patents and, where appropriate, we file patent applications for new products and technologies. For example, we use our AquaView® technology to quantify volumes and flow rates to verify current and potential water availability and volumes when analyzing a new water source. We also currently own multiple U.S. patents relating to completions technology including borate cross-linkers, slurry monitoring systems and others. We also have a robust program to seek patents on new developments.
We have a meaningful backlog of pending patents, including a proprietary water analytics and automation tool, as well as creating fracturing fluids with produced water, evaporation methodologies, cross-linker/breaker mechanisms and liquid distribution metering systems. While a presumption of validity exists with respect to issued U.S. patents, we cannot assure that any of our patents will not be challenged, invalidated, circumvented or rendered unenforceable. Furthermore, we cannot assure the issuance of any pending patent application, or that if patents do issue, that these patents will provide meaningful protection against competitors or against competitive technologies. Additionally, our competitors or other third parties may obtain patents that restrict or preclude our ability to lawfully produce or sell our products in a competitive manner.
We also rely upon continuing technological innovation and trade secrets to develop and maintain our competitive position. There can be no assurance that confidentiality and other agreements into which we enter and have entered will not be breached, that these agreements will provide meaningful protection for our trade secrets or
31
proprietary know-how, or that adequate remedies will be available in the event of an unauthorized use or disclosure of such trade secrets and know-how. In addition, there can be no assurance that others will not obtain knowledge of these trade secrets through independent development or other access by legal means.
We also own a number of trademarks, which we use in connection with our businesses. In addition to protections through federal registration, we also rely on state common law protections to protect our brand. There can be no assurance that the trademark registrations will provide meaningful protection against the use of similar trademarks by competitors, or that the value of our trademarks will not be diluted.
Because of the breadth and nature of our intellectual property rights and our business, we do not believe that any single intellectual property right (other than certain trademarks for which we intend to maintain the applicable registrations) is material to our business. Moreover, we do not believe that the termination of intellectual property rights expected to occur over the next several years, either individually or in the aggregate, will materially adversely affect our business, financial condition or results of operations.
Risk Management and Insurance
Our operations are subject to hazards inherent in the oil and gas industry, including accidents, blowouts, explosions, craterings, fires, oil spills and hazardous materials spills. These conditions can cause:
| ● | personal injury or loss of life; |
| ● | damage to, or destruction of, property, the environment and wildlife; and |
| ● | the suspension of our or our customers’ operations. |
In addition, claims for loss of oil and gas production and damage to formations can occur in the well services industry. If a serious accident were to occur at a location where our equipment and services are being used, it could result in us being named as a defendant in lawsuits asserting large claims.
Because our business involves the transportation of heavy equipment, freight and materials, we may also experience traffic accidents, which may result in spills, property damage and personal injury.
Despite our efforts to maintain high safety standards, including the installation of vehicle surveillance systems, from time to time we have suffered accidents, and there is a risk that we will experience accidents in the future. In addition to the property and personal losses from these accidents, the frequency and severity of these incidents affect our operating costs and insurability, and our relationship with customers, employees and regulatory agencies. In particular, in recent years many of our large customers have placed an increased emphasis on the safety records of their service providers. Any significant increase in the frequency or severity of these incidents, or the general level of compensatory payments, could adversely affect the cost of, or our ability to obtain, workers’ compensation and other forms of insurance, and could have other material adverse effects on our financial condition and results of operations.
We maintain insurance coverage of types and amounts that we believe to be customary in the industry, including workers’ compensation, employer’s liability, sudden & accidental pollution, umbrella, directors & officers, comprehensive commercial general liability, business automobile and property, cybersecurity and equipment physical damage insurance. Our insurance coverage may be inadequate to cover our liabilities. In addition, we may not be able to maintain adequate insurance in the future at rates we consider reasonable and commercially justifiable or on terms as favorable as our current arrangements.
We enter into master service agreements (“MSAs”) with most of our customers. Our MSAs delineate our and our customer’s respective indemnification obligations with respect to the services we provide. Generally, under our MSAs, including those relating to our Water Services, Water Infrastructure, Oilfield Chemical product sales, accommodations and rentals and completion and construction services, we assume responsibility for pollution or
32
contamination originating above the surface from our equipment or handling of the equipment of others. However, our customers generally assume responsibility for all other pollution or contamination that may occur during operations, including that which may generally result from seepage or any other uncontrolled flow of drilling fluids. The assumed responsibilities include the control, removal and cleanup of any pollution or contamination. In such cases, we may be exposed to additional liability if we are grossly negligent or commit willful acts causing the pollution or contamination. Generally, our customers also agree to indemnify us against claims arising from the personal injury or death of the customers’ employees or those of the customers’ other contractors, in the case of our hydraulic fracturing operations, to the extent that such employees are injured by such operations, unless the loss is a result of our gross negligence or willful misconduct. Similarly, we generally agree to indemnify our customers for liabilities arising from personal injury to or death of any of our employees or employees of any of our subcontractors, unless resulting from the gross negligence or willful misconduct of our customer. The same principles apply to mutual indemnification for loss or destruction of customer-owned property or equipment, except such indemnification is not limited in an instance of gross negligence or willful misconduct. Losses arising from catastrophic events, such as blowouts, are generally the responsibility of the customer. However, despite this general allocation of risk, we may be unsuccessful in enforcing contractual terms, incur an unforeseen liability that is not addressed by the scope of the contractual provisions or be required to enter into an MSA with terms that vary from our standard allocations of risk, as described above. Consequently, we may incur substantial losses that could materially and adversely affect our financial condition and results of operations.
Available Information
We file or furnish annual, quarterly and current reports and other documents with the SEC under the Exchange Act. The SEC also maintains an internet website at www.sec.gov that contains reports, proxy and information statements and other information regarding issuers, including us, that file electronically with the SEC.
We also make available free of charge through our website, www.selectwater.com, electronic copies of certain documents that we file with the SEC, including our Annual Reports on Form 10-K, Quarterly Reports on Form 10-Q, Current Reports on Form 8-K and amendments to those reports filed or furnished pursuant to Section 13(a) or 15(d) of the Exchange Act as soon as reasonably practicable after we electronically file such material with, or furnish it to, the SEC. Information on our website is not a part of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
ITEM 1A. RISK FACTORS
The following risks could affect our financial performance or could cause actual results to differ materially from estimates contained in our forward-looking statements. We may encounter risks in addition to those described below. Additional risks and uncertainties not currently known to us, or that we currently deem to be immaterial, may also impair or adversely affect our business, results of operation, financial condition and prospects.
Risks Related to Our Business Operations
Our business depends on capital spending by the oil and gas industry in the U.S. and reductions in capital spending could have a material adverse effect on our liquidity, results of operations and financial condition.
Demand for our services is directly affected by capital spending by our customers to explore for, develop and produce oil and gas in the U.S. Capital spending is generally dependent on our customers’ views of future demand for oil and gas and future oil and gas prices, as well as our customers’ ability to access capital. Such demand may be impacted by a variety of factors, including the Russia-Ukraine war, the conflict in the Israel-Gaza region and related instability in the Middle East, including from the Houthi rebels in Yemen, accelerated substitution of renewable forms of energy for oil and gas and actions of OPEC+. During the year ended December 31, 2023, the average West Texas Intermediate (“WTI”) spot price was $77.58, versus an average price of $94.90 for the year ended December 31, 2022 and $68.16 for the year ended December 31, 2021.
Volatility in oil prices or natural gas prices (or the perception that oil prices or natural gas prices will decrease) affects the spending patterns of our customers and may result in the drilling or completion of fewer new wells or lower
33
spending on existing wells. This, in turn, could lead to lower demand for our services and may cause lower rates and lower utilization of our assets. While customer budgets for U.S. onshore development during 2023 were generally flat on a year over year basis and materially recovered from COVID-19 lows, factors outside of our control can alter these budgets, or lead customers to underspend their budgets. Even in an environment of strong oil and gas prices, fewer oil and gas well completions in our market areas as a result of decreased capital spending may have a negative long-term impact on our business. Any of these conditions or events could adversely affect our operating results and may continue to do so into the future. Sustained market uncertainty could also result in lower demand for our services, which could adversely affect our liquidity, results of operations and financial condition.
Industry conditions are influenced by numerous factors over which we have no control, including:
| ● | domestic and foreign economic conditions, including sustained periods of inflation, high interest rates and associated policies of the Federal Reserve, and supply of and demand for oil and gas; |
| ● | the level of prices, and expectations regarding future prices, of oil and gas; |
| ● | the level of global oil and gas exploration and production and utilization of storage capacity; |
| ● | actions by the members of OPEC+ with respect to oil production levels and announcements of potential changes in such levels, including the ability of the OPEC+ countries to agree on and comply with supply limitations; |
| ● | governmental regulations, including the policies of governments regarding the exploration for and production and development of, their oil and gas reserves; |
| ● | taxation and governmental royalty charges; |
| ● | political and economic conditions in oil and gas producing countries, including any political or social unrest; |
| ● | global weather conditions, pandemics or other public health crises and natural disasters; |
| ● | worldwide political, military and economic conditions; |
| ● | political or civil unrest in the U.S. or elsewhere, including the Russia-Ukraine war and the conflict in the Israel-Gaza region and related instability in the Middle East, including from Houthi rebels in Yemen; |
| ● | the cost of producing and delivering oil and gas; |
| ● | the discovery rates of new oil and gas reserves; |
| ● | the effects of consolidation on our customers or competitors; |
| ● | activities by non-governmental organizations to limit certain sources of funding for the energy sector or restrict the exploration, development and production of oil and gas; |
| ● | the ability of oil and gas producers to access capital; |
| ● | technical advances affecting production efficiencies and overall energy consumption; and |
| ● | the potential acceleration of the development of alternative fuels, including as a result of the IRA 2022 or otherwise. |
34
Political instability or armed conflict in crude oil or natural gas producing regions, such as the ongoing war between Russia and Ukraine, the conflict in the Israel-Gaza region and related instability in the Middle East, including from the Houthi rebels in Yemen, and OPEC+ policy decisions could have a material adverse impact on our business, financial condition or future results.
Our business, financial condition and future results are subject to political and economic risks and uncertainties, including instability resulting from civil unrest, political demonstrations, mass strikes or armed conflict or other crises in crude oil or natural gas producing areas. For example, in late February 2022, Russian military forces commenced a military operation and invasion against Ukraine. The United States and other countries and certain international organizations have imposed broad-ranging economic sanctions on Russia and certain Russian individuals, banking entities and corporations as a response. The length, impact, and outcome of the ongoing war between Russia and Ukraine is highly unpredictable, which has created uncertainty for financial and commodity markets. An end to the Russia-Ukraine conflict and an easing or elimination of the related sanctions against Russia could result in a significant fall in commodity prices as Russian hydrocarbons become more readily accessible on global markets, which could have an adverse effect on our customers and therefore adversely affect our customers’ demand for our services. In addition, the attack on Israel by Hamas militants on October 7, 2023 and the ensuing conflict has resulted in increased hostilities and instability in oil and gas producing regions in the Middle East. Following such attack, Israel’s security cabinet declared war against Hamas and a military campaign against such terrorist organizations commenced. In tandem with such conflict, the Houthi movement, which controls parts of Yemen, has targeted and launched numerous attacks on Israeli, American and international commercial marine vessels in the Red Sea as the ships approach the Suez Canal, resulting in many shipping companies re-routing to avoid the region altogether and worsening existing supply chain issues, including delays in supplier deliveries, extended lead times and increased cost of freight, insurance and materials. Further escalation of conflict in the Middle East, in particular with Iran, a major oil producer, the Houthi movement in Yemen or the Hezbollah movement in Lebanon, could have an adverse effect on our customers and therefore adversely affect our customers’ demand for our services.
The ultimate geopolitical and macroeconomic consequences of these conflicts, and any associated sanctions or geopolitical actions, cannot be predicted, and such events, or any further hostilities, could severely impact the world economy and may adversely affect our financial condition. Although the Company does not have operations overseas, these conflicts elevate the likelihood of supply chain disruptions, heightened volatility in crude oil and natural gas prices and negative effects on our ability to raise additional capital when required and could have a material adverse impact on our business, financial condition or future results.
In October 2022, OPEC+ determined to reduce production beginning in November 2022 through December 2023 by two million barrels per day, due to the uncertainty surrounding the global economic and crude oil market outlooks. A number of other production cuts have followed, most recently, in November 2023, OPEC+ announced voluntary output cuts totaling 2.2 million barrels per day into the first quarter of 2024, including an additional cut of 900,000 barrels per day. Although OPEC+ increased its output in December 2023 due to, among other things, the ongoing conflicts in the Middle East, OPEC+ may, at its discretion, continue to decrease, or increase, production, which will continue to impact crude oil and natural gas price volatility.
Due to the above and other factors, crude oil and natural gas prices experienced increased levels of volatility during 2023, ranging from a high of $93.67 per barrel (“bbl”) at one point, primarily due to global supply and demand imbalances, to a low of $66.61 per bbl. Crude oil and natural gas prices will continue to decrease or increase with any changes in supply or demand due to, among other things, uncertainty and volatility from global supply chain disruptions attributable to the pandemic, the ongoing conflict in Ukraine, the conflict in the Israel-Gaza region and resultant increased instability in the Middle East, international sanctions, speculation as to future actions by OPEC+, outbreaks of illnesses and any other public health crises, increasing inflation and government efforts to reduce inflation, including high interest rates, and possible changes in the overall health of the global economy, including a prolonged recession. Further, the volatility in crude oil and natural gas prices could accelerate a transition away from fossil fuels, resulting in reduced demand over the longer term. To what extent these and other external factors (such as government action with respect to climate change regulation) ultimately impact our future business, liquidity, financial condition, and results of operations is highly uncertain and dependent on numerous factors, including future developments, which are not within our control and cannot be accurately predicted.
35
Continuing or worsening inflationary issues and associated changes in monetary policy have resulted in and may result in additional increases to the cost of our goods, services and personnel, which in turn could cause our capital expenditures and operating costs to rise.
The U.S. inflation rate steadily increased during 2021 and 2022. Although the rate of inflation has generally declined since the second half of 2022, the rate of inflation remains higher than historical averages, and inflationary pressures remain volatile and have resulted in and may result in additional increases to the costs of our goods, services and personnel, which would in turn cause our capital expenditures and operating costs to rise. Sustained levels of high inflation have likewise caused the U.S. Federal Reserve and other central banks to increase interest rates multiple times throughout 2022 and 2023. The U.S. Federal Reserve may continue to raise benchmark interest rates in 2024 in response to, among other things, inflationary pressure on the costs of goods and services across the U.S., which could have the effect of raising the cost of capital and depressing economic growth, either of which—or the combination thereof—could hurt the financial and operating results of our business. To the extent elevated inflation remains, we may experience further cost increases for our operations, including labor costs and equipment if our operating activity increases.
We cannot predict any future trends in the rate of inflation, or any resultant changes in monetary policy, and a significant increase in inflation, to the extent we are unable to recover higher costs, and/or higher interest rates would negatively impact our business, financial condition and results of operations.
The failure to successfully integrate acquired assets or operations in the expected time frame or at all may adversely affect our future results.
If we fail to integrate acquired properties and successfully combine our business with the businesses of such acquired properties, the anticipated benefits of such acquisitions may not be realized fully or at all or may take longer to realize than expected. In addition, the actual integration may result in additional and unforeseen expenses, which could reduce the anticipated benefits of such acquisitions.
It is possible that the integration process could result in the loss of key employees, as well as the disruption of our ongoing businesses or inconsistencies in our standards, controls, procedures and policies. Any or all of those occurrences could adversely affect our ability to maintain relationships with customers and employees or to achieve the anticipated benefits of our acquisition activities. Integration efforts will also divert management attention and resources. These integration matters could have an adverse effect on us.
The IRA 2022 could accelerate the transition to new energy sources and could impose new costs on our customers’ operations.
In August 2022, President Biden signed the IRA 2022 into law. The IRA 2022 contains hundreds of billions of dollars in incentives for the development of renewable energy, clean hydrogen, clean fuels, electric vehicles and supporting infrastructure and carbon capture and sequestration, amongst other provisions. These incentives could further accelerate the transition from the use of fossil fuels to alternative energy sources, which could decrease demand for oil and gas and consequently adversely affect the business of our customers, thereby reducing demand for our services. In addition, the IRA 2022 imposes the first ever federal fee on the emission of GHGs through a methane emission charge. The IRA 2022 amends the Clean Air Act to impose a fee on the emission of methane from sources required to report their GHG emissions to the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (“EPA”), including those sources in the onshore petroleum and natural gas production and gathering and boosting source categories. The methane emission charge began in 2024 at $900 per ton of methane, is set to increase to $1,200 in 2025, and be set at $1,500 for 2026 and each year after. Calculation of the fee is based on certain thresholds established in the IRA 2022. A rule to implement the methane fee was proposed by EPA in January 2024 and will be subject to public comment. The methane emissions charge could increase our customers’ operating costs and adversely affect their businesses, thereby reducing demand for our services.
Additional fuel conservation measures, alternative fuel requirements and increased consumer demand for alternatives to oil and natural gas could reduce demand for oil and natural gas. The increased competitiveness of alternative energy sources (such as wind, solar, geothermal, tidal, fuel cells and biofuels), as such sources are developed, supported through government actions, improved and promoted, could reduce demand for hydrocarbons and therefore
36
for our services, which would lead to a reduction in our revenues. The impact of declining demand for oil and natural gas may have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, prospects, results of operations and cash flows.
Almost half of our revenues are derived from our operations in the Permian Basin of Texas and New Mexico, making us vulnerable to risks associated with geographic concentration generally and the Permian Basin specifically, including Basin-specific supply and demand factors, regulatory changes and severe weather impacts that could materially and adversely affect our business.
The Permian Basin of Texas and New Mexico is presently our largest operating region, accounting for approximately 48% of our revenue in 2023 and 47% of our revenue in 2022. As a result of this concentration, we are vulnerable to risks associated with geographic concentration generally and the Permian Basin specifically. For example, we are disproportionately exposed to the impact in the Permian Basin of regional supply and demand factors, production delays or interruptions, as a result of governmental regulation or otherwise, processing or transportation capacity constraints, severe weather, market limitations, curtailment of production or interruption of the processing or transportation of produced oil and natural gas. Certain pricing factors have contributed to increased consolidation activity recently in the Permian Basin, which may lead to reductions in capital spending that could have an adverse affect on our business. In addition, the effect of fluctuations on supply and demand may become more pronounced within specific geographic oil and natural gas producing areas such as the Permian Basin, which may cause these conditions to occur with greater frequency or magnify the effects of these conditions. Due to the concentrated nature of our revenue-generating operations, we could experience any of the same conditions at the same time, resulting in a relatively greater impact on our revenue than they might have on other companies that have more geographically diverse revenue-generating operations.
Weather events that disproportionately impact the Permian Basin will adversely affect our results of operations as compared to our competitors that operate in other basins or that have more geographically diverse operations. Similarly, a significant portion of our current business relates to water and water-related services in the New Mexico portion of the Permian Basin. However, the future availability of, and/or access to, water in New Mexico will be affected by the results of a case, Texas v. New Mexico and Colorado, which is currently stayed pending further order by a special master. In this lawsuit, Texas is alleging that New Mexico is unlawfully allowing diversion of Rio Grande surface water, including groundwater hydrologically connected to the Rio Grande, and thereby depriving Texas of the full amount of Rio Grande water it is due under the Rio Grande Compact, which agreement was created in 1938 to ensure that the two states and the state of Colorado would get their fair share of water from the river. To the extent that this lawsuit is adversely decided against New Mexico, the state could, among other things, be required to provide more water downstream to Texas, which could reduce the availability of, and/or access to, water to existing or new water rights holders in New Mexico, resulting in limitations in our ability to obtain or maintain access to water for certain of our customers’ operations in New Mexico. The states reached a water-sharing agreement in 2022, which has been supported by the state of New Mexico, that determines an annual delivery amount for New Mexico and allows the state to accrue debt if it cannot make the annual delivery amount. In July 2023 the special master recommended that the U.S. Supreme Court approve the agreement, which approval remains pending. The risk of any adverse development could reduce our ability to obtain or maintain access to water for our customers’ operations in the vicinity of our assets in New Mexico and have a corresponding adverse effect on our financial condition, results of operations and cash flows.
To the extent that the types of basin-specific events discussed above continue to arise or worsen, our operations and those of our customers may be materially and adversely affected.
Restrictions on the ability to procure water or changes in water sourcing or disposal requirements could add costs or decrease the demand for our water-related services.
Our business includes water transfer for use in our customers’ oil and gas E&P activities. Our access to the water we supply may be limited due to prolonged drought or our inability to acquire or maintain water sourcing permits or other rights. In addition, some state and local governmental authorities have begun to monitor or restrict the use of water subject to their jurisdiction for hydraulic fracturing to ensure adequate local water supply. For instance, some states require E&P companies to report certain information regarding the water they use for hydraulic fracturing and to
37
monitor the quality of groundwater surrounding some wells stimulated by hydraulic fracturing. Any such decrease in the availability of water, or demand for water services, could adversely affect our business and results of operations.
For example, our operations in New Mexico are subject to the risk of decreased access to water in New Mexico as a result of Texas v. New Mexico and Colorado. For more information, see our risk factor titled “Almost half of our revenues are derived from our operations in the Permian Basin of Texas and New Mexico, making us vulnerable to risks associated with geographic concentration generally and the Permian Basin specifically, including Basin-specific supply and demand factors, regulatory changes and severe weather impacts that could materially and adversely affect our business.”
The adoption of more stringent trucking legislation or regulations may increase our costs and could have an adverse effect on our liquidity, results of operations, and financial condition.
In connection with the services we provide, we operate as a motor carrier and therefore are subject to regulation by the DOT and analogous state agencies, which govern such activities as the authorization to engage in motor carrier operations and regulatory safety. The trucking industry is subject to possible legislative and regulatory changes that may affect the economics of the industry by requiring changes in operating practices or by changing the demand for common or contract carrier services or the cost of providing truckload services.
Moreover, from time to time, various legislative proposals are introduced, including proposals to increase federal, state or local taxes, including taxes on motor fuels and environmental regulations pertaining to motor vehicles, which may increase our costs, limit our ability to utilize our trucks on schedule, require us to undertake repairs or sales of certain trucks or adversely affect the recruitment of drivers. Management cannot predict whether, or in what form, any increase in such taxes applicable to us will be enacted. We may be required to increase operating expenses or capital expenditures in order to comply with any new laws, regulations or other restrictions. See Part I, Item 1. “Business – Environmental and Occupational Safety and Health Matters” for more discussion on the DOT and associated trucking matters.
We may be unable to implement price increases or maintain existing prices on our core services.
We periodically seek to increase the prices on our services to offset rising costs and to improve returns on investment for our stockholders. However, we operate in a very competitive industry and as a result, we are not always successful in raising, or maintaining, our existing prices. Additionally, during periods of increased market demand, a significant amount of new service capacity, including new water transfer equipment, fluid hauling trucks and pipelines, may enter the market, which also puts pressure on the pricing of our services and limits our ability to increase prices.
Even when we are able to increase our prices, we may not be able to do so at a rate that is sufficient to offset rising costs. In periods of high demand for oilfield services, a tighter labor market may result in higher labor costs. During such periods, our labor costs could increase at a greater rate than our ability to raise prices for our services. Also, we may not be able to successfully increase prices without adversely affecting our activity levels. The inability to maintain our pricing and to increase our pricing as costs increase could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial position and results of operations.
We have operated at a loss in the past, including in 2021, and there is no assurance of our profitability in the future.
Historically, we have experienced periods of low demand for our services and have incurred operating losses, including during 2021. In the future, we may not be able to reduce our costs, increase our revenues or reduce our debt service obligations sufficient to achieve or maintain profitability and generate positive operating income. Under such circumstances, we may incur further operating losses and experience negative operating cash flow.
38
We may be subject to claims for personal injury and property damage, which could materially adversely affect our financial condition and results of operations.
We operate with most of our customers under MSAs. We endeavor to allocate potential liabilities and risks between the parties in the MSAs. Generally, under our MSAs, including those relating to our services, we assume responsibility for, including control and removal of, pollution or contamination that originates above the surface and originates from our equipment or services. Our customers generally assume responsibility for, including control and removal of, all other pollution or contamination that may occur during operations, including that which may result from seepage or any other uncontrolled flow of drilling fluids. We may have liability in such cases if we are negligent or commit willful acts. Generally, our customers also agree to indemnify us against claims arising from their employees’ personal injury or death to the extent that, in the case of our operations, their employees are injured or their properties are damaged by such operations unless resulting from our gross negligence or willful misconduct. Similarly, we generally agree to indemnify our customers for liabilities arising from personal injury to, or death of, any of our employees, unless resulting from gross negligence or willful misconduct of the customer. In addition, our customers generally agree to indemnify us for loss or destruction of customer-owned property or equipment and in turn, we agree to indemnify our customers for loss or destruction of property or equipment we own. Losses due to catastrophic events, such as blowouts, are generally the responsibility of the customer. However, despite this general allocation of risk, we might not succeed in enforcing such contractual allocation, might incur an unforeseen liability falling outside the scope of such allocation or may be required to enter into an MSA with terms that vary from the above allocations of risk. As a result, we may incur substantial losses, which could materially and adversely affect our financial condition and results of operations.
We operate in a highly competitive industry, which may intensify as our competitors expand their operations, thereby causing us to lose market share, and which could negatively affect our ability to expand our operations.
The oilfield water management business is highly competitive and includes numerous small companies capable of competing effectively in our markets on a local basis. Some of our larger diversified competitors have a similarly broad geographic scope, as well as greater financial and other resources than us, while others focus on specific basins only and may have locally competitive cost efficiencies as a result. Additionally, there may be new companies that enter our markets, or our existing and potential customers may choose to develop their own water management solutions. Our ability to maintain current revenue and cash flows, and our ability to expand our operations, could be adversely affected by the activities of our competitors and our customers. We may be unable to effectively compete if our competitors substantially increase the resources they devote to the development and marketing of the services that we offer, or substantially decrease the prices at which they offer their services. If our existing and potential customers develop their own water solutions, we may not be able to effectively replace that revenue. All of these competitive pressures could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations and financial condition.
The oil and gas services industry is intensely competitive, and in certain businesses we compete with other companies that have greater resources than us. Many of our larger competitors provide a broader base of services on a regional, national or worldwide basis. These companies may have a greater ability to continue oilfield service activities during periods of low commodity prices, to contract for equipment, to secure trained personnel, to secure contracts and permits and to absorb the burden of present and future federal, state, provincial, local and other laws and regulations (as applicable). Any inability to compete effectively with larger companies could have a material adverse impact on our financial condition and results of operations.
Our operations involve risks that may increase our operating costs, which could reduce our profitability.
Although we take precautions to enhance the safety of our operations and minimize the risk of disruptions, our operations are subject to hazards inherent in the manufacturing and marketing of chemical and other products. These hazards include chemical spills, pipeline leaks and ruptures, storage tank leaks, discharges or releases of toxic or hazardous substances or gases and other hazards incident to the manufacturing, processing, handling, transportation and storage of hazardous chemicals. We are also potentially subject to other hazards, including natural disasters and severe weather; explosions and fires; transportation problems, including interruptions, spills and leaks; mechanical failures; unscheduled downtimes; labor difficulties; remediation complications; and other risks. Many potential hazards can cause
39
bodily injury and loss of life, severe damage to or destruction of property and equipment and environmental damage, and may result in suspension of operations and the imposition of civil or criminal penalties and liabilities. Furthermore, we are subject to present and future claims with respect to workplace exposure, exposure of contractors on our premises as well as other persons located nearby, workers’ compensation and other matters.
We maintain property, business interruption, products liability, cybersecurity and casualty insurance policies that we believe are in accordance with customary industry practices, as well as insurance policies covering other types of risks, including pollution legal liability insurance, but we are not fully insured against all potential hazards and risks incident to our business. Our operations are subject to hazards inherent in the oil and gas industry, such as, but not limited to, accidents, blowouts, explosions, craterings, fires, oil spills and releases of drilling, completion or fracturing fluids or wastewater into the environment. These conditions can cause:
| ● | disruption in operations; |
| ● | substantial repair or remediate costs; |
| ● | personal injury or loss of human life; |
| ● | significant damage to or destruction of property, plant and equipment; |
| ● | environmental pollution, including groundwater contamination; |
| ● | impairment or suspension of operations; and |
| ● | substantial revenue loss. |
We do not have insurance against all foreseeable risks, either because insurance is not available or because of the high premium costs. The occurrence of an event not fully insured against or the failure of an insurer to meet its insurance obligations could result in substantial losses. In addition, we may not be able to maintain adequate insurance in the future at rates we consider reasonable. Insurance may not be available to cover any or all of the risks to which we are subject, or, even if available, it may be inadequate, or insurance premiums or other costs could rise significantly in the future so as to make such insurance prohibitively expensive. Our insurance policies are subject to customary exclusions, deductibles and coverage limits, in accordance with industry standards and practices. As a result of market conditions, premiums and deductibles for certain insurance policies can increase substantially and, in some instances, certain insurance may become unavailable or available only for reduced amounts of coverage. If we were to incur a significant liability for which we were not fully insured, it could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations, financial condition and liquidity.
The occurrence of a significant event or adverse claim in excess of the insurance coverage that we maintain or that is not covered by insurance could have a material adverse effect on our liquidity, results of operations and financial condition. Any interruption in our services due to pipeline breakdowns or necessary maintenance or repairs could reduce sales revenues and earnings. In addition, claims for loss of oil and gas production and damage to formations can occur in the well services industry. Litigation arising from a catastrophic occurrence at a location where our equipment and services are being used may result in our being named as a defendant in lawsuits asserting large claims.
In addition, we are subject to various claims and litigation in the ordinary course of business. We are a party to various pending lawsuits and proceedings. For more information, see Part I, Item 3. “Legal Proceedings.”
Delays or restrictions in obtaining permits by us for our operations or by our E&P customers for their operations could impair our business.
Our operations and the operations of our E&P customers in most states require permits from one or more governmental agencies in order to perform drilling and completion activities, secure water rights, construct
40
impoundment tanks and operate pipelines or trucking services. Such permits are typically issued by state agencies, but federal and local governmental permits may also be required. In addition, some of our customers’ drilling and completion activities in the U.S. may take place on federal land or Native American lands, requiring leases and other approvals from the federal government or Native American tribes to conduct such drilling and completion activities. Under certain circumstances, federal agencies may cancel proposed leases for federal lands and refuse to grant or delay required approvals. Moreover, President Biden issued an executive order in January 2021 to suspend new federal leasing activities on federal lands and waters, which suspension also restricts the ability to conduct hydraulic fracturing on those federal lands that are not leased; however, a nationwide injunction issued by a federal judge in Louisiana in August 2022 has effectively halted implementation of the leasing suspension. However, additional rules and regulations on federal lands may impact our customers. For example, the BLM has proposed new rules that would limit flaring from well sites on federal lands, as well as allow for the delay or denial of permits if the BLM finds that an operator’s methane waste minimization plan is insufficient. Any delay or denial of permits faced by our customers may impact demand for our services. See Part I, Item 1. “Business – Environmental and Occupational Safety and Health Matters” for more discussion on possible actions under the Biden Administration that may adversely affect oil and natural gas leasing and permitting activities.
We are implementing a new enterprise resource planning system, and challenges with the implementation of the system may impact our business and operations.
We are in the process of completing a multi-year implementation of a complex new enterprise resource planning system (“ERP”). The ERP implementation has required the integration of the new ERP with multiple information systems and business processes, and has been designed to continue to accurately maintain our books and records and provide timely information to our management team important to maximizing the operating efficiency of the business. Conversion from our old systems to the new ERP may cause inefficiencies until the ERP is stabilized and mature. The implementation of our new ERP will mandate subtle changes to our procedures and controls over financial reporting. If we are unable to adequately implement and maintain procedures and controls relating to our new ERP, our ability to produce timely and accurate financial statements or comply with applicable regulations could be impaired and impact our assessment of the effectiveness of our internal controls over financial reporting. Our Chemical Technologies segment went live with the new ERP in August of 2023 and we expect Water Services and Water Infrastructure to go live during 2024.
We are subject to cybersecurity risks. A cyber incident or systems failure could occur and result in information theft, data corruption, operational disruption and/or financial loss.
Our industry has become increasingly dependent on digital technologies to conduct certain processing activities. For example, we depend on digital technologies to perform many of our services and to process and record financial and operating data. At the same time, cyber incidents, including deliberate attacks or unintentional events, have increased in frequency. Cyber-attacks have the potential to significantly affect the energy industry and its service providers, including our operations and those of our business partners, suppliers and customers, as well as general economic conditions, consumer confidence and spending and market liquidity.
There was a high profile ransomware attack on a U.S. pipeline in 2021, and the U.S. government has since issued public warnings that indicate that energy assets might be specific targets of cybersecurity threats. Our technologies, systems and networks, and those of our vendors, suppliers and other business partners, may become the target of cyber-attacks or information security breaches that could result in the unauthorized release, gathering, monitoring, misuse, loss or destruction of proprietary and other information, or other disruption of business operations. In addition, certain cyber incidents may remain undetected for an extended period. Our systems for protecting against cybersecurity risks may not be sufficient. As cyber incidents continue to evolve, we may be required to expend additional resources to continue to modify or enhance our protective measures or to investigate and remediate any vulnerability to cyber incidents. Our insurance coverage for cyber-attacks may not be sufficient to cover all the losses we may experience as a result of such cyber-attacks.
We also collect and store sensitive data in the ordinary course of our business, including personally identifiable information as well as our proprietary business information and that of our customers, suppliers, investors and other
41
stakeholders. To protect this sensitive information, we follow practices and procedures designed to ensure that our networks, systems and electronic data are secured. These include the use of protected drives, secure passwords standards, cybersecurity training, endpoint protection systems, network monitoring, multi-factor authentication, among others. Despite our security measures, our information technology (“IT”) systems may undergo cyber-attacks or security breaches including as a result of employee error, malfeasance or other threat vectors, which could lead to the corruption, loss, or disclosure of proprietary and sensitive data, misdirected wire transfers, and an inability to: perform services for our customers; complete or settle transactions; maintain our books and records; prevent environmental damage; maintain communications or operations resulting in the unauthorized release, gathering, monitoring, misuse, loss or destruction of proprietary and other information, or adversely disrupt our business operations. Significant liability to the Company or third parties may result. We are not able to anticipate, detect or prevent all cyber-attacks, particularly because the methods used by attackers change frequently or may not be recognized until an attack is already underway or significantly thereafter, and because attackers are increasingly using technologies specifically designed to circumvent cybersecurity measures and avoid detection. Cybersecurity attacks are also becoming more sophisticated and include, but are not limited to, ransomware, credential stuffing, spear phishing, social engineering, use of deepfakes (i.e., highly realistic synthetic media generated by artificial intelligence) and other attempts to gain unauthorized access to data for purposes of extortion or other malfeasance.
Although we aim to maintain dedicated cybersecurity insurance coverage and have procedures for monitoring cybersecurity risk and identifying and reporting incidents, there can be no guarantee they will be effective at preventing cyber-attacks or ensuring incidents are timely identified or reported. Advances in computer capabilities, discoveries in the field of artificial intelligence, cryptography, or other developments may result in a compromise or breach of the technology we use to safeguard confidential, personal, or otherwise protected information. As cyber-attacks continue to evolve, we may be required to expend significant additional resources to continue to modify or enhance our protective measures or to investigate and remediate any vulnerabilities to cyber-attacks. In particular, our implementation of various procedures and controls to monitor and mitigate security threats and to increase security for our personnel, information, facilities and infrastructure may result in increased capital and operating costs. A cyberattack or security breach could result in liability resulting from data privacy or cybersecurity claims or legislation, regulatory penalties, damage to our reputation, long-lasting loss of confidence in us, or additional costs for remediation and modification or enhancement of our information systems to prevent future occurrences, all of which could have a material and adverse effect on our business, financial condition or results of operations. There can be no assurance that we will not suffer such losses in the future. No security measure is infallible. Consequently, it is possible that any of these occurrences, or a combination of them, could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
Further, if we are unable to fully protect our intellectual property rights and/or are subjected to infringement claims and other litigation, we may suffer a loss in our competitive advantage or market share. We do not have patents or patent applications relating to many of our proprietary chemicals. We protect formulas and methods of manufacture of our proprietary chemicals as trade secrets. If we are not able to maintain the confidentiality of our trade secrets, or if our competitors are able to replicate our technology or services, our competitive advantage would be diminished. There is no assurance that any patents we may obtain in the future would provide us with any significant commercial benefit or would allow us to prevent our competitors from employing comparable technologies or processes.
Technology advancements in well completion and service technologies, including those involving the replacement of water in fracturing fluid, could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
The oilfield services industry is characterized by rapid and significant technological advancements and introductions of new products and services using new technologies. As competitors and others use or develop new technologies or technologies comparable to ours in the future, we may lose market share or be placed at a competitive disadvantage. For example, some oil and gas producers may be developing and utilizing non-water fracturing techniques, including those utilizing propane, carbon dioxide or nitrogen instead of water. Further, we may face competitive pressure to implement or acquire certain new technologies at a substantial cost. Some of our competitors may have greater financial, technical and personnel resources than we do, which may allow them to gain technological advantages or implement new technologies before we can. Additionally, we may be unable to implement new technologies or products at all, on a timely basis or at an acceptable cost. New technology could also make it easier for
42
our customers to vertically integrate their operations or reduce the amount of waste produced in oil and gas drilling and production activities, thereby reducing or eliminating the need for third-party disposal. Limits on our ability to effectively use or implement new technologies may have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
We may be adversely affected by uncertainty in the global financial markets and a worldwide economic downturn.
Our future results may be impacted by uncertainty caused by a worldwide economic downturn, continued volatility or deterioration in the debt and equity capital markets, inflation, deflation or other adverse economic conditions that may negatively affect us or parties with whom we do business resulting in a reduction in our customers’ spending and their non-payment or inability to perform obligations owed to us, such as the failure of customers to honor their commitments or the failure of major suppliers to complete orders. The Russia-Ukraine war, conflict in the Israel-Gaza region and related instability in the Middle East, increases in interest rates and the associated policies of the Federal Reserve, public health crises and outbreaks of illnesses and other global events have created global uncertainty that has negatively affected our business and industry and will continue to do so. Additionally, credit market conditions may change, slowing our collection efforts as customers may experience increased difficulty in obtaining requisite financing, potentially leading to lost revenue and higher than normal accounts receivable. During times when the gas or crude oil markets weaken, our customers are more likely to experience financial difficulties, including being unable to access debt or equity financing. In addition, due to the high levels of inflation in the U.S., the Federal Reserve and other central banks increased interest rates multiple times throughout 2022 and 2023 and may continue such increases in 2024. Such increased interest rates may prevent our customers from being able to obtain debt financing at favorable rates, or at all, which could result in a reduction in our customers’ spending for our services. In addition, in the course of our business we hold accounts receivable from our customers. In the event of the financial distress or bankruptcy of a customer, we could lose all or a portion of such outstanding accounts receivable associated with that customer. Further, all or a portion of our contracts could be cancelled at significant expense or loss of expected revenues to us if a customer was to enter into bankruptcy.
The current global economic environment may adversely impact our ability to issue debt, including due to high interest rates as a result of the monetary policy of the Federal Reserve. Any economic uncertainty may cause financial institutions to respond to their borrowers by increasing interest rates, enacting tighter lending standards or refusing to refinance existing debt upon its maturity or on terms similar to the expiring debt. Due to the above-listed factors, we cannot be certain that additional funding will be available if needed and, to the extent required, on acceptable terms.
Seasonal weather conditions and natural disasters could severely disrupt normal operations and harm our business.
Our water solutions operations are located across multiple regions of the U.S. Certain of these areas are adversely affected by seasonal weather conditions, primarily in the winter and spring. During periods of heavy snow, ice or rain, we may be unable to move our equipment between locations, thereby reducing our ability to provide services and generate revenues. Additionally, extended drought conditions in our operating regions could impact our ability to source sufficient water for our customers or increase the cost for such water. As a result, a natural disaster or inclement weather conditions could severely disrupt the normal operation of our business and adversely impact our financial condition and results of operations.
A terrorist attack, armed conflict or unrest could harm our business.
The occurrence or threat of terrorist attacks in the U.S. or other countries, anti-terrorist efforts and other armed conflicts involving the U.S. or other countries, including increased and continued hostilities in the Middle East, and political or civil unrest in the U.S. may adversely affect the U.S. and global economies and could prevent us from meeting our financial and other obligations. Additionally, destructive forms of protest and opposition by extremists, including acts of sabotage or eco-terrorism, against oil and natural gas development and production activities could potentially result in personal injury to persons, damages to property, natural resources or the environment, or lead to extended interruptions of our or our customers’ operations. If any of these events occur, the resulting political instability and societal disruption could reduce overall demand for oil and gas, potentially putting downward pressure on demand for our services and causing a reduction in our revenues. Oil and gas related facilities could be direct targets of such
43
terrorist attacks or unrest, and our operations could be adversely impacted if infrastructure integral to our customers’ operations is destroyed or damaged. Costs for insurance and other security may increase as a result of these threats, and some insurance coverage may become more difficult to obtain, if available at all.
Disruptions in the transportation services of logistics companies transporting wastewater and other oilfield products could have an adverse effect on our results.
In areas where pipeline gathering systems have not yet been developed, we use trucks to transport produced water and other fluids to our wastewater disposal facilities. In recent years, certain states, such as North Dakota, Texas, Oklahoma, Louisiana and New Mexico and certain state counties have increased enforcement of weight limits on trucks used to transport raw materials on their public roads. It is possible that the states, counties and municipalities in which we operate our business may modify their laws or regulations to further reduce truck weight limits or impose curfews or other restrictions on the use of roadways. Such legislation and regulations and associated enforcement efforts could result in delays, and increased costs, with respect to the transport of produced water to our wastewater disposal facilities, which may either increase our operating costs or reduce the amount of produced water transported to our facilities. Such developments could decrease our operating margins or amounts of produced water and thereby have a material adverse effect on our results of operations and financial condition.
A significant increase in fuel prices may adversely affect our transportation costs, which could have a material adverse effect on our results of operations and financial condition.
Fuel is one of our significant operating expenses, and a significant increase in fuel prices could result in increased transportation costs. The price and supply of fuel is unpredictable and fluctuates based on events such as geopolitical developments, supply and demand for oil and gas, actions by oil and gas producers, war and unrest in oil producing countries and regions, regional production patterns and weather concerns. At times we have been able to pass along increases in fuel costs to customers, though we cannot guarantee our ability to do so in the future. Although the average price of fuel was lower in 2023 as compared to 2022, fuel prices constantly fluctuate and a significant increase in fuel prices could increase the price of, and therefore reduce demand for, our services, or force us to accept lower margins, both of which could affect our results of operations and financial condition.
44
Risks Related to Customers and Suppliers
Disruptions in production at our chemical manufacturing facilities may have a material adverse impact on our business, results of operations and/or financial condition.
Chemical manufacturing facilities in our industry are subject to outages and other disruptions. Serious disruptions at any of our facilities could impair our ability to use our facilities and have a material adverse impact on our revenue and increase our costs and expenses. Unplanned production disruptions may occur for external reasons including natural disasters, weather, disease, world health events, strikes, transportation interruption, government regulation, political or civil unrest or terrorism, or internal reasons, such as fire, unplanned maintenance or other manufacturing problems. Moreover, alternative facilities with sufficient capacity may not be available, may cost substantially more or may take a significant time to increase production or qualify with our customers, any of which could negatively impact our business, results of operations and/or financial condition. Long-term production disruptions may cause our customers to seek alternative supply, which could further adversely affect our profitability.
Additionally, we rely on a number of vendors, suppliers, and in some cases sole-source suppliers, service providers, toll manufacturers and collaborations with other industry participants to provide us with chemicals, feedstocks and other raw materials, along with energy sources and, in certain cases, facilities that we need to operate our business. If the business of these third parties is disrupted, some of these companies could be forced to reduce their output, shut down their operations or file for bankruptcy protection. If this were to occur, it could adversely affect their ability to provide us with the raw materials, energy sources or facilities that we need, which could materially disrupt our operations, including the production of certain of our chemical products. Moreover, it could be difficult to find replacements for certain of our business partners without incurring significant delays or cost increases. All of these risks could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations, financial condition and liquidity.
While we maintain business recovery plans that are intended to allow us to recover from natural disasters or other events that could disrupt our business, we cannot provide assurances that our plans would fully protect us from the effects of all such disasters or from events that might increase in frequency or intensity due to climate change. In addition, insurance may not adequately compensate us for any losses incurred as a result of natural or other disasters. In areas prone to frequent natural or other disasters, insurance may become increasingly expensive or not available at all.
Unsatisfactory safety performance may negatively affect our E&P customer relationships and, to the extent we fail to retain existing customers or attract new customers, adversely impact our revenues.
Our ability to retain existing E&P customers and attract new business is dependent on many factors, including our ability to demonstrate that we can reliably and safely operate our business and stay current on constantly changing rules, regulations, training and laws. Existing and potential customers consider the safety record of their service providers to be of high importance in their decision to engage third-party services. If one or more accidents were to occur at one of our operating sites, the affected customer may seek to terminate or cancel its use of our facilities or services and may be less likely to continue to use our services, which could cause us to lose substantial revenues. Further, our ability to attract new customers may be impaired if they elect not to purchase our third-party services because they view our safety record as unacceptable. In addition, it is possible that we will experience numerous or particularly severe accidents in the future, causing our safety record to deteriorate. This may be more likely as we continue to grow, if we experience high employee turnover or labor shortage, or add inexperienced personnel. See Part I, Item 1. “Business – Environmental and Occupational Safety and Health Matters” for more discussion on worker safety matters.
Constraints in the supply of equipment used in providing services to our customers and replacement parts for such could affect our ability to execute our growth strategies.
Equipment used in providing services to our customers is normally readily available given our existing quantity of owned, leased and rented equipment. However, market conditions could trigger constraints in the supply chain of certain equipment or replacement parts for such equipment, which could have a material adverse effect on our business.
45
The majority of our risk associated with supply chain constraints occurs in those situations where we have a relationship with a single supplier for a particular equipment set.
Significant price volatility or interruptions in supply of our raw materials for our chemicals business may result in increased costs that we may be unable to pass on to our customers, which could reduce profitability.
We purchase a substantial portion of our raw materials for our chemicals business from third-party suppliers and the cost of these raw materials represents a substantial portion of our operating expenses. The prices of the raw materials that we purchase from third parties are cyclical and volatile. Our supply agreements provide us only limited protection against price volatility because they are entered into either on a short-term basis or are longer-term volume contracts, which provide for market-based pricing renegotiated several times per year. While we attempt to match cost increases with corresponding product price increases, we are not always able to raise product prices immediately or at all. Timing differences between raw material prices, which may change daily, and contractual product prices, which in many cases are negotiated only monthly or less often, have had and may continue to have a negative effect on our cash flow. Any cost increase that we are not able to pass on to our customers could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations, financial condition and liquidity.
There are several raw materials for which there are only a limited number of suppliers or a single supplier. To mitigate potential supply constraints, we enter into supply agreements with particular suppliers, evaluate alternative sources of supply and evaluate alternative technologies to avoid reliance on limited or sole-source suppliers. Where supply relationships are concentrated, particular attention is paid by the parties to ensure strategic intentions are aligned to facilitate long-term planning. If certain of our suppliers are unable to meet their obligations under present supply agreements, we may be forced to pay higher prices to obtain the necessary raw materials from other sources and we may not be able to increase prices for our finished products to recoup the higher raw materials costs. Any interruption in the supply of raw materials could increase our costs or decrease our revenue, which could reduce our cash flow. The inability of a supplier to meet our raw material needs could have a material adverse effect on our financial condition and results of operations.
The number of sources for and availability of certain raw materials is also specific to the particular geographical region in which a facility is located. Political and economic instability in the countries from which we purchase our raw material supplies could adversely affect their availability. In addition, if raw materials become unavailable within a geographic area from which they are now sourced, we may not be able to obtain suitable or cost-effective substitutes. The importation of internationally sourced chemicals has, and may continue to, present new and additional challenges, such as increased freight costs, limited container space, and reduced production of certain chemicals. We may also experience higher operating costs, such as energy costs, which could affect our profitability. We may not always be able to increase our selling prices to offset the impact of any higher production costs or reduced production levels, which could reduce our earnings and decrease our liquidity.
Risks Related to Compliance with Regulations
Laws, regulations, executive actions and other regulatory initiatives in the U.S. relating to hydraulic fracturing could increase our costs of doing business and result in additional operating restrictions, delays or cancellations in the drilling and completion of oil and gas wells, or possible restrictions on the performance of hydraulic fracturing that may reduce demand for our services and could have a material adverse effect on our liquidity, results of operations and financial condition.
Although we do not directly engage in hydraulic fracturing, our operations support many of our E&P customers in such activities. The practice continues to be controversial in certain parts of the country, resulting in increased scrutiny and regulation of the hydraulic fracturing process, including by federal and state agencies and local municipalities. See Part I, Item 1. “Business – Environmental and Occupational Safety and Health Matters” for more discussion on these hydraulic fracturing and seismicity matters.
The adoption of any federal, state or local laws or the implementation of regulations or issuance of executive orders regarding hydraulic fracturing activities or leasing activities on federal properties could potentially cause a
46
decrease in the completion of new oil and gas wells and an associated decrease in demand for our services and increased compliance costs and time, which could have a material adverse effect on our liquidity, results of operations, and financial condition.
Our and our E&P customers' operations are subject to a number of risks arising out of the threat of climate change, energy conservation measures or initiatives that stimulate demand for alternative forms of energy, which could result in increased operating and capital costs for our customers, restrictions on drilling for our customers and reduced demand for the products and services we provide.
The issue of climate change continues to attract considerable attention in the U.S. and foreign countries. As a result, numerous proposals have been made and are likely to continue to be made at the international, national, regional and state levels of government to monitor and limit emissions of GHGs as well as to eliminate such future emissions. As a result, our operations as well as the operations of our E&P customers are subject to a series of regulatory, political, litigation and financial risks associated with the production and processing of fossil fuels and emission of GHGs. See Part I, Item 1. “Business – Environmental and Occupational Safety and Health Matters” for more discussion on the threat of climate and restriction of GHG emissions. The adoption and implementation of any international, federal, regional or state legislation, executive actions, regulations or other regulatory initiatives that impose more stringent standards for GHG emissions from the oil and natural gas sector or otherwise restrict the areas in which this sector may produce oil and natural gas or generate GHG emissions could result in increased compliance costs or costs of consuming fossil fuels. Such legislation, executive actions or regulations could result in increased costs of compliance or costs of consuming, and thereby reduce demand for oil and natural gas, which could reduce demand for our products and services. Additionally, political, financial and litigation risks may result in our customers restricting, delaying or canceling production activities, incurring liability for infrastructure damages as a result of climatic changes, or impairing the ability to continue to operate in an economic manner, which also could reduce demand for our products and services. The occurrence of one or more of these developments could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations and cash flows. Moreover, the increased competitiveness of alternative energy sources (such as wind, solar geothermal, tidal and biofuels) could reduce demand for hydrocarbons, and therefore for our products and services, which would lead to a reduction in our revenues.
Our chemical products are subject to stringent chemical control laws that could result in increased costs on our business.
We are subject to a wide array of laws and regulations governing chemicals, including the regulation of chemical substances and inventories, such as the TSCA. These laws and regulations change frequently and have the potential to limit or ban altogether the types of chemicals we may use in our products, as well as result in increased costs related to testing, storing, and transporting our products prior to providing them to our customers. Any new restrictions on the development of new products or use of existing products, increases in regulation of those products, or disclosure of confidential, competitive information relating to the products could have an adverse effect on our operations and our cost of doing business. Furthermore, governmental, regulatory and societal demands for increasing levels of product safety and environmental protection could result in increased pressure for more stringent regulatory control with respect to the chemical industry. See Part I, Item 1. “Business – Environmental and Occupational Safety and Health Matters” for more discussion on chemical product use and safety.
In the future, we may face increased obligations relating to the closing of our wastewater disposal facilities and may be required to provide an increased level of financial assurance to guarantee that the appropriate closure activities will occur for a wastewater disposal facility.
Our ability to obtain permits to own or operate wastewater disposal facilities generally requires us to establish performance bonds, letters of credit or other forms of financial assurance to address remediation and closure obligations. As we acquire additional wastewater disposal facilities or expand our existing wastewater disposal facilities, these obligations will increase. Additionally, in the future, regulatory agencies may require us to increase the amount of our closure bonds at existing wastewater disposal facilities. Moreover, actual costs could exceed our current expectations, as a result of, among other things, federal, state or local government regulatory action, increased costs charged by service providers that assist in closing wastewater disposal facilities and additional environmental remediation requirements. Increased regulatory requirements regarding our existing or future wastewater disposal facilities, including the
47
requirement to pay increased closure and post-closure costs or to establish increased financial assurance for such activities could substantially increase our operating costs and adversely affect our business, financial condition and results of operations.
State and federal legislation and regulatory initiatives relating to our disposal operations and seismicity could harm our business.
Our disposal business and the number of SWDs we operate has significantly increased since 2021. This disposal process has been linked to increased induced seismicity events in certain areas of the country, particularly in certain counties in Oklahoma, Texas, Colorado, and New Mexico. For example, Texas and Oklahoma have issued rules for wastewater disposal wells that imposed certain permitting and operating restrictions and reporting requirements on disposal wells in proximity to faults. Other states, such as Texas and Oklahoma, have also issued orders, from time to time, for certain wells where seismic incidents have occurred to restrict or suspend disposal well operations. Another consequence of seismic events may be lawsuits alleging that disposal well operations have caused damage to neighboring properties or otherwise violated state and federal rules regulating waste disposal. These and other states have begun to consider or adopt laws and regulations that may restrict or otherwise prohibit oilfield fluid disposal in certain areas or underground disposal wells, and state agencies implementing these requirements may issue orders directing certain wells where seismic incidents have occurred to restrict or suspend disposal well operations or impose standards related to disposal well construction and monitoring. For example, in December 2023 the Texas Railroad Commission suspended the permits of 23 deep disposal wells in a seismic response area in Culberson and Reeves Counties. Any one or more of these developments may result in our having to limit disposal well volumes, disposal rates or locations, or to cease disposal well activities, which could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, and results of operations. See Part I, Item 1. “Business – Environmental and Occupational Safety and Health Matters” for more discussion on seismic matters.
Changes in U.S. and international trade policies, particularly involving China, may adversely impact our business and operating results.
Though a comprehensive trade agreement was signed in 2020, the U.S. government has previously imposed tariffs affecting certain goods produced in China. Approximately 5% of the raw material feedstock for our chemicals we produced in 2023 originated in China and were sold to us by our supplier partners. As a result, tariffs incurred by our supplier partners could increase our costs and reduce profitability. Additionally, delays or interruptions in the supply of some chemicals for any reason could impact our ability to generate chemicals revenue. If we are forced to source chemicals currently originating in China from other countries, such compounds might be more expensive, inferior in quality, or take longer to source. If we incur higher costs that we cannot pass on to our customers or if we are unable to adequately replace the chemicals we currently source with chemicals produced elsewhere, our business could be adversely affected.
Changes to applicable tax laws and regulations or exposure to additional tax liabilities could adversely affect our operating results and cash flows.
We are subject to various complex and evolving U.S. federal, state and local tax laws. U.S. federal, state and local tax laws, policies, statutes, rules, regulations or ordinances could be interpreted, changed, modified or applied adversely to us, in each case, possibly with retroactive effect. Any significant variance in our interpretation of current tax laws or a successful challenge of one or more of our tax positions by the U.S. Internal Revenue Service or other tax authorities could increase our future tax liabilities and adversely affect our operating results and cash flows.
We are subject to environmental and occupational health and safety laws and regulations that may expose us to significant liabilities for penalties, damages or costs of remediation or compliance.
Our operations and the operations of our E&P customers are subject to federal, state and local laws and regulations in the U.S. relating to protection of natural resources and the environment, health and safety aspects of our operations and waste management, including the transportation and disposal of waste and other materials. These laws
48
and regulations may take the form of laws, regulations, executive actions and various other legal initiatives and result in the imposition of numerous obligations on our operations and the operations of our customers. See Part I, Item 1. “Business – Environmental and Occupational Safety and Health Matters” for more discussion on these matters. Compliance with these regulations and other regulatory initiatives, or any other new environmental laws, regulations and executive actions could, among other things, require us or our customers to install new or modified emission controls on equipment or processes, incur longer permitting timelines, and incur significantly increased capital or operating expenditures, which costs may be significant. One or more of these developments that impact our customers could reduce demand for our services, which could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations and financial condition.
The Endangered Species Act and Migratory Bird Treaty Act govern both our and our E&P customers’ operations and additional restrictions may be imposed in the future, which constraints could have an adverse impact on our ability to expand some of our existing operations or limit our customers’ ability to develop new oil and gas wells.
The ESA and comparable state laws restrict activities that may affect endangered or threatened species or their habitats. Similar protections are offered to migratory birds under the MBTA. To the degree that species listed under the ESA or similar state laws, or are protected under the MBTA, live in the areas where we or our E&P customers’ operate, both our and our customers’ abilities to conduct or expand operations and construct facilities could be limited or be forced to incur additional material costs. Additionally, the FWS may make determinations on the listing of unlisted species as endangered or threatened under the ESA. See Part I, Item 1. “Business – Environmental and Occupational Safety and Health Matters” for more discussion on ESA and MBTA matters. The designation of previously unidentified endangered or threatened species could indirectly cause us to incur additional costs, cause our or our E&P customers’ operations to become subject to operating restrictions or bans and limit future development activity in affected areas, which developments could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations and financial condition.
Increasing investor attention to ESG matters may impact our business.
Companies across all industries are facing increased scrutiny from stakeholders related to their ESG practices. Companies that do not adapt to or comply with investor or stakeholder expectations and standards, which are evolving, or which are perceived to have not responded appropriately to the growing concern for ESG issues, regardless of whether there is a legal requirement to do so, may suffer from reputational damage and the business, financial condition, and/or stock price of such a company could be materially and adversely affected. Increasing attention to climate change, increasing societal expectations on companies to address climate change, and potential consumer use of substitutes to energy commodities may result in increased costs, reduced demand for our products and services, reduced profits, increased governmental investigations and private litigation against us.
Moreover, to an increasing extent, many institutional investors have announced plans to transition their portfolios to net-zero greenhouse gas emissions over the next 2-3 decades as part of a commitment to combat climate change. This has resulted, and will likely continue to result, in some (and perhaps a growing number of) institutions removing from their portfolios the shares of companies that do not meet their minimum investment standards. Further, banks and other capital providers are reassessing their capital allocation to our industry or making their participation conditional. This trend towards the divestment or limitation of future investment in companies involved in the development, production, transportation and utilization of fossil fuels, may adversely affect the price of our stock and limit our access to the debt and equity markets for capital to fund our growth.
In addition, organizations that provide proxy advisory services to investors on corporate governance and related matters have developed ratings processes for evaluating companies on their approach to ESG matters. Currently, there are no universal standards for such scores or ratings, but the importance of sustainability evaluations is becoming more broadly accepted by investors and shareholders. Such ratings are used by some investors to inform their investment and voting decisions. Additionally, certain investors use these scores to benchmark companies against their peers and if a company is perceived as lagging, these investors may engage with companies to require improved ESG disclosure or performance. Unfavorable ESG ratings may lead to increased negative investor sentiment toward us or our customers and to the diversion of investment to other industries, which could have a negative impact on our stock price and/or our access to and costs of capital.
49
Risks Related to Personnel and Related Parties
Our industry typically experiences a high rate of employee turnover. Any difficulty we experience replacing or adding personnel could have a material adverse effect on our operational performance, customer satisfaction, ability to retain existing business or secure new business, and therefore on our liquidity, results of operations and financial condition.
We are dependent upon the available labor pool of skilled employees and may not be able to find enough skilled labor to meet our needs, which could have a negative effect on our growth. We are also subject to the Fair Labor Standards Act, which governs such matters as minimum wage, overtime and other working conditions. Our operations require skilled workers who can perform physically demanding work. As a result of our industry volatility, as well as the demanding nature of the work, many workers have left the oilfield services section to pursue employment in different fields. If we are unable to retain or meet the growing demand for skilled technical personnel, our operating results and our ability to execute our growth strategies may be adversely affected.
We engage in transactions with related parties and such transactions present possible conflicts of interest that could have an adverse effect on us.
We have historically entered into a number of transactions with related parties. Related party transactions create the possibility of conflicts of interest with regard to our management. Such a conflict could cause an individual in our management to seek to advance his or her economic interests above ours. Further, the appearance of conflicts of interest created by related party transactions could impair the confidence of our investors. While our board of directors regularly reviews these transactions, in accordance with our Related Party Transactions policy, a related party transaction presenting a conflict of interest could have a material adverse effect on our liquidity, results of operations and financial condition.
Risks Related to Our Capital Structure
We may not be able to continue to pay or maintain our cash dividends and the failure to do so may negatively affect our share price.
During the fourth quarter of 2022, we initiated a quarterly dividend and distribution program of $0.05 per share and $0.05 per unit for holders of Class A common stock and SES Holdings, LLC Units (along with Class B shares), respectively. In October, 2023, we announced a 20% increase to our quarterly dividend payment, from $0.05 per share to $0.06 per share. Our ability to pay cash dividends depends on, among other things, our cash flows from operations, our cash requirements, our financial condition, the degree to which we are/or become leveraged, contractual restrictions binding on us, provisions of applicable law and other factors that our board of directors may deem relevant. There can be no assurance that we will generate sufficient cash from continuing operations in the future or have sufficient cash surplus or net profits to pay dividends on our Class A common stock. Our dividend policy is based upon our directors’ current assessment of our business and the environment in which we operate, and that assessment could change based on business development opportunities (which could, for example, increase our need for capital expenditures) or new growth opportunities. All future dividend payments are subject to quarterly review and approval by our board of directors. Our board of directors may, in its discretion, decrease the level of cash dividends or entirely discontinue the payment of cash dividends. A reduction or elimination of cash dividends could negatively affect the market price of our Class A common stock.
If we fail to maintain and enhance an effective system of internal controls, we may not be able to accurately report our financial results or prevent fraud. As a result, current and potential stockholders could lose confidence in our financial reporting, which would harm our business and the trading price of our Class A common stock.
Effective internal controls are necessary for us to provide reliable financial reports, prevent fraud and operate successfully as a public company. We are subject to Section 404 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 (“Sarbanes-Oxley”) and therefore are required to make a formal assessment of the effectiveness of our internal controls over financial
50
reporting for that purpose. We cannot be certain that our efforts to maintain and enhance our internal controls will be successful, that we will be able to maintain adequate controls over our financial processes and reporting in the future or that we will be able to comply with our obligations under Sections 302 and 404 of Sarbanes-Oxley. Any failure to maintain effective internal controls, or difficulties encountered in implementing or improving our internal controls, could harm our operating results or cause us to fail to meet our reporting obligations. Ineffective internal controls could also cause investors to lose confidence in our reported financial information, which would likely have a negative effect on the trading price of our Class A common stock.
We may incur indebtedness or issue additional equity securities to execute our long-term growth strategy, which may reduce our profitability or result in significant dilution to our stockholders.
Constructing and maintaining water infrastructure used in the oil and gas industry requires significant capital. We may require additional capital in the future to develop and construct water sourcing, transfer, recycling and other related infrastructure to execute our growth strategy. For the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021, we spent $135.9 million, $71.9 million and $40.0 million, respectively, in capital expenditures (excluding expenditures connected with business combinations). Historically, we have financed these investments through cash flows from operations, external borrowings, capital contributions and proceeds from the issuance of equity securities. These sources of capital may not be available to us in the future. If we are unable to fund capital expenditures for any reason, we may not be able to capture available growth opportunities or effectively maintain our existing assets and any such failure could have a material adverse effect on our results of operations and financial condition. If we incur additional indebtedness or issue additional equity securities, our profitability may be reduced and our stockholders may experience significant dilution.
Our Sustainability-Linked Credit Facility subjects us to various financial and other restrictive covenants. These restrictions may limit our operational or financial flexibility and could subject us to potential defaults under our Sustainability-Linked Credit Facility.
Our Sustainability-Linked Credit Facility subjects us to significant financial and other restrictive covenants, including restrictions on our ability to consolidate or merge with other companies, conduct asset sales, incur additional indebtedness, grant liens, issue guarantees, make investments, loans or advances, pay dividends and enter into certain transactions with affiliates.
Our Sustainability-Linked Credit Facility contains certain financial covenants, including the maintenance of a fixed charge coverage ratio of at least 1.0 to 1.0 at any time availability under the Sustainability-Linked Credit Facility is less than the greater of (i) 10% of the lesser of (A) the maximum revolver amount and (B) the then-effective borrowing base and (ii) $15.0 million and continuing through and including the first day after such time that availability under the Sustainability-Linked Credit Facility has equaled or exceeded the greater of (i) 10% of the lesser of (A) the maximum revolver amount and (B) the then-effective borrowing base and (ii) $15.0 million for 60 consecutive calendar days. Our ability to comply with such financial condition tests can be affected by events beyond our control and we may not be able to do so. The scheduled maturity date for our Sustainability-Linked Credit Facility is March 17, 2027. In addition, the Sustainability-Linked Credit Facility restricts SES Holdings’ and Select LLC’s ability to make distributions on, or redeem or repurchase, its respective equity interests, except for certain distributions, including distributions of cash so long as, both at the time of the distribution and after giving effect to the distribution, no default exists under the Sustainability-Linked Credit Facility and either (a) excess availability at all times during the preceding 30 consecutive days, on a pro forma basis and after giving effect to such distribution, is not less than the greater of (1) 25% of the lesser of (A) the maximum revolver amount and (B) the then-effective borrowing base and (2) $33.75 million or (b) if SES Holdings’ and Select LLC’s fixed charge coverage ratio is at least 1.0 to 1.0 on a pro forma basis, and excess availability at all times during the preceding 30 consecutive days, on a pro forma basis and after giving effect to such distribution, is not less than the greater of (1) 20% of the lesser of (A) the maximum revolver amount and (B) the then-effective borrowing base and (2) $27.0 million. For additional information regarding our Sustainability-Linked Credit Facility, please read Part II, Item 7. “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations – Liquidity and Capital Resources – Sustainability-Linked Credit Facility.”
Our Sustainability-Linked Credit Facility also contains a sustainability adjustments feature that could result in up to a 0.05% increase or reduction to the effective interest rate pursuant to an Applicable Sustainability Margin
51
Adjustment depending on Select LLC’s ability to meet certain sustainability targets and thresholds. For each calendar year, the “Applicable Sustainability Margin Adjustment” will equal the number of basis points (whether positive, negative or zero) equal to the sum of (i) the Applicable Water Stewardship Fee Adjustment and (ii) the Applicable Health and Safety Fee Adjustment (each as defined in the Sustainability-Linked Credit Facility).
The “Applicable Water Stewardship Fee Adjustment” is based on Select LLC’s ability to (i) remain above the Water Stewardship Threshold and (ii) reach the Water Stewardship Target, both metrics that are measured by the total number of barrels of produced water recycled by SES Holdings and its Subsidiaries. The “Applicable Employee Health and Safety Fee Adjustment” is based on Select LLC’s ability to (i) remain above the Employee Health and Safety Threshold and (ii) reach the Employee Health and Safety Target, both metrics that are measured by the total recordable incident rates of employees with respect to SES Holdings and its Subsidiaries.
If we are unable to remain in compliance with the covenants of our Sustainability-Linked Credit Facility, then the lenders may declare all amounts outstanding under the Sustainability-Linked Credit Facility to be immediately due and payable. Any such acceleration could have a material adverse effect on our financial condition and results of operations.
Future sales of our equity securities, or the perception that such sales may occur, may depress our share price, and any additional capital raised through the sale of equity or convertible securities may dilute your ownership in us.
Subject to certain limitations and exceptions, Crestview and its permitted transferees may exchange their SES Holdings LLC Units (together with a corresponding number of shares of Class B common stock) for shares of Class A common stock (on a one-for-one basis, subject to conversion rate adjustments for stock splits, stock dividends and reclassification and other similar transactions) and then sell those shares of Class A common stock. Additionally, we may in the future issue our previously authorized and unissued securities. We are authorized to issue 350 million shares of Class A common stock, 150 million shares of Class B common stock and 50 million shares of preferred stock with such designations, preferences and rights as determined by our board of directors. The potential issuance of such additional shares of equity securities will result in the dilution of the ownership interests of the holders of our Class A common stock and may create downward pressure on the trading price, if any, of our Class A common stock.
In addition, Legacy Owner Holdco, Crestview Partners II SES Investment B, LLC and the SCF Group (as defined below) (collectively, the “Registration Rights Holders”), who collectively own in excess of 20 million shares of our common stock, are party to a registration rights agreement that provides, among other things, for parties to that agreement to initiate or participate in an underwritten public offering of all or a portion of their shares. The Registration Rights Holders may exercise their rights under such agreement in their sole discretion, and sales pursuant to such rights may be material in amount and occur at any time. The sales of substantial amounts of our Class A common stock or the perception that these sales may occur, could cause the market price of our Class A common stock to decline and impair our ability to raise capital. We also may grant additional registration rights in connection with any future issuance of our capital stock.
We cannot predict the size of future issuances of our Class A common stock or securities convertible into Class A common stock or the effect, if any, that future issuances and sales of shares of our Class A common stock will have on the market price of our Class A common stock. Sales of substantial amounts of our Class A common stock (including shares issued in connection with an acquisition), or the perception that such sales could occur, may adversely affect prevailing market prices of our Class A common stock.
Provisions in our amended and restated certificate of incorporation and amended and restated bylaws and Delaware law may discourage a takeover attempt even if a takeover might be beneficial to our stockholders.
Provisions contained in our Fifth Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation and our Third Amended and Restated Bylaws, which we refer to herein as our “amended and restated certificate of incorporation” and “amended and restated bylaws,” respectively, could make it more difficult for a third party to acquire us. Provisions of our amended and restated certificate of incorporation and amended and restated bylaws impose various procedural and other requirements, which could make it more difficult for stockholders to effect certain corporate actions. For example, our
52
amended and restated certificate of incorporation authorizes our board of directors to determine the rights, preferences, privileges and restrictions of unissued series of preferred stock without any vote or action by our stockholders. Thus, our board of directors can authorize and issue shares of preferred stock with voting or conversion rights that could adversely affect the voting or other rights of holders of our capital stock. These rights may have the effect of delaying or deterring a change of control of our company. Additionally, our amended and restated bylaws establish limitations on the removal of directors and on the ability of our stockholders to call special meetings and include advance notice requirements for nominations for election to our board of directors and for proposing matters that can be acted upon at stockholder meetings. These provisions could limit the price that certain investors might be willing to pay in the future for shares of our Class A common stock.
In addition, certain change of control events have the effect of accelerating the payment due under our Tax Receivable Agreements (as defined herein), which could be substantial and accordingly serve as a disincentive to a potential acquirer of our company. See “—Risks Related to Our Organizational Structure—In certain cases, payments under the Tax Receivable Agreements may be accelerated and/or significantly exceed the actual benefits, if any, we realize in respect of the tax attributes subject to the Tax Receivable Agreements.”
Our amended and restated certificate of incorporation contains a provision renouncing our interest and expectancy in certain corporate opportunities, which could adversely affect our business or prospects.
Our amended and restated certificate of incorporation provides that, to the fullest extent permitted by applicable law, we renounce any interest or expectancy in any business opportunity that involves any aspect of the energy business or industry and that may be from time to time presented to any member of (i) Legacy Owner Holdco; Crestview Partners II SES Investment, LLC; any funds, limited partnerships or other investment entities or vehicles managed by Crestview Partners or controlled by Crestview GP; B-29 Investments, LP; Sunray Capital, LP; Proactive Investments, LP and their respective affiliates, other than us (collectively, the “SES Group”); (ii) SCF-VI, L.P., SCF-VII, L.P. and SCF-VII(A), L.P. and their respective affiliates, other than us (collectively, the “SCF Group”); (iii) the other entities (existing and future) that participate in the energy industry and in which the SES Group and SCF Group own substantial equity interests (the “Portfolio Companies”) or (iv) any director or officer of the corporation who is also an employee, partner, member, manager, officer or director of any member of the SES Group, the SCF Group or the Portfolio Companies, including our Chairman, President and CEO, John D. Schmitz, and our Executive Vice President, Business Strategy, Cody Ortowski, even if the opportunity is one that we might reasonably have pursued or had the ability or desire to pursue if granted the opportunity to do so. Mr. Schmitz controls both B-29 Investments, LP and Sunray Capital, LP and is a direct and indirect beneficiary of these provisions in our amended and restated certificate of incorporation. Our amended and restated certificate of incorporation further provides that no such person or party shall be liable to us by reason of the fact that such person pursues any such business opportunity, or fails to offer any such business opportunity to us.
As a result, any member of the SES Group, SCF Group or the Portfolio Companies or any director or officer of the corporation who is also an employee, partner, member, manager, officer or director of any member of the SES Group, SCF Group or the Portfolio Companies may become aware, from time to time, of certain business opportunities, such as acquisition opportunities, and may direct such opportunities to other businesses in which they have invested, in which case we may not become aware of or otherwise have the ability to pursue such opportunity. Further, such businesses may choose to compete with us for these opportunities. As a result, by renouncing our interest and expectancy in any business opportunity that may be from time to time presented to any member of the SES Group, SCF Group or the Portfolio Companies or any director or officer of the corporation who is also an employee, partner, member, manager, officer or director of any member of the SES Group, SCF Group or the Portfolio Companies, our business or prospects could be adversely affected if attractive business opportunities are procured by such parties for their own benefit rather than for ours. See Part III, Item 13. “Certain Relationships and Related Transactions, and Director Independence.”
53
We may issue preferred stock whose terms could adversely affect the voting power or value of our Class A common stock.
Our amended and restated certificate of incorporation authorizes us to issue, without the approval of our stockholders, one or more classes or series of preferred stock having such designations, preferences, limitations and relative rights, including preferences over our Class A common stock respecting dividends and distributions, as our board of directors may determine. The terms of one or more classes or series of preferred stock could adversely impact the voting power or value of our Class A common stock. For example, we might grant holders of preferred stock the right to elect some number of our directors in all events or on the happening of specified events or the right to veto specified transactions. Similarly, the repurchase or redemption rights or liquidation preferences we might assign to holders of preferred stock could affect the residual value of the Class A common stock.
Our amended and restated certificate of incorporation designates the Court of Chancery of the State of Delaware as the sole and exclusive forum for certain types of actions and proceedings that may be initiated by our stockholders, which could limit our stockholders’ ability to obtain a favorable judicial forum for disputes with us or our directors, officers, employees or agents.
Our amended and restated certificate of incorporation provides that, unless we consent in writing to the selection of an alternative forum, the Court of Chancery of the State of Delaware will, to the fullest extent permitted by applicable law, be the sole and exclusive forum for (i) any derivative action or proceeding brought on our behalf, (ii) any action asserting a claim of breach of a fiduciary duty owed by any of our directors, officers, employees or agents to us or our stockholders, (iii) any action asserting a claim against us or any director or officer or other employee or agent of ours arising pursuant to any provision of the Delaware General Corporation Law, our amended and restated certificate of incorporation or our amended and restated bylaws, or (iv) any action asserting a claim against us or any director or officer or other employee or agent of ours that is governed by the internal affairs doctrine, in each such case subject to such Court of Chancery having personal jurisdiction over the indispensable parties named as defendants therein.
The exclusive forum provision would not apply to suits brought to enforce any liability or duty created by the Securities Act or the Exchange Act or any other claim for which the federal courts have exclusive jurisdiction. To the extent that any such claims may be based upon federal law claims, Section 27 of the Exchange Act creates exclusive federal jurisdiction over all suits brought to enforce any duty or liability created by the Exchange Act or the rules and regulations thereunder. Furthermore, Section 22 of the Securities Act creates concurrent jurisdiction for federal and state courts over all suits brought to enforce any duty or liability created by the Securities Act or the rules and regulations thereunder.
The enforceability of similar choice of forum provisions in other companies’ certificates of incorporation or similar governing documents has been challenged in legal proceedings, and it is possible that a court could find the choice of forum provisions contained in our amended and restated certificate of incorporation to be inapplicable or unenforceable, including with respect to claims arising under the U.S. federal securities laws.
To the fullest extent permitted by law, any person or entity purchasing or otherwise acquiring any interest in shares of our capital stock will be deemed to have notice of, and consented to, the provisions of our amended and restated certificate of incorporation described in the preceding sentence. This choice of forum provision may limit a stockholder’s ability to bring a claim in a judicial forum that it finds favorable for disputes with us or our directors, officers, employees or agents, which may discourage such lawsuits against us and such persons. Alternatively, if a court were to find these provisions of our amended and restated certificate of incorporation inapplicable to, or unenforceable in respect of, one or more of the specified types of actions or proceedings, we may incur additional costs associated with resolving such matters in other jurisdictions, which could adversely affect our business, financial condition or results of operations.
54
Risks Related to Our Organizational Structure
We are a holding company. Our sole material asset consists of SES Holdings LLC Units, and accordingly, we are dependent upon distributions and payments from SES Holdings to pay taxes, pay dividends, make payments under the Tax Receivable Agreements and cover our corporate and other overhead expenses.
We are a holding company and have no material assets other than our equity interest in SES Holdings. We have no independent means of generating revenue. To the extent SES Holdings has available cash, we intend to cause SES Holdings to make (i) generally pro rata distributions to its unitholders, including us, in an amount at least sufficient to allow us to pay our taxes, pay dividends and to make payments under the Tax Receivable Agreements that we entered into in connection with our restructuring at the Select 144A Offering and any subsequent tax receivable agreements that we may enter into in connection with future acquisitions and (ii) non-pro rata payments to us to reimburse us for our corporate and other overhead expenses. We will be limited, however, in our ability to cause SES Holdings and its subsidiaries to make these and other distributions or payments to us due to certain limitations, including the restrictions under our Sustainability-Linked Credit Facility and the cash requirements and financial condition of SES Holdings. To the extent that we need funds and SES Holdings or its subsidiaries are restricted from making such distributions or payments under applicable law or regulations or under the terms of their financing arrangements or are otherwise unable to provide such funds, our liquidity and financial condition could be adversely affected.
We will be required to make payments under the Tax Receivable Agreements for certain tax benefits we may claim, and the amounts of such payments could be significant.
In connection with our restructuring at the Select 144A Offering, we entered into the Tax Receivable Agreements with certain affiliates of the then-holders of SES Holdings LLC Units (each such person and any permitted transferee thereof, a “TRA Holder,” and together, the “TRA Holders”) which generally provide for the payment by us to the TRA Holders of 85% of the net cash savings, if any, in U.S. federal, state and local income and franchise tax that we actually realize (computed using simplifying assumptions to address the impact of state and local taxes) or are deemed to realize in certain circumstances as a result of certain tax basis increases, net operating losses available to us as a result of certain reorganization transactions entered into in connection with the Select 144A Offering, and certain tax benefits attributable to imputed interest. We will retain the benefit of the remaining 15% of these cash savings.
The term of each Tax Receivable Agreement commenced upon the completion of the Select 144A Offering and will continue until all tax benefits that are subject to such Tax Receivable Agreement have been utilized or expired, unless we exercise our right to terminate the Tax Receivable Agreements (or the Tax Receivable Agreements are terminated due to other circumstances, including our breach of a material obligation thereunder or certain mergers or other changes of control) and we make the termination payment specified in the Tax Receivable Agreements. In addition, payments we make under the Tax Receivable Agreements will be increased by any interest accrued from the due date (without extensions) of the corresponding tax return. In the event that the Tax Receivable Agreements are not terminated and we have sufficient taxable income to utilize all of the tax benefits subject to the Tax Receivable Agreements, the payments due under the Tax Receivable Agreement entered into with Legacy Owner Holdco and Crestview GP are expected to commence at a yet to be determined future date, and continue until the benefits of the last exchange of SES Holdings LLC Units are realized or expire, and the payments due under the Tax Receivable Agreement entered into with certain Legacy Owners are expected to commence at a yet to be determined future date, and to continue until the benefits of the exchanges are realized or expire.
The payment obligations under the Tax Receivable Agreements are our obligations and not obligations of SES Holdings, and we expect that the payments we will be required to make under the Tax Receivable Agreements will be substantial. Estimating the amount and timing of payments that may become due under the Tax Receivable Agreements is by its nature imprecise. For purposes of the Tax Receivable Agreements, cash savings in tax generally will be calculated by comparing our actual tax liability (using the actual applicable U.S. federal income tax rate and an assumed combined state and local income and franchise tax rate) to the amount we would have been required to pay had we not been able to utilize any of the tax benefits subject to the Tax Receivable Agreements. The amounts payable, as well as the timing of any payments, under the Tax Receivable Agreements are dependent upon future events and significant assumptions, including the timing of the exchanges of SES Holdings LLC Units, the market price of our Class A
55
common stock at the time of each exchange (since such market price will determine the amount of tax basis increases resulting from the exchange), the extent to which such exchanges are taxable transactions, the amount of the exchanging unitholder’s tax basis in its SES Holdings LLC Units at the time of the relevant exchange, the depreciation and amortization periods that apply to the increase in tax basis, the amount of net operating losses available to us as a result of reorganization transactions entered into in connection with the Select 144A Offering, the amount and timing of taxable income we generate in the future, the U.S. federal income tax rate then applicable, and the portion of our payments under the Tax Receivable Agreements that constitute imputed interest or give rise to depreciable or amortizable tax basis.
Certain of the TRA Holders’ rights under the Tax Receivable Agreements are transferable in connection with a permitted transfer of SES Holdings LLC Units or if the TRA Holder no longer holds SES Holdings LLC Units. The payments under the Tax Receivable Agreements are not conditioned upon the continued ownership interest in either SES Holdings or us of any holder of rights under the Tax Receivable Agreements. See Part III, Item 13. “Certain Relationships and Related Transactions, and Director Independence.”
In certain cases, payments under the Tax Receivable Agreements may be accelerated and/or significantly exceed the actual benefits, if any, we realize in respect of the tax attributes subject to the Tax Receivable Agreements.
If we elect to terminate the Tax Receivable Agreements early or they are terminated early due to our failure to honor a material obligation thereunder or due to certain mergers, asset sales, other forms of business combinations or other changes of control, our obligations under the Tax Receivable Agreements would accelerate and we would be required to make an immediate payment equal to the present value of the anticipated future payments to be made by us under the Tax Receivable Agreements (determined by applying a discount rate of the lesser of 6.50% per annum, compounded annually, or the 12-month term SOFR published by CME Group Benchmark Administration plus 171.513 basis points; and such payment is expected to be substantial. The discount rate used as of December 31, 2023 was 6.49%. The calculation of anticipated future payments will be based upon certain assumptions and deemed events set forth in the Tax Receivable Agreements, including (i) the assumption that we have sufficient taxable income to fully utilize the tax benefits covered by the Tax Receivable Agreements, (ii) the assumption that any SES Holdings LLC Units (other than those held by us) outstanding on the termination date are exchanged on the termination date and (iii) certain loss or credit carryovers will be utilized in the taxable year that includes the termination date. Any early termination payment may be made significantly in advance of the actual realization, if any, of the future tax benefits to which the termination payment relates.
As a result of either an early termination or a “change of control” (as defined in the Tax Receivable Agreements, as amended), we could be required to make payments under the Tax Receivable Agreements that exceed our actual cash tax savings under the Tax Receivable Agreements. In these situations, our obligations under the Tax Receivable Agreements could have a substantial negative impact on our liquidity and could have the effect of delaying, deferring or preventing certain mergers, asset sales or other forms of business combinations or changes of control. For example, if the Tax Receivable Agreements were terminated on December 31, 2023, the estimated termination payments would have been approximately $62.0 million (calculated using a 6.49% discount rate, applied against an undiscounted liability of approximately $88.2 million, based upon the last reported closing sale price of our Class A common stock on December 31, 2023) in the aggregate. The foregoing number is merely an estimate and the actual payment could differ materially. There can be no assurance that we will be able to finance our obligations under the Tax Receivable Agreements.
Payments under the Tax Receivable Agreements will be based on the tax reporting positions that we will determine. The TRA Holders will not reimburse us for any payments previously made under the Tax Receivable Agreements if any tax benefits that have given rise to payments under the Tax Receivable Agreements are subsequently disallowed, except that excess payments made to the TRA Holders will be netted against payments that would otherwise be made to the TRA Holders, if any, after our determination of such excess. As a result, in such circumstances, we could make payments that are greater than our actual cash tax savings, if any, and may not be able to recoup those payments, which could adversely affect our liquidity. See Part III, Item 13. “Certain Relationships and Related Transactions, and Director Independence.”
56
If SES Holdings were to become a publicly-traded partnership taxable as a corporation for U.S. federal income tax purposes, we and SES Holdings might be subject to potentially significant tax inefficiencies, and we would not be able to recover payments previously made by us under the Tax Receivable Agreements even if the corresponding tax benefits were subsequently determined to have been unavailable due to such status.
We intend to operate such that SES Holdings does not become a publicly-traded partnership taxable as a corporation for U.S. federal income tax purposes. A “publicly-traded partnership” is a partnership, the interests of which are traded on an established securities market or are readily tradable on a secondary market or the substantial equivalent thereof. Under certain circumstances, exchanges of SES Holdings LLC Units for shares of our Class A common stock or cash pursuant to the Eighth Amended and Restated Limited Liability Company Agreement of SES Holdings (the “SES Holdings LLC Agreement”) or other transfers of SES Holdings LLC Units could cause SES Holdings to be treated as a publicly-traded partnership. Applicable U.S. Treasury regulations provide for certain safe harbors from treatment as a publicly-traded partnership, and we intend to operate such that exchanges or other transfers of SES Holdings LLC Units qualify for one or more such safe harbors. For example, we intend to limit the number of unitholders of SES Holdings and Legacy Owner Holdco, and the SES Holdings LLC Agreement provides for limitations on the ability of unitholders of SES Holdings to transfer their SES Holdings LLC Units and will provide us, as managing member of SES Holdings, with the right to impose restrictions (in addition to those already in place) on the ability of unitholders of SES Holdings to exchange their SES Holdings LLC Units pursuant to the SES Holdings LLC Agreement to the extent we believe it is necessary to ensure that SES Holdings will continue to be treated as a partnership for U.S. federal income tax purposes. If SES Holdings were to become a publicly-traded partnership, significant tax inefficiencies might result for us and for SES Holdings. In addition, we may not be able to realize tax benefits covered under the Tax Receivable Agreements, and we would not be able to recover any payments previously made by us under the Tax Receivable Agreements, even if the corresponding tax benefits (including any claimed increase in the tax basis of SES Holdings’ assets) were subsequently determined to have been unavailable.
Crestview GP may have interests that conflict with the interests of holders of the Class A common stock.
As of December 31, 2023, Crestview GP, through its ownership interest in Legacy Owner Holdco, beneficially owned 100% of our outstanding Class B common stock which represented approximately 13.7% of our outstanding voting capital stock and an equivalent ownership interest in SES Holdings LLC. Because it holds a portion of its ownership interest in our business in the form of direct ownership interests in SES Holdings rather than through us, Crestview GP may have conflicting interests with holders of shares of Class A common stock. For example, Crestview GP may have different tax positions from us and decisions we make in the course of running our business, such as with respect to mergers, asset sales, other forms of business combinations or other changes in control, may affect the timing and amount of payments that are received by the TRA Holders under the Tax Receivable Agreements. See Part III, Item 13. “Certain Relationships and Related Transactions, and Director Independence.”
Our ability to use certain of our current and future net operating loss carryforwards may be limited and could adversely affect our operating results and cash flows.
As of December 31, 2023, we had approximately $168.6 million of tax-affected U.S. federal net operating loss carryforwards (“NOLs”), $88.3 million of which we expect to expire unused beginning in 2031 due to limitations under Section 382 of the Internal Revenue Code of 1986, as amended (the “Code”). As of December 31, 2023, we also had approximately $24.2 million of tax-affected state NOLs, $10.4 million of which we expect to expire unused and the remaining $13.8 million of which we expect to expire beginning in 2024, and tax-affected non-U.S. NOLs of approximately $1.8 million, which we expect to expire beginning in 2035. Utilization of these NOLs (which include historic NOLs of Rockwater Energy Solutions Inc. (“Rockwater”) and Nuverra Environmental Solutions Inc. (“Nuverra”)) depends on many factors, including our future income, which cannot be assured. In addition, Section 382 of the Code generally imposes an annual limitation on the amount of NOLs that may be used to offset taxable income when a corporation has undergone an “ownership change” (as determined under Section 382 of the Code). An ownership change generally occurs if one or more stockholders (or groups of stockholders) who are each deemed to own at least 5% of the relevant corporation’s stock change their ownership by more than 50 percentage points over their lowest ownership percentage within a rolling three-year period. In the event that an ownership change has occurred, or were to occur, utilization of the relevant corporation’s NOLs would be subject to an annual limitation under Section 382 of the
57
Code, determined by multiplying the value of the relevant corporation’s stock at the time of the ownership change by the applicable long-term tax-exempt rate as defined in Section 382 of the Code, and potentially increased for certain gains recognized within five years after the ownership change to the extent of certain net built-in gains at the time of the ownership change. Any unused annual limitation may be carried over to later years until they expire. Limitations similar to those applicable under Section 382 of the Code apply for U.S. state and non-U.S. income tax purposes.
While we do not believe that the acquisitions of either Rockwater or Nuverra resulted in an ownership change under Section 382 of the Code with respect to us, future issuances, sales and/or exchanges of our stock (including in connection with an exercise of the Exchange Right or other transactions beyond our control), taken together with prior transactions with respect to our stock, could cause us to undergo an ownership change. As a result, we cannot assure you that we will not undergo an ownership change in the future. We believe that the acquisitions of Rockwater and Nuverra resulted in ownership changes with respect to each of Rockwater and Nuverra, respectively. Accordingly, as described above, some or all of our U.S. federal or state or non-U.S. NOLs could expire before they can be used. In addition, future ownership changes or changes to the U.S. tax laws could limit our ability to utilize our NOLs. To the extent we are not able to offset our future income with our NOLs, this would adversely affect our operating results and cash flows.
General Risks
We may not be able to finance future growth of our operations or future acquisitions, which could adversely affect our operations and financial position.
The successful execution of our growth strategy depends on our ability to generate sufficient cash flows and our access to capital, both of which are impacted by numerous factors beyond our control, including financial, business, economic and other factors, such as volatility in commodity prices, inflationary pressures and associated monetary policy and pressure from competitors. There have been recent increases in the cost of capital and interest rates, which may affect future borrowings and impact the financial benefit we may receive. If we are unable to generate sufficient cash flows or obtain additional capital on favorable terms or at all, we may be unable to continue growing our business, conduct necessary corporate activities, take advantage of business opportunities that arise or engage in activities that may be in our long-term best interest, which may adversely impact our ability to sustain or improve our current level of profitability.
The growth of our business through acquisitions may expose us to various risks, including those relating to difficulties in identifying suitable, accretive acquisition opportunities and integrating businesses, assets and personnel, as well as difficulties in obtaining financing for targeted acquisitions and the potential for increased leverage or debt service requirements.
As a component of our business strategy, we intend to pursue selected, accretive acquisitions of complementary assets, businesses and technologies. Acquisitions involve numerous risks, including:
| ● | unanticipated costs and assumption of liabilities and exposure to unforeseen liabilities of the acquired business, including but not limited to environmental liabilities and plug and abandonment obligations; |
| ● | difficulties in integrating the operations and assets of the acquired business and the acquired personnel; |
| ● | limitations on our ability to properly assess and maintain an effective internal control environment over an acquired business; |
| ● | potential losses of key employees and customers of the acquired business; |
| ● | risks of entering markets in which we have limited prior experience; and |
| ● | increases in our expenses and working capital requirements. |
58
In evaluating acquisitions, we generally prepare one or more financial cases based on a number of business, industry, economic, legal, regulatory and other assumptions applicable to the proposed transaction. Although we expect a reasonable basis will exist for those assumptions, the assumptions will generally involve current estimates of future conditions. Realization of many of the assumptions will be beyond our control. Moreover, the uncertainty and risk of inaccuracy associated with any financial projection will increase with the length of the forecasted period. Some acquisitions may not be accretive in the near term and will be accretive in the long-term only if we are able to timely and effectively integrate the underlying assets and such assets perform at or near the levels anticipated in our acquisition projections.
The process of integrating an acquired business may involve unforeseen costs and delays or other operational, technical and financial difficulties and may require a significant amount of time and resources. Our failure to successfully incorporate the acquired business and assets into our existing operations or to minimize any unforeseen operational difficulties could have a material adverse effect on our financial condition and results of operations. Furthermore, there is intense competition for acquisition opportunities in our industry. Competition for acquisitions may increase the cost of, or cause us to refrain from, completing acquisitions.
In addition, we may not have sufficient capital resources to complete any additional acquisitions. We may incur substantial indebtedness to finance future acquisitions and also may issue equity, debt or convertible securities in connection with such acquisitions. Debt service requirements could represent a significant burden on our results of operations and financial condition and the issuance of additional equity or convertible securities could be dilutive to our existing stockholders. Furthermore, we may not be able to obtain additional financing on satisfactory terms, or at all. Even if we have access to the necessary capital, we may be unable to continue to identify suitable acquisition opportunities, negotiate acceptable terms or successfully acquire identified targets.
Our success depends on key members of our management, the loss of any of whom could disrupt our business operations.
We depend to a large extent on the services of some of our executive officers. The loss of the services of one or more of our key executives could increase our exposure to the other risks described in this “Risk Factors” section. We do not maintain key person insurance on any of our personnel.
We may be required to take write-downs of the carrying values of our long-lived assets and finite-lived intangible assets.
We evaluate our long-lived assets, such as property and equipment, and finite-lived intangible assets for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that their carrying value may not be recoverable. Recoverability is measured by a comparison of their carrying amount to the estimated undiscounted cash flows to be generated by those assets. Based on specific market factors and circumstances at the time of prospective impairment reviews and the continuing evaluation of development plans, economics and other factors, we may be required to write down the carrying value of our long-lived and finite-lived intangible assets. For the year ended December 31, 2023, we recorded $11.1 million and $1.5 million of abandonment charges to write down the carrying value of our definite-lived intangible assets and long-lived assets, respectively.
We may be required to take a write-down of the carrying value of goodwill.
For the year ended December 31, 2023, we recorded $4.7 million of goodwill in connection with the Breakwater acquisition. When applicable, we conduct our annual goodwill impairment assessment during the fourth quarter of each year, or more frequently if an event or circumstance indicates that the carrying value of a reporting unit may exceed the fair value. When possible impairment is indicated, we value the implied goodwill to compare it with the carrying amount of goodwill. If the carrying amount of goodwill exceeds its implied fair value, an impairment charge is recorded. The fair value of goodwill is based on estimates and assumptions applied by us such as revenue growth rates, operating margins, weighted-average costs of capital, market multiples, and future market conditions and as affected by numerous factors, including the general economic environment and levels of exploration and production activity of oil
59
and gas companies, our financial performance and trends, and our strategies and business plans, among others. As a result of this annual impairment assessment, we may be required to write down the carrying value of goodwill.
ITEM 1B. UNRESOLVED STAFF COMMENTS
None.
ITEM 1C. CYBERSECURITY
Processes for Assessing, Identifying, and Managing Cybersecurity Risks
Our industry has become increasingly dependent on digital technologies to conduct certain processing activities. For example, we depend on digital technologies to perform many of our services and to process and record financial and operating data. We recognize the importance of assessing and managing material risks associated with cybersecurity threats. We seek to assess, identify and manage cybersecurity risks for our IT environment, leveraging the National Institute of Standards and Technology Cybersecurity Framework (“NIST CSF”), through the processes described below:
| ● | Risk Assessment: |
We recognize that cybersecurity threats are constantly evolving, and we have implemented risk management procedures designed to protect our systems and data. We conduct vulnerability assessments, and periodic audits to identify and address potential cybersecurity vulnerabilities. We conduct periodic assessments to identify material cybersecurity risks, and we endeavor to update cybersecurity infrastructure, procedures, policies, and education programs in response to those findings. As part of our efforts to safeguard our systems and data, we have sought to implement industry-standard security controls, including firewalls, encryption, and multi-factor authentication.
| ● | Incident Identification and Response: |
A monitoring and detection system has been implemented to help promptly identify cybersecurity incidents and recommend mitigating actions. Despite our best efforts, no security measure is entirely foolproof. In the event of a cybersecurity incident, we utilize a range of standard incident response practices that identify, analyze, contain, and recover the event with the goal of minimizing the impact and restoring normal operations. In the event of a cybersecurity incident, we have standard incident response practices that contain, analyze, and recover with the goal of minimizing the impact and restoring normal operations after each event.
| ● | Cybersecurity Training and Awareness: |
Employees receive periodic cybersecurity trainings including phishing campaigns and general awareness campaigns.
| ● | Access Controls: |
Users are provided with access consistent with the principle of least privilege, which requires that users be given no more access than necessary to complete their job functions. A multi-factor authentication process has been implemented for employees accessing company information.
We engage third-party vendors, assessors, consultants, auditors, and other third party service providers in connection with the above processes. We recognize that third-party service providers introduce cybersecurity risks. We aim to assess the risks from cybersecurity threats that impact select suppliers and third-party service providers with whom we share personal identifying and confidential information. The above cybersecurity risk management processes are integrated into the Company’s overall enterprise risk management processes.
60
Impact of Risks from Cybersecurity Threats
As of the date of this Report, we are not aware of any previous cybersecurity threats that have materially affected or are reasonably likely to materially affect the Company. While we have implemented cybersecurity measures, it is important to note that the threat landscape is constantly evolving, and new risks may emerge. A successful attack on our information or operational technology systems could have significant consequences to the business. While we devote resources to our security measures to protect our systems and information, these measures cannot provide absolute security. No security measure is infallible. See “Risk Factors” for additional information about the risks to our business associated with a breach or compromise to our information or operational technology systems.
Board of Directors’ Oversight and Management’s Role
Our Board of Directors and our Audit Committee oversee risks from cybersecurity threats and our cybersecurity practices. Accordingly, our Board of Directors and our Audit Committee receive regular updates on potential cybersecurity risks and mitigation strategies from the Chief Technology Officer.
Management is responsible for assessing and managing risks from cybersecurity threats and implementing the Company’s cybersecurity strategies. The Company has a Chief Technology Officer (“CTO”) that focuses on current and emerging cybersecurity matters and is responsible for establishing and maintaining the Company’s cybersecurity-related policies and procedures. Our CTO has an Engineering degree from Rice University, a Master of Business Administration from Harvard Business School, more than 20 years' work experience, and a background in leading digital / software development organizations. Supporting our CTO is the Company’s Vice President of Corporate Platform and Infrastructure and our team of cybersecurity experts. Our Vice President has an undergraduate degree from The University of Houston and has served in various Information Technology and Information Security roles for over 20 years across Oil & Gas, Consulting, and Power Generation sectors. This team is collectively responsible for upward reporting on an as-needed basis of emerging cybersecurity incidents to senior management and, if appropriate, the Audit Committee of the Board of Directors. To facilitate effective oversight, our Technology Team holds regular discussions with our management team and the Board of Directors around cybersecurity risks, incident trends, and the effectiveness of our cybersecurity measures.
ITEM 2. PROPERTIES
We lease space for our principal executive offices in Houston and Gainesville, Texas and we also lease local office space in the regions in which we operate. Additionally, we own and lease numerous storage facilities, trucking facilities and sales and administrative offices throughout the geographic areas in which we operate. In connection with our Chemical Technologies segment, we own two primary manufacturing facilities in Texas, and we lease three primary regional distribution centers through which we provide products to our customers in all major U.S. shale basins. Our leased properties are subject to various lease terms and expirations.
We believe all the properties that we currently occupy are suitable for their intended uses. We believe that our current facilities are sufficient to conduct our operations. However, we continue to evaluate the purchase or lease of additional properties or the sale or consolidation of our properties, as our business requires.
The following table shows our active leased and owned properties categorized by segment as of December 31, 2023:
Region |
Water Services |
Water Infrastructure |
Chemical Technologies |
Corporate & Other |
Total |
|||||
Leased |
59 |
16 |
4 |
3 |
82 |
|||||
Owned |
36 |
28 |
5 |
— |
69 |
|||||
95 |
44 |
9 |
3 |
151 |
61
ITEM 3. LEGAL PROCEEDINGS
We are not currently a party to any legal proceedings that, if determined adversely against us, individually or in the aggregate, would have a material adverse effect on our financial position, results of operations or cash flows. We are, however, named defendants in certain lawsuits, investigations and claims arising in the ordinary course of conducting our business, including certain environmental claims and employee-related matters, and we expect that we will be named defendants in similar lawsuits, investigations and claims in the future. While the outcome of these lawsuits, investigations and claims cannot be predicted with certainty, we do not expect these matters to have a material adverse impact on our business, results of operations, cash flows or financial condition. We have not assumed any liabilities arising out of these existing lawsuits, investigations and claims.
ITEM 4. MINE SAFETY DISCLOSURES
Not applicable.
PART II
ITEM 5. MARKET FOR REGISTRANT’S COMMON EQUITY, RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS AND ISSUER PURCHASES OF EQUITY SECURITIES
Our Class A common stock is listed on the New York Stock Exchange (the “NYSE”) under the ticker symbol “WTTR.” As of February 19, 2024, there were 189 stockholders of record of our Class A common stock.
Dividend Policy
The Company’s board of directors initiated a dividend program in 2022 under which the Company intends to pay regular quarterly dividends, which commenced with the first payment of a quarterly cash dividend of $0.05 per share of Class A common stock on November 17, 2022 (along with a comparable distribution of $0.05 per unit for holders of units of SES Holdings, LLC who also hold an equal number of shares of Class B common stock). The Company paid quarterly dividends at the same rate through the third quarter of 2023, then the board of directors increased the quarterly dividend paid on November 17, 2023 to $0.06 per share of Class A common stock (along with a comparable distribution of $0.06 per unit to the unitholders of SES Holdings, LLC). Our future dividend policy is within the discretion of our board of directors, and all future dividend payments are subject to quarterly review and approval by our board of directors, and will depend upon then-existing conditions, including our results of operations and financial condition, capital requirements, business prospects, statutory and contractual restrictions on our ability to pay dividends, including restrictions contained in our Sustainability-Linked Credit Facility and other factors our board of directors may deem relevant.
Securities Authorized for Issuance under Equity Compensation Plans
The Company maintains the Select Energy Services, Inc. 2016 Equity Incentive Plan (as amended, the “2016 Plan”), the Select Energy Services, Inc. Employee Stock Purchase Plan (the "ESPP"), the Nuverra Environmental Solutions, Inc. 2017 Long Term Incentive Plan (the “2017 Plan”), and the Nuverra Environmental Solutions, Inc. 2018 Restricted Stock Plan for Directors (the “2018 Plan” and, together with the 2017 Plan, the “Assumed Plans”). The 2016 Plan was approved by our stockholders prior to our initial public offering but has not been approved by our public stockholders; however, the first amendment to the 2016 Plan was approved by our public stockholders in October 2017 and the second amendment to the 2016 Plan was approved by our public stockholders in May 2020. The ESPP was approved by our stockholders on May 4, 2018. On November 3, 2022, our board of directors approved an amendment to the ESPP, which suspended all offerings on or after December 1, 2022. Our board of directors reserves the right to recommence offerings pursuant to its discretion and the terms of the ESPP. The Assumed Plans were assumed in our acquisition of Nuverra, were not approved by our stockholders, and may only be used to grant awards to legacy Nuverra employees and service providers. See “Note 12—Equity-Based Compensation” for a description of our equity compensation plans.
62
The following table provides information about our Class A common stock that may be issued under our equity compensation plans as of December 31, 2023.
Plan Category |
Number of securities to be issued upon exercise of outstanding options, warrants and rights |
Weighted-average exercise price of outstanding options, warrants and rights(1) |
Number of securities remaining available for future issuance under equity compensation plans (excluding securities reflected in column (a))(2) |
|
(a) |
(b) |
(c) |
Equity compensation plans approved by security holders |
1,654,952 |
$17.01 |
1,873,435 |
Equity compensation plans not approved by security holders |
— (3) |
— |
70,505 (4) |
Total |
1,654,952 |
$17.01 |
1,943,940 |
(1) |
Only stock options have an exercise price. |
(2) |
Reflects the total number of shares of Class A common stock (i) subject to outstanding rights under the ESPP and (ii) remaining available for issuance under the 2016 Plan and the ESPP. For the avoidance of doubt, while shares of Class A common stock technically remain available for issuance under the ESPP, the Company does not currently have an offering period open with respect to the ESPP. Shares remaining available under the 2016 Plan may be issued other than with respect to options, warrants or rights. |
(3) |
All awards assumed under the Assumed Plans have either fully vested or been forfeited such that as of December 31, 2022, there were no outstanding awards under the Assumed Plans. |
(4) |
Reflects the total number of shares of Class A common stock remaining available for issuance under the Assumed Plans to legacy Nuverra employees and service providers. Shares remaining available under the Assumed Plans may be issued other than with respect to options, warrants or rights. |
Features of the Assumed Plans
On February 23, 2022, the Company assumed the Assumed Plans and certain equity awards outstanding under the Assumed Plans in connection with the Nuverra acquisition. Under the 2017 Plan, the Company may grant to certain eligible participants who were employees, directors or other service providers of Nuverra prior to the Nuverra acquisition options, stock appreciation rights, restricted stock, restricted stock units, stock awards, dividend equivalents, other stock-based awards, cash awards, substitute awards, performance awards, or any combination of the foregoing, with respect to up to 1,772,058 shares of Nuverra common stock. Under the 2018 Plan, the Company may grant to certain eligible participants who were directors of Nuverra prior to the Nuverra acquisition restricted stock awards with respect to up to 100,000 shares of Nuverra common stock. The shares remaining available for issuance under the Assumed Plans were converted into shares of the Company’s Class A common stock at a conversion rate of one Nuverra share to 0.2551 shares of the Company’s Class A common stock such that at the time of the Nuverra acquisition an aggregate of 131,110 shares of the Company’s Class A common stock was available for issuance with respect to assumed awards and future awards under the 2017 Plan and an aggregate of 24,984 shares of the Company’s Class A common stock was available for issuance with respect to assumed awards and future awards under the 2018 Plan.
The aggregate number of shares of the Company’s Class A common stock available for issuance under the Assumed Plans will be reduced by one share of the Company’s Class A common stock for every one share of the Company’s Class A common stock subject to an award granted under the Assumed Plans. If any award granted under the 2017 Plan (in whole or in part) is cancelled, forfeited, exchanged, settled in cash, or otherwise terminated, the shares of the Company’s Class A common stock subject to such award will again be available at a rate of one share of the Company’s Class A common stock for every one share of the Company’s Class A common stock subject to such award, and if any award granted under the 2018 Plan (in whole or part) is forfeited, the shares of the Company’s Class A common stock subject to such award will again be available at a rate of one share of the Company’s Class A common stock for every one share of the Company’s Class A common stock subject to such award. The Company registered the securities issuable under the Assumed Plans by filing a registration statement on Form S-8 with the Securities and Exchange
63
Commission on February 23, 2022. As of December 31, 2023, the maximum number of shares of the Company’s Class A common stock available for future issuance under the 2017 Plan is 55,769 and under the 2018 Plan is 14,736.
Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities
Total Number of Shares |
Maximum Dollar Value of |
|||||||||
Total Number of |
Weighted-Average Price |
Purchased as Part of Publicly |
Shares that May Yet be Purchased |
|||||||
Period |
Shares Purchased |
Paid Per Share(1) |
Announced Plans or Programs |
Under the Plans or Programs(2) |
||||||
October 1, 2023 to October 31, 2023 |
22,494 |
$7.49 |
— |
$12,463,632 |
||||||
November 1, 2023 to November 30, 2023 |
748,521 |
$7.33 |
709,165 |
$27,323,825 |
||||||
December 1, 2023 to December 31, 2023 |
862,596 |
$7.20 |
853,627 |
$21,177,432 |
||||||
(1) |
The average price paid per share includes commissions. |
(2) |
On March 21, 2023, our board of directors authorized a share repurchase program of up to $50 million of outstanding shares of Class A common stock. This new authorization was in addition to the $5.1 million remaining outstanding under our previous $25 million authorization, as of March 21, 2023. On November 8, 2023, our board of directors authorized a share repurchase program of up to $25 million of outstanding shares of Class A common stock. This new authorization was in addition to the $7.5 million remaining outstanding under our previous authorization, as of November 8, 2023. Repurchases under the share repurchase program may be made at any time or from time to time, without prior notice, in the open market or in privately negotiated transactions at prevailing market prices, or such other means as will comply with applicable state and federal securities laws and regulations, including the provisions of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, including Rule 10b5-1 and, to the extent practicable or advisable, Rule 10b-18 thereunder, and consistent with the Company’s contractual limitations and other requirements. |
64
STOCK PERFORMANCE GRAPH
The following performance graph and related information shall not be deemed “soliciting material” or to be “filed” with the SEC, nor shall the information be incorporated by reference into any future filing under the Securities Act or the Exchange Act, except to the extent that the Company specifically incorporates it by reference into such filing.
Set forth below is a line graph comparing the cumulative total stockholder return for the Company’s Class A common stock, based on the market price of the Class A common stock and assuming reinvestment of dividends, with the cumulative total stockholder return of companies with the New York Stock Exchange Market Value Index (the Company’s broad equity market index) and the Philadelphia Stock Exchange Oil Service Sector Index for the period commencing on December 31, 2018 and ending on December 31, 2023. The stock price performance included in this graph is not necessarily indicative of future stock price performance.
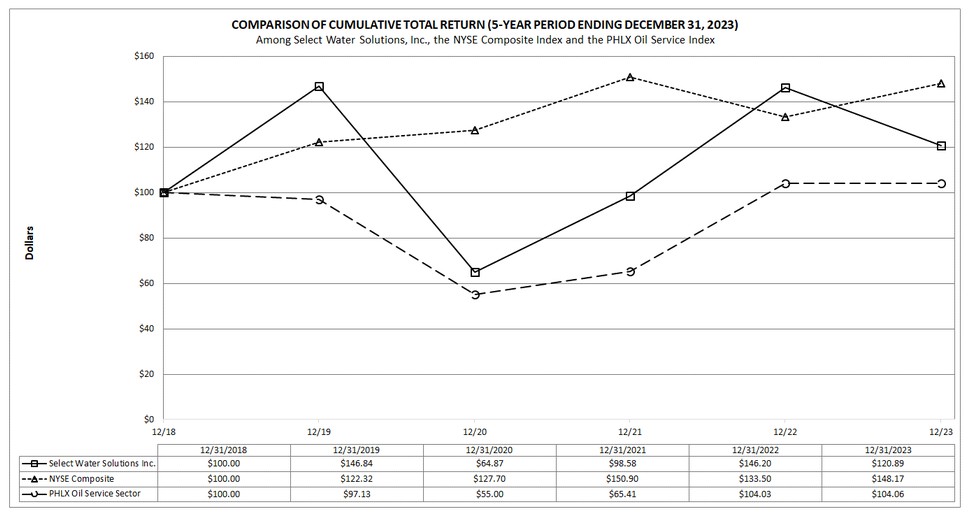
65
ITEM 6. RESERVED
ITEM 7. MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS
The following discussion and analysis of our financial condition and results of operations should be read in conjunction with our consolidated financial statements and related notes thereto in Part II, Item 8. “Financial Statements and Supplementary Data”. This discussion and analysis contains forward-looking statements based on our current expectations that involve risks and uncertainties. Our actual results may differ materially from those anticipated in these forward-looking statements as a result of various factors as described under “Cautionary Note Regarding Forward-Looking Statements” and Part I, Item 1A. “Risk Factors.” We assume no obligation to update any of these forward-looking statements.
Overview
We are a leading provider of sustainable water-management and chemical solutions to the energy industry in the U.S. As a leader in the water solutions industry, we place the utmost importance on safe, environmentally responsible management of oilfield water throughout the lifecycle of a well. Additionally, we believe that responsibly managing water resources through our operations to help conserve and protect the environment in the communities in which we operate is paramount to our continued success.
In many regions of the country, there has been growing concern about the volumes of water required for new oil and gas well completions, as well as volumes of water injected into subterranean zones where seismicity can be triggered. Working with our customers and local communities, we strive to be an industry leader in the development of sustainable cost-effective alternatives to fresh water. Specifically, we offer solutions through our infrastructure networks that enable our E&P customers to gather, treat and reuse produced water, thereby reducing the demand for freshwater while also reducing the volumes of saltwater that must be disposed by injection. In many areas, we have also acquired sources of non-potable water, such as brackish water or municipal or industrial effluent. Through our expertise in chemical technologies and our FluidMatch™ design solutions, we provide water profiling and fluid assessment services for our customers to support the optimization of their fluid systems, enabling the economic use of these alternative sources. We also work with our E&P customers to lower their emissions through methane combustion technology, and reduce the environmental footprint of their operations through the use of temporary hose and permanent pipeline systems, which are supported by extensive monitoring and automation technology solutions that provide safer and more efficient water resource management. These solutions significantly reduce the demand for trucking operations, thereby reducing gasoline and diesel exhaust emissions, increasing safety and decreasing traffic congestion in nearby communities.
Recent Trends and Outlook
On January 29, 2024, we announced the acquisition of strategic water infrastructure assets in the Haynesville Shale and Rockies regions for approximately $90 million of aggregate cash consideration. These acquisitions encompassed the gathering and disposal assets and operations of Tri-State Water Logistics, LLC, the fluids and solids treatment and disposal assets and operations of Iron Mountain Energy, LLC, and produced water gathering and disposal infrastructure and additional permitted disposal and recycling capacity in the Rockies region. These acquisitions will add approximately 450,000 barrels per day of permitted disposal capacity to our Water Infrastructure segment across 21 saltwater disposal wells, two slurry injection wells and a solids treatment facility. The disposal assets are supported by a significant portfolio of interconnected gathering pipelines, strategic surface acreage and right-of-way, and multiple long-term pipeline gathering and dedication contracts.
Select is prioritizing investments in water infrastructure projects, which often bring a more predictable and steady revenue stream through long-term contracts. These investments typically produce higher gross margins and also foster stronger partnerships with customers, as Select becomes an integral partner in ensuring well integrity for ongoing customer production. The focus is on integrated solutions that enhance contracted infrastructure projects with logistics services and chemical solutions, and expanding our value provided to the customer. Our approach, historically and as we
66
head into 2024, has been to streamline operations and offer a more comprehensive and valuable overall package to customers built around optimizing the entire water lifecycle as such integrated solutions to drive revenue growth and enhance overall value to clients.
Effective June 1, 2023, our chief operating decision maker began to strategically view and manage certain water sourcing and transfer operations, previously included in our Water Infrastructure segment, as part of our Water Services segment. These changes were driven by a number of factors, including the preponderance of our water sourcing business that integrates with our water transfer operations, the continued transition of completions water demand from fresh and brackish water to recycled water, as well as the diversifying demand for these water transfer services beyond the immediate vicinity of our pipeline infrastructure. Due to these changes, we believe the Water Services segment management is best suited to manage these operations. As a result of these changes, we anticipate more efficient sharing and utilization of resources and to realize potential synergies. Prior periods have been recast to include the water sourcing and transfer operations within the Water Services segment and remove the results of those operations from the Water Infrastructure segment.
Concurrently, the Company also decided to rename its Oilfield Chemicals segment as Chemical Technologies. This change was based on a number of factors, including the continued success of our chemicals business in delivering customized, specialty chemicals products developed through our own research and development efforts and the de-emphasis of certain traditional commoditized chemistry products within the oil and gas industry, as well as the continued investments in time and resources we make to manufacture and sell our specialty chemical products into non-oilfield industrial-related applications. We believe these segment changes better align the business with the current and future state of the Company’s operations, capital allocations and strategic objectives. This change was a naming convention only change that did not impact any numbers for all years presented.
On May 8, 2023, we announced that our stockholders approved the Company’s Fifth Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation, which, among other things, changed the name of the Company from Select Energy Services, Inc. to Select Water Solutions, Inc. to reflect our strategic focus as a water-first company. We retained our current stock ticker “WTTR” trading on the New York Stock Exchange.
The armed conflict between Ukraine and Russia continued throughout 2023, and additional conflicts arose in Israel and elsewhere in the Middle East. As a result of the Russian invasion of the Ukraine, the U.S., the United Kingdom, the member states of the European Union and other public and private actors have sustained severe sanctions on Russian financial institutions, businesses and individuals. In October 2023, Hamas militants conducted attacks in Israel and an armed conflict has ensued between Israel and Hamas. The ensuing conflict has resulted in increased hostilities and instability in oil and gas producing regions in the Middle East as well as in key adjacent shipping lanes. In tandem with such conflict, the Houthi movement, which controls parts of Yemen, has targeted and launched numerous attacks on Israeli, American and international commercial marine vessels in the Red Sea, resulting in many shipping companies re-routing to avoid the region altogether and worsening existing supply chain issues, including delays in supplier deliveries, extended lead times and increased cost of freight, insurance and materials. The potential for an international conflict with Iran, a major oil producer, the Houthi movement in Yemen or the Hezbollah movement in Lebanon has been perceived by many to have increased due to continued increasing hostilities in the Middle East. The Russia-Ukraine conflict, and the resulting sanctions and concerns regarding global energy security, has contributed to, and the conflict in the Israel-Gaza region and any heightened hostilities in the Middle East may contribute to, increases and volatility in the prices for oil and natural gas. Such volatility, coupled with an increased cost of capital, due, in part to higher rates of inflation and interest rates, may lead to a more difficult investing and planning environment for us and our customers. The ultimate geopolitical and macroeconomic consequences of these conflicts and associated sanctions and/or international responses cannot be predicted, and such events, or any further hostilities elsewhere, could severely impact the world economy and may adversely affect our financial condition. An end to these conflicts and an easing or elimination of the related sanctions and/or international response could result in a significant fall in commodity prices as hydrocarbons become more readily accessible in global markets, which could have an adverse effect on our customers, and therefore adversely affect our customers’ demand for our services. An intensification of that conflict could also have an adverse effect on our customers and their demand for our services.
67
In addition, OPEC+ countries announced production cuts of around 1.16 million barrels per day in April 2023, bringing its total volume cuts to 3.66 million barrels per day since 2021. A number of other production cuts have followed, most recently, in November 2023, OPEC+ announced voluntary output cuts totaling 2.2 million barrels per day into the first quarter of 2024, including an additional cut of 900,000 barrels per day. Although OPEC+ increased its output in December 2023 due to, among other things, the ongoing conflicts in the Middle East, OPEC+ may, at its discretion, continue to decrease, or increase, production, which will continue to impact crude oil and natural gas price volatility. The actions of OPEC+ countries with respect to oil production levels and announcements of potential changes in such levels, including agreement on and compliance with production targets, may result in volatility in the industry in which we and our customers operate. The average price of West Texas Intermediate (“WTI”) crude oil decreased in 2023 versus 2022 as a result of increased production coupled with a moderate decrease in global demand. During the year ended December 31, 2023, the average spot price of WTI crude oil was $77.58 versus an average price of $94.90 for the year ended December 31, 2022. While WTI price levels declined during 2023 relative to 2022, these WTI price levels remain supportive of our customers’ drilling and completion programs in the major shale basins. The average Henry Hub natural gas spot price during the year ended December 31, 2023, was $2.54 versus an average of $6.42 for the year ended December 31, 2022. Henry Hub natural gas price levels in 2023 have declined materially relative to 2022 and have negatively impacted activity levels, resulting in incremental development activity cuts.
While the ongoing effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on our operations have largely ended, some impacts related to the COVID-19 pandemic, such as increased inflation and supply chain constraints, have resulted in higher interest rates and cost of capital, which in turn increase the risk of economic stagnation or an economic recession. The pandemic had a material negative impact on our financial results for prior periods and may affect the comparability of our results.
Many of our customers have demonstrated their resolve to manage their capital spending within budgets and cash flow from operations and increase redemptions of debt and/or returns of capital to investors. Additionally, consolidation among our customers, such as the current consolidation of E&P companies in the Permian Basin, can disrupt our market in the near term and the resulting demand for our services. Overall however, the financial health of the oil and gas industry and many of our customers specifically, as reflected in debt metrics, recent capital raises, and equity valuations, has greatly improved over the course of the year ended December 31, 2022, and through the year ended December 31, 2023.
When one customer acquires another, it can lead to larger blocks of consolidated development and production acreage, which can increase the demand for our longer term integrated full water lifecycle solutions. This consolidation may streamline operations, as Select can offer integrated solutions to clients with larger water volumes to manage in certain areas. The Company's position in the market may strengthen, as it becomes an essential partner for long term production integrity in larger, more comprehensive water projects. However, it also means Select must meet the changing needs and structures of these consolidated entities to maintain and grow these relationships. While customers involved in acquisitions may initially slow activity to focus on integration and portfolio management, we believe Select is well-positioned to meet the increased responsibilities of overall water management, including water reuse, recycling, transmitting and balancing across customers and regions, and ultimately disposal, for these larger customers and blocks of contiguous acreage.
While the financial health of the broader oil and gas industry has continued to improve, the potential inability of broader banking and other financial services firms to access liquidity has at times resulted in significant disruptions to global markets. Central bank policy actions, bank failures and associated liquidity risks and other factors may negatively impact the value of our equity and that of our customers, and may reduce our and their ability to access liquidity in the bank and capital markets or result in capital being available on less favorable terms, which could negatively affect our financial condition and that of our customers.
From an operational standpoint, many of the recent trends still apply to ongoing unconventional oil and gas development. The continued trend towards multi-well pad development, executed within a limited time frame, combined with service price inflation and high interest rates, has increased the overall intensity, complexity and cost of well completions, while increasing fracturing efficiency and the use of lower-cost in-basin sand has decreased total costs for our customers. However, we note the continued efficiency gains in the well completions process can limit the days we
68
spend on the wellsite and, therefore, negatively impact the total revenue opportunity for certain of our services utilizing day-rate pricing models.
This multi-well pad development, combined with recent upstream acreage consolidation and corporate mergers as well as the growing trends around the recycling and reuse applications of produced water provides a significant opportunity for companies like us that can deliver increasingly complex solutions for our E&P customers across large swathes of acreage through our regional infrastructure networks, delivering solutions for the full completion and production lifecycle of wells. While these trends have advanced the most in the Permian Basin to date, they are emerging in other basins as well.
The increased reuse of produced water requires additional chemical treatment solutions. We have a dedicated team of specialists focused every day on developing and deploying innovative water treatment and reuse services for our customers. Our FluidMatch™ design solutions enable our customers to economically use these alternative sources to optimize their fluid systems by providing water profiling and fluid assessment services working towards real-time. This trend also supports more complex “on-the-fly” solutions that treat, proportion, and blend various streams of water and chemicals at the wellsite. This complexity favors service companies that are able to provide advanced technology solutions. Ultimately, we intend to play an important role in the advancement of water and chemical solutions that are designed to meet the sustainability goals of key stakeholders.
Our water logistics, treatment, and chemical application expertise, in combination with advanced technology solutions, are applicable to other industries beyond oil and gas. We are working to further commercialize our services in other businesses and industries through our industrial solutions group.
Our Segments
Our services are offered through three reportable segments: (i) Water Services; (ii) Water Infrastructure; and (iii) Chemical Technologies.
| ● | Water Services. The Water Services segment consists of the Company’s services businesses, including water sourcing, water transfer, flowback and well testing, fluids hauling, water monitoring, water containment and water network automation, primarily serving E&P companies. Additionally, this segment includes the operations of our accommodations and rentals business. |
| ● | Water Infrastructure. The Water Infrastructure segment consists of the Company’s fixed infrastructure assets, including operations associated with our water distribution pipeline infrastructure, our water recycling solutions, and our produced water gathering systems and SWDs, as well as solids disposal facilities, primarily serving E&P companies. |
| ● | Chemical Technologies. The Chemical Technologies segment provides technical solutions, products and expertise related to chemical applications in the oil and gas industry. We develop, manufacture, manage logistics and provide a full suite of chemicals used in hydraulic fracturing, stimulation, cementing and well completions for customers ranging from pressure pumpers to major integrated and independent oil and gas producers. This segment also utilizes its chemical experience and lab testing capabilities to customize tailored water treatment solutions designed to optimize the fracturing fluid system in conjunction with the quality of water used in well completions. |
How We Generate Revenue
We currently generate most of our revenue through our water-management services associated with well completions as well as ongoing produced water management, provided through our Water Services and Water Infrastructure segments. Most of this revenue is realized through customer agreements with fixed pricing terms and is recognized when delivery of services is provided, generally at our customers’ sites. While we have some long-term pricing arrangements, particularly in our Water Infrastructure segment, most of our water and water-related services are priced based on prevailing market conditions, giving due consideration to the customer’s specific requirements.
69
We also generate revenue by providing completion and specialty chemicals through our Chemical Technologies segment. We invoice the majority of our Chemical Technologies customers for services provided based on the quantity of chemicals used or pursuant to short-term contracts as customer needs arise.
Costs of Conducting Our Business
The principal expenses involved in conducting our business are labor costs, vehicle and equipment costs (including depreciation, rental, repair and maintenance and leasing costs), raw materials and water sourcing costs and fuel costs. Our fixed costs are relatively low. Most of the costs of serving our customers are variable, i.e., they are incurred only when we provide water and water-related services, or chemicals and chemical-related services to our customers.
Labor costs associated with our employees and contract labor comprise the largest portion of our costs of doing business. We incurred labor and labor-related costs of $554.4 million, $476.2 million and $285.7 million for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021, respectively. The majority of our recurring labor costs are variable and dependent on the market environment and are incurred only while we are providing our operational services. We also incur costs to employ personnel to ensure safe operations, sell and supervise our services and perform maintenance on our assets, which is not directly tied to our level of business activity. Additionally, we incur selling, general and administrative costs for compensation of our administrative personnel at our field sites and in our operational and corporate headquarters, as well as for third-party support, licensing and services.
We incur significant vehicle and equipment costs in connection with the services we provide, including depreciation, repairs and maintenance, rental and leasing costs. We incurred vehicle and equipment costs of $318.9 million, $266.6 million and $165.1 million for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021, respectively.
We incur raw material costs in manufacturing our chemical products, as well as for water that we source for our customers. We incurred raw material costs of $300.7 million, $300.8 million and $209.7 million for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021, respectively.
We incur variable transportation costs associated with our service lines, predominately fuel and freight. We incurred fuel and freight costs of $115.7 million, $118.1 million and $58.5 million for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021, respectively. Rising fuel prices impact our transportation costs, which affect the results of our operations.
How We Evaluate Our Operations
We use a variety of operational and financial metrics to assess our performance. Among other measures, management considers each of the following:
| ● | Revenue; |
| ● | Gross Profit; |
| ● | Gross Margins; |
| ● | EBITDA; and |
| ● | Adjusted EBITDA. |
Revenue
We analyze our revenue and assess our performance by comparing actual monthly revenue to our internal projections and across periods. We also assess incremental changes in revenue compared to incremental changes in direct operating costs and selling, general and administrative expenses across our reportable segments to identify
70
potential areas for improvement, as well as to determine whether segment performance is meeting management’s expectations.
Gross Profit
To measure our financial performance, we analyze our gross profit, which we define as revenues less direct operating expenses (including depreciation and amortization expenses). We believe gross profit provides insight into profitability and the true operating performance of our assets. We also compare gross profit to prior periods and across segments to identify trends as well as underperforming segments.
Gross Margins
Gross margins provide an important gauge of how effective we are at converting revenue into profits. This metric works in tandem with gross profit to ensure that we do not seek to increase gross profit at the expense of lower margins, nor pursue higher gross margins at the expense of declining gross profits. We track gross margins by segment and service line and compare them across prior periods and across segments and service lines to identify trends as well as underperforming segments.
EBITDA and Adjusted EBITDA
We view EBITDA and Adjusted EBITDA as important indicators of performance. We define EBITDA as net income/(loss), plus interest expense, income taxes, and depreciation and amortization. We define Adjusted EBITDA as EBITDA plus/(minus) loss/(income) from discontinued operations, plus any impairment and abandonment charges or asset write-offs pursuant to generally accepted accounting principles in the U.S. (“GAAP”), plus non-cash losses on the sale of assets or subsidiaries, non-recurring compensation expense, non-cash compensation expense, and non-recurring or unusual expenses or charges, including severance expenses, transaction costs, or facilities-related exit and disposal-related expenditures, plus/(minus) foreign currency losses/(gains), plus/(minus) losses/(gains) on unconsolidated entities and plus tax receivable agreements expense less bargain purchase gains from business combinations. The adjustments to EBITDA are generally consistent with such adjustments described in our Sustainability-Linked Credit Facility. See “—Comparison of Non-GAAP Financial Measures—EBITDA and Adjusted EBITDA” for more information and a reconciliation of EBITDA and Adjusted EBITDA to net income (loss), the most directly comparable financial measure calculated and presented in accordance with GAAP.
Factors Affecting the Comparability of Our Results of Operations to Our Historical Results of Operations
Our future results of operations may not be comparable to our historical results of operations for the periods presented, primarily for the reasons described below and those described in “—Recent Trends and Outlook” above.
Acquisition Activity
As described above, we continuously evaluate potential investments, particularly in water infrastructure and other water-related services and technology. To the extent we consummate acquisitions, any incremental revenues or expenses from such transactions are not included in our historical results of operations.
Between January 2022 and June 2023, we completed three business combinations, four asset acquisitions and the buyout of all noncontrolling interests in a recycling system joint venture, including the acquisitions of Breakwater, Cypress and Nuverra among others. Our historical financial statements for periods prior to the respective date each acquisition was completed do not include the results of operations of that acquisition. See “—Recent Developments” and “Note 3—Acquisitions” for a description of these transactions.
71
Results of Operations
The following table sets forth our results of operations, including revenue by segment, for the year ended December 31, 2023 compared to the year ended December 31, 2022. The results of operations for the year ended December 31, 2022 compared to the year ended December 31, 2021 is set forth in Part II, Item 7 of our Annual Report on Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2022 under the caption “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations.”
Year Ended December 31, 2023 Compared to the Year Ended December 31, 2022
Year ended December 31, |
Change |
|
|||||||||||
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
Dollars |
|
Percentage |
|
|||||
(in thousands) |
|
||||||||||||
Revenue |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Water Services |
$ |
1,032,896 |
$ |
944,497 |
$ |
88,399 |
|
9.4 |
% |
||||
Water Infrastructure |
229,970 |
125,284 |
104,686 |
83.6 |
% |
||||||||
Chemical Technologies |
322,487 |
317,639 |
|
4,848 |
|
1.5 |
% |
||||||
Total revenue |
|
1,585,353 |
|
1,387,420 |
|
197,933 |
|
14.3 |
% |
||||
Costs of revenue |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
Water Services |
|
814,609 |
|
764,569 |
|
50,040 |
|
6.5 |
% |
||||
Water Infrastructure |
138,191 |
82,941 |
|
55,250 |
|
66.6 |
% |
||||||
Chemical Technologies |
262,078 |
265,648 |
(3,570) |
(1.3) |
% |
||||||||
Depreciation and amortization |
|
138,813 |
|
113,507 |
|
25,306 |
|
22.3 |
% |
||||
Total costs of revenue |
|
1,353,691 |
|
1,226,665 |
|
127,026 |
|
10.4 |
% |
||||
Gross profit |
|
231,662 |
|
160,755 |
|
70,907 |
|
44.1 |
% |
||||
Operating expenses |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
Selling, general and administrative |
|
155,548 |
118,935 |
|
36,613 |
|
30.8 |
% |
|||||
Depreciation and amortization |
|
2,276 |
2,209 |
|
67 |
|
3.0 |
% |
|||||
Impairments and abandonments |
12,607 |
— |
12,607 |
NM |
|||||||||
Lease abandonment costs |
|
42 |
449 |
|
(407) |
|
(90.6) |
% |
|||||
Total operating expenses |
|
170,473 |
|
121,593 |
|
48,880 |
|
40.2 |
% |
||||
Income from operations |
|
61,189 |
|
39,162 |
|
22,027 |
|
56.2 |
% |
||||
Other income (expense) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
(Loss) gain on sales of property and equipment and divestitures, net |
(210) |
2,192 |
(2,402) |
|
109.6 |
% |
|||||||
Interest expense, net |
|
(4,393) |
(2,700) |
|
(1,693) |
|
62.7 |
% |
|||||
Bargain purchase gain |
— |
13,352 |
(13,352) |
|
NM |
||||||||
Tax receivable agreements expense |
(38,187) |
— |
(38,187) |
|
NM |
||||||||
Other |
|
2,424 |
4,718 |
|
(2,294) |
|
NM |
||||||
Income before income tax benefit (expense) |
|
20,823 |
|
56,724 |
|
(35,901) |
|
(63.3) |
% |
||||
Income tax benefit (expense) |
|
60,196 |
|
(957) |
|
61,153 |
|
(6390.1) |
% |
||||
Equity in losses of unconsolidated entities |
(1,800) |
|
(913) |
|
(887) |
|
NM |
||||||
Net income |
$ |
79,219 |
$ |
54,854 |
$ |
24,365 |
|
44.4 |
% |
||||
Revenue
Our revenue increased $197.9 million, or 14.3%, to $1.6 billion for the year ended December 31, 2023, compared to $1.4 billion for the year ended December 31, 2022. The increase was composed of an $88.4 million increase in Water Services revenue, a $104.7 million increase in Water Infrastructure revenue and a $4.8 million increase in Chemical Technologies revenue. These increases were driven primarily by higher demand for our services
72
coupled with increased pricing in comparison to the year ended December 31, 2022. Included in the increases in Water Services and Water Infrastructure were incremental revenue contributions from the Breakwater, Nuverra, Cypress and other asset acquisitions. For the year ended December 31, 2023, our Water Services, Water Infrastructure and Chemical Technologies revenues constituted 65.2%, 14.5% and 20.3% of our total revenue, respectively, compared to 68.1%, 9.0% and 22.9%, respectively, for the year ended December 31, 2022. The revenue changes by reportable segment are as follows:
Water Services. Revenue increased $88.4 million, or 9.4%, to $1.0 billion for the year ended December 31, 2023, compared to $944.5 million for the year ended December 31, 2022. The increase was primarily attributable to incremental revenue contributions from the Breakwater acquisition and higher demand for our services coupled with increased pricing in comparison to the year ended December 31, 2022. The increase in demand was due to market activity increases across most of our areas of operations, market share gains in the Permian Basin in our poly and containment business line and new service offerings in our accommodations and rentals business line.
Water Infrastructure. Revenue increased by $104.7 million, or 83.6%, to $230.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2023, compared to $125.3 million for the year ended December 31, 2022. The increase was primarily attributable to incremental revenue contributed by Breakwater, Nuverra, Cypress and other asset acquisitions. Revenue during the year ended December 31, 2023 also benefitted by the ramp-up of recycling and treatment operations associated with two long-term agreements in the Rockies region and one long-term agreement in the Permian region.
Chemical Technologies. Revenue increased $4.8 million, or 1.5%, to $322.5 million for the year ended December 31, 2023 compared to $317.6 million for the year ended December 31, 2022. The increase was primarily attributable to higher demand for our services in comparison to the year ended December 31, 2022 and was not directly impacted by acquisition activity.
Costs of Revenue
Costs of revenue increased $127.0 million, or 10.4%, to $1.4 billion for the year ended December 31, 2023, compared to $1.2 billion for the year ended December 31, 2022. The increase was comprised of a $50.0 million increase in Water Services costs and a $55.3 million increase in Water Infrastructure costs due to supporting the higher revenue-producing activity discussed above partially offset by a $3.6 million decrease in Chemical Technologies costs. Depreciation and amortization expense also increased by $25.3 million.
Water Services. Costs of revenue increased $50.0 million, or 6.5%, to $814.6 million for the year ended December 31, 2023, compared to $764.6 million for the year ended December 31, 2022. Cost of revenue as a percent of revenue decreased to 78.9% from 80.9%, due primarily to higher pricing for our services and economies of scale from higher revenue activity.
Water Infrastructure. Costs of revenue increased $55.3 million, or 66.6%, to $138.2 million for the year ended December 31, 2023, compared to $82.9 million for the year ended December 31, 2022. Cost of revenue as a percent of revenue decreased to 60.1% from 66.2%, due primarily to increased water treatment and recycling margins, which were favorably impacted by the Breakwater acquisition and the ramp-up of three long-term treatment and recycling agreements.
Chemical Technologies. Costs of revenue decreased $3.6 million, or 1.3%, to $262.1 million for the year ended December 31, 2023, compared to $265.6 million for the year ended December 31, 2022. Cost of revenue as a percent of revenue decreased to 81.3% from 83.6%, due primarily to realizing additional higher-margin market share within our portfolio of products as well as manufacturing process efficiencies.
Depreciation and Amortization. Depreciation and amortization expense increased $25.3 million, or 22.3%, to $138.8 million for the year ended December 31, 2023, compared to $113.5 million for the year ended December 31, 2022, due primarily to a higher fixed asset base related to the Breakwater acquisition and investments in pipeline and recycling infrastructure in our Water Infrastructure segment.
73
Gross Profit
Gross profit was $231.7 million for the year ended December 31, 2023 compared to $160.8 million for the year ended December 31, 2022. Gross profit increased by $38.4 million in our Water Services segment, $49.4 million in our Water Infrastructure segment and $8.4 million in our Chemical Technologies segment. Partially offsetting the increase in gross profit was a $25.3 million increase in depreciation and amortization expense. Gross margin as a percent of revenue was 14.6% and 11.6% during the years ended December 31, 2023 and December 31, 2022, respectively.
Selling, General and Administrative Expenses
Selling, general and administrative expenses increased $36.6 million, or 30.8%, to $155.5 million for the year ended December 31, 2023, compared to $118.9 million for the year ended December 31, 2022. The increase was due primarily to $14.7 million in rebranding costs, $9.5 million in higher wages, associated payroll taxes and employer 401(k) match contributions, a $6.6 million increase in legal and professional fees, a $3.2 million increase in bad debt expense, a $3.0 million increase in incentive and equity-based compensation cost, $2.0 million in higher contract labor, $1.9 million in higher information technology costs, and $1.8 million from a combination of other expenses partially offset by a $3.0 million decrease in transaction costs, a $2.4 million decrease in vehicle lease costs, and a $0.6 million decrease in insurance costs.
Impairments and Abandonments
We recorded $11.1 million of trademark abandonment in the Chemical Technologies segment during the year ended December 31, 2023. Also, we recorded $1.4 million of abandonment that was primarily attributable to abandoned property and equipment and $0.1 million of impairment in our Water Services segment to write-off the remaining value of a cost-method investment. We did not record any impairments and abandonments during the year ended December 31, 2022.
Net Interest Expense
Net interest expense increased by $1.7 million, or 62.7%, to $4.4 million for the year ended December 31, 2023, compared to $2.7 million for the year ended December 31, 2022, due primarily to higher average borrowings on our Sustainability-Linked Credit Facility and higher interest rates during the year ended December 31, 2023 prior to repaying such borrowings.
Bargain Purchase Gain
A bargain purchase gain of $13.4 million in 2022 was comprised of $6.7 million related to the Nuverra acquisition and $6.7 million in adjustments related to acquisitions that occurred in 2021. The Nuverra acquisition resulted in a bargain purchase gain as Nuverra was experiencing financial distress and actively evaluating strategic alternatives leading up to the transaction. We did not record any bargain purchase gain during the year ended December 31, 2023.
Tax Receivable Agreements Expense
As of December 31, 2023, we determined that we were in a position to reasonably estimate the amount of the liability associated with the Tax Receivable Agreements and determined that future payment under the terms of the Tax Receivable Agreements were probable, and therefore recorded expense of $38.2 million as of December 31, 2023.
Other
Other income was $2.4 million for the year ended December 31, 2023, compared to $4.7 million for the year ended December 31, 2022. The $2.3 million decrease is primarily due to the removal of the $1.1 million UltRecovery contingent consideration liability in 2022.
74
Net Income
Net Income increased by $24.4 million, to a net income of $79.2 million for the year ended December 31, 2023 compared to $54.9 million for the year ended December 31, 2022, driven primarily by the release of a valuation allowance associated with deferred tax assets, increased revenue with improved margins, including contributions from our recent acquisitions, partially offset by tax receivable agreements expense, an increase in selling, general and administrative expenses and the abandonment costs referenced above.
Comparison of Non-GAAP Financial Measures
We view EBITDA and Adjusted EBITDA as important indicators of performance. We define EBITDA as net income (loss), plus interest expense, income taxes, and depreciation and amortization. We define Adjusted EBITDA, as EBITDA plus/(minus) loss/(income) from discontinued operations, plus any impairment and abandonment charges or asset write-offs pursuant to GAAP, plus non-cash losses on the sale of assets or subsidiaries, non-recurring compensation expense, non-cash compensation expense, and non-recurring or unusual expenses or charges, including severance expenses, transaction costs, or facilities-related exit and disposal-related expenditures, plus/(minus) foreign currency losses/(gains), plus/(minus) losses/(gains) on unconsolidated entities and plus tax receivable agreements expense less bargain purchase gains from business combinations. The adjustments to EBITDA are generally consistent with such adjustments described in our Sustainability-Linked Credit Facility. See “—Note Regarding Non-GAAP Financial Measures” for more information and a reconciliation of EBITDA and Adjusted EBITDA to net income (loss), the most directly comparable financial measure calculated and presented in accordance with GAAP.
Our board of directors, management and investors use EBITDA and Adjusted EBITDA to assess our financial performance because it allows them to compare our operating performance on a consistent basis across periods by removing the effects of our capital structure (such as varying levels of interest expense), asset base (such as depreciation and amortization) and items outside the control of our management team. We present EBITDA and Adjusted EBITDA because we believe they provide useful information regarding the factors and trends affecting our business in addition to measures calculated under GAAP.
Note Regarding Non-GAAP Financial Measures
EBITDA and Adjusted EBITDA are not financial measures presented in accordance with GAAP. We believe that the presentation of these non-GAAP financial measures will provide useful information to investors in assessing our financial performance and results of operations. Net income is the GAAP measure most directly comparable to EBITDA and Adjusted EBITDA. Our non-GAAP financial measures should not be considered as alternatives to the most directly comparable GAAP financial measure. Each of these non-GAAP financial measures has important limitations as an analytical tool due to the exclusion of some but not all items that affect the most directly comparable GAAP financial measures. One should not consider EBITDA or Adjusted EBITDA in isolation or as substitutes for an analysis of our results as reported under GAAP. Because EBITDA and Adjusted EBITDA may be defined differently by other companies in our industry, our definitions of these non-GAAP financial measures may not be comparable to similarly titled measures of other companies, thereby diminishing their utility.
75
The following table sets forth our reconciliation of EBITDA and Adjusted EBITDA to our net (loss) income, which is the most directly comparable GAAP measure, for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022. The reconciliation of EBITDA and Adjusted EBITDA for the years ended December 31, 2022 and 2021 is set forth in Part II, Item 7 of our Annual Report on Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2022 under the caption “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations.”
Year ended December 31, |
||||||
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|||
Net income |
$ |
79,219 |
$ |
54,854 |
||
Interest expense, net |
4,393 |
2,700 |
||||
Income tax (benefit) expense |
(60,196) |
957 |
||||
Depreciation and amortization |
141,089 |
115,716 |
||||
EBITDA |
164,505 |
174,227 |
||||
Tax receivable agreements expense |
38,187 |
— |
||||
Non-cash compensation expenses |
17,369 |
15,570 |
||||
Non-cash loss on sale of assets or subsidiaries(1) |
3,350 |
4,400 |
||||
Transaction and rebranding costs(2) |
20,447 |
11,672 |
||||
Lease abandonment costs |
42 |
449 |
||||
Impairments and abandonments |
12,607 |
— |
||||
Bargain purchase gain |
— |
(13,352) |
||||
Equity in losses of unconsolidated entities |
1,800 |
913 |
||||
Other |
6 |
926 |
||||
Adjusted EBITDA |
$ |
258,313 |
$ |
194,805 |
||
(1) |
For all periods presented, the losses were primarily due to sales of real estate and underutilized, excess or obsolete property and equipment. |
(2) |
For all periods presented, these costs were primarily legal-related due diligence costs as well as costs related to certain acquired subsidiaries and rebranding costs. |
EBITDA was $164.5 million for the year ended December 31, 2023 compared to $174.2 million for the year ended December 31, 2022. The $9.7 million decrease in EBITDA was driven primarily by $38.2 million in tax receivable agreements expense in 2023, a $36.6 million increase in selling, general and administrative expense in 2023, a $13.4 million bargain purchase gain in 2022 and abandonment costs of $12.6 million in 2023 partially offset by an increase of $96.2 million in gross profit. Adjusted EBITDA was $258.3 million for the year ended December 31, 2023 compared to $194.8 million for the year ended December 31, 2022. The $63.5 million increase is primarily attributable to the items discussed above.
Liquidity and Capital Resources
Overview
Our primary sources of liquidity are cash on hand, borrowing capacity under the Sustainability-Linked Credit Facility, cash flows from operations and proceeds from the sale of excess property and equipment. Our primary uses of capital have been to fund current operations, maintain our asset base, implement technological advancements, make capital expenditures to support organic growth, fund acquisitions and minority investments, pay dividends and distributions, and when appropriate, repurchase shares of Class A common stock in the open market. Depending on available opportunities, market conditions and other factors, we may also issue debt and equity securities, in the future, if needed.
As of December 31, 2023, we had no outstanding bank debt. We prioritize sustained positive free cash flow and a strong balance sheet, and evaluate potential acquisitions and investments in the context of those priorities, in addition to the economics of the opportunity. We believe this approach provides us with additional flexibility to evaluate larger investments as well as improved resilience in a sustained downturn versus many of our peers.
76
Based on our current cash and cash equivalents balance, operating cash flow, available borrowings under our Sustainability-Linked Credit Facility and the ongoing actions discussed above, we believe that we will be able to maintain sufficient liquidity to satisfy our obligations and remain in compliance with our existing debt covenants through the next twelve months and beyond, prior to giving effect to any future financing that may occur.
We intend to finance most of our capital expenditures, contractual obligations and working capital needs with cash on hand, cash generated from operations and borrowings under our Sustainability-Linked Credit Facility. For a discussion of the Sustainability-Linked Credit Facility, see “—Sustainability-Linked Credit Facility” below. Although we cannot provide any assurance, we believe that our current cash balance, operating cash flow and available borrowings under our Sustainability-Linked Credit Facility will be sufficient to fund our operations for at least the next twelve months.
During the fourth quarter of 2022, we initiated a quarterly dividend and distribution program of $0.05 per share and $0.05 per unit for holders of Class A and Class B shares, respectively. We paid quarterly dividends at the same rate through the third quarter of 2023, then the board of directors increased the quarterly dividend paid on November 17, 2023 to $0.06 per share and $0.06 per unit for holders of Class A and Class B shares, respectively. This program resulted in a financing outflow of $24.9 million and $6.0 million during the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022, respectively. This quarterly dividend program is expected to continue into 2024 and beyond. All future dividend payments are subject to quarterly review and approval by our board of directors.
As of December 31, 2023, cash and cash equivalents totaled $57.1 million and we had approximately $250.3 million of available borrowing capacity under our Sustainability-Linked Credit Facility. As of December 31, 2023, the borrowing base under the Sustainability-Linked Credit Facility was $267.4 million, we had zero in outstanding borrowings, and outstanding letters of credit totaled $17.1 million. As of February 19, 2024, we had $55.0 million in outstanding indebtedness, the borrowing base under the Sustainability-Linked Credit Facility was $218.4 million, the outstanding letters of credit totaled $17.1 million, and the available borrowing capacity under the Sustainability-Linked Credit Facility was $146.3 million.
In 2022, our trade accounts receivable experienced a notable surge, rising from $232.8 million to $430.0 million. This increase was attributed to multiple factors, including the growth in our revenue, the addition of receivables from acquired entities, and the complexities encountered during the integration of these acquisitions. During 2023, in parallel with integration efforts related to previously acquired companies, we implemented enhancements to our billing and collection processes, yielding tangible benefits. These improvements resulted in a more efficient management of our working capital, thereby augmenting our generation of cash. This increased cash flow provides us with greater flexibility to reinvest in our business or return capital to our shareholders.
As of December 31, 2023, we had no material off-balance sheet arrangements. As such, we are not exposed to any material financing, liquidity, market or credit risk that could arise if we had engaged in such financing arrangements.
Our contractual obligations include, among other things, our Sustainability-Linked Credit Facility and operating leases. Refer to “Note 6—Leases” for operating lease obligations as of December 31, 2023 and “Note 10—Debt” for an update to our Sustainability-Linked Credit Facility as of December 31, 2023.
77
Cash Flows
The following table summarizes our cash flows for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022. The summary of our cash flows for the years ended December 31, 2022 and 2021 is set forth in Part II, Item 7 of our Annual Report on Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2022 under the caption “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations.”
Cash Flow Changes Between the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
Year ended December 31, |
Change |
|||||||||||
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
Dollars |
|
Percentage |
|||||
(in thousands) |
||||||||||||
Net cash provided by operating activities |
$ |
285,355 |
$ |
33,231 |
$ |
252,124 |
758.7 |
% |
||||
Net cash used in investing activities |
(137,168) |
(53,246) |
(83,922) |
(157.6) |
% |
|||||||
Net cash used in financing activities |
(98,423) |
(58,451) |
(39,972) |
(68.4) |
% |
|||||||
Subtotal |
49,764 |
(78,466) |
||||||||||
Effect of exchange rate changes on cash and cash equivalents |
(3) |
(13) |
10 |
NM |
||||||||
Net increase (decrease) in cash and cash equivalents |
$ |
49,761 |
$ |
(78,479) |
||||||||
Operating Activities. Net cash provided by operating activities was $285.4 million for the year ended December 31, 2023, compared to $33.2 million for the year ended December 31, 2022. The $252.1 million improvement is comprised of an increase of $64.5 million of net income combined with non-cash adjustments and $187.6 million of decreased working capital primarily due to collecting trade receivables favorably impacted by improvements in the billing and collection process. These trade receivables were previously elevated due to the factors noted above.
Investing Activities. Net cash used in investing activities was $137.2 million for the year ended December 31, 2023, compared to $53.2 million for the year ended December 31, 2022. The $83.9 million increase in net cash used in investing activities was due primarily to a $64.0 million increase in purchases of property and equipment, a $14.4 million decrease in proceeds received from sales of property and equipment and an increase of $10.7 million spent for acquisitions, net of cash and restricted cash received partially offset by a decrease of $7.2 million in investments made in non-controlled entities.
Financing Activities. Net cash used in financing activities was $98.4 million for the year ended December 31, 2023, compared to $58.5 million for the year ended December 31, 2022. The $40.0 million increase in net cash used in financing activities was due primarily to a $41.6 million increase in repurchases of shares of Class A common stock, an $18.9 million increase in dividends paid and debt repayments net of borrowings increasing $9.9 million partially offset by a $22.0 million purchase of noncontrolling interests in 2022 resulting in 100% ownership of the Big Spring Recycling System, which includes significant pipeline, storage, recycling and disposal infrastructure assets in the Midland Basin, $6.3 million of cash received net of cash paid from/to noncontrolling interest holders during the year ended December 31, 2023, and $2.1 million in debt issuance costs paid during the year ended December 31, 2022.
Sustainability-Linked Credit Facility
On March 17, 2022 (the “Restatement Date”), SES Holdings and Select Water Solutions, LLC (“Select LLC”), formerly Select Energy Services, LLC and a wholly-owned subsidiary of SES Holdings, entered into a $270.0 million amended and restated senior secured sustainability-linked revolving credit facility (the “Sustainability-Linked Credit Facility”), by and among SES Holdings, as parent, Select LLC, as borrower and certain of SES Holdings’ subsidiaries, as guarantors, each of the lenders party thereto and Wells Fargo Bank, N.A., as administrative agent, issuing lender and swingline lender (the “Administrative Agent”) (which amended and restated the Prior Credit Agreement dated November 1, 2017). The Sustainability-Linked Credit Facility also has a sublimit of $40.0 million for letters of credit and a sublimit of $27.0 million for swingline loans. Subject to obtaining commitments from existing or new lenders, Select LLC has the option to increase the maximum amount under the senior secured credit facility by $135.0 million during the first three years following the Restatement Date.
78
Our Sustainability-Linked Credit Facility also contains a sustainability adjustments feature that could result in up to a 0.05% increase or reduction to the effective interest rate pursuant to an Applicable Sustainability Margin Adjustment depending on Select LLC’s ability to meet certain sustainability targets and thresholds starting in 2022. For each calendar year, the “Applicable Sustainability Margin Adjustment” will equal the number of basis points (whether positive, negative or zero) equal to the sum of (i) the Applicable Water Stewardship Fee Adjustment plus (ii) Applicable Health and Safety Fee Adjustment (each as defined in the Sustainability-Linked Credit Facility.
The “Applicable Water Stewardship Fee Adjustment" is based on Select LLC’s ability to (i) remain above the Water Stewardship Threshold and (ii) reach the Water Stewardship Target, both metrics which are measured by the total number of barrels of recycled produced water recycled by SES Holdings and its Subsidiaries. The “Applicable Employee Health and Safety Fee Adjustment" is based on Select LLC’s ability to (i) remain above the Employee Health and Safety Threshold and (ii) reach the Employee Health and Safety Target, both metrics which are measured by the total recordable incident rates of employees with respect to SES Holdings and its Subsidiaries.
Refer to “Note 10—Debt” for further discussion of the Sustainability-Linked Credit Facility.
Critical Accounting Policies and Estimates
The preparation of consolidated financial statements in conformity with GAAP requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and disclosures about any contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the financial statements and the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting period. Actual results could differ from those estimates. Our critical accounting policies are described below to provide a better understanding of how we develop our assumptions and judgments about future events and related estimations and how they can impact our financial statements. The following accounting policies involve critical accounting estimates because they are dependent on our judgment and assumptions about matters that are inherently uncertain.
We base our estimates on historical experience and on various other assumptions we believe to be reasonable according to the current facts and circumstances, the results of which form the basis for making judgments about the carrying values of assets and liabilities that are not readily apparent from other sources. Estimates and assumptions about future events and their effects are subject to uncertainty and, accordingly, these estimates may change as new events occur, as more experience is acquired, as additional information is obtained, and as the business environment in which we operate changes. We believe the current assumptions, judgments and estimates used to determine amounts reflected in our consolidated financial statements are appropriate, however, actual results may differ under different conditions. This discussion and analysis should be read in conjunction with our consolidated financial statements and related notes included in this Annual Report.
Other intangible assets: The purchase price of acquired businesses is allocated to its identifiable assets and liabilities based upon estimated fair values as of the acquisition date. Other intangible assets are initially recorded at their fair values. Other intangible assets not subject to amortization are tested for impairment annually or more frequently if events or changes in circumstances indicate that the asset might be impaired. Intangible assets with finite useful lives are amortized either on a straight-line basis over the asset’s estimated useful life or on a basis that reflects the pattern in which the economic benefits of the intangible assets are realized.
Impairment of long-lived assets and intangible assets: Long-lived assets, such as property and equipment and finite-lived intangible assets, are evaluated for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that their carrying value may not be recoverable. Recoverability is measured by a comparison of their carrying amount to the estimated undiscounted cash flows to be generated by those assets. If the undiscounted cash flows are less than the carrying amount, we record impairment losses for the excess of their carrying value over the estimated fair value. Fair value is determined, in part, by the estimated cash flows to be generated by those assets. Our cash flow estimates are based upon, among other things, historical results adjusted to reflect our best estimate of future market rates, utilization levels, and operating performance. Development of future cash flows also requires management to make assumptions and to apply judgment, including the timing of future expected cash flows, using the appropriate discount rates and determining salvage values. The estimate of fair value represents our best estimates of these factors based on current
79
industry trends and reference to market transactions and is subject to variability. Assets are generally grouped at the lowest level of identifiable cash flows. We operate within the oilfield service industry, and the cyclical nature of the oil and gas industry that we serve and our estimates of the period over which future cash flows will be generated, as well as the predictability of these cash flows, can have a significant impact on the estimated fair value of these assets and, in periods of prolonged down cycles, may result in impairment charges. Changes to our key assumptions related to future performance, market conditions and other economic factors could adversely affect our impairment valuation.
Retentions: We assume risk of loss through deductibles and self-insured retentions, up to certain levels for losses related to general liability, workers’ compensation and employer’s liability, vehicle liability, and health insurance. Our exposure (i.e., the self-insured retention or deductible) per occurrence is $0.5 million for general liability, $0.25 million for workers’ compensation and employer’s liability, $0.25 million for auto liability and $0.3 million for health insurance. We also have an excess loss policy over these coverages with a limit of $100.0 million in the aggregate. Management reviews its estimates of reported and unreported claims and provides for losses through reserves. We use actuarial estimates to record our liability for future periods. If the number of claims or the costs associated with those claims were to increase significantly over our estimates, additional charges to earnings could be necessary to cover required payments. As of December 31, 2023, we estimate the range of exposure to be from $16.2 million to $19.2 million and have recorded liabilities of $17.3 million, which represents management’s best estimate of probable loss related to workers’ compensation and employer’s liability, and auto liability. Additionally, as of December 31, 2023, accrued health insurance and accrued general liabilities were $6.7 million and $1.3 million, respectively.
Tax Receivable Agreements: We intend to fund any obligation under the Tax Receivable Agreements with cash from operations or borrowings under our Sustainability-Linked Credit Facility. With respect to obligations under each of our Tax Receivable Agreements (except in cases where we elect to terminate the Tax Receivable Agreements early, the Tax Receivable Agreements are terminated early due to certain mergers or other changes of control or we have available cash but fail to make payments when due), generally we may elect to defer payments due under the Tax Receivable Agreements if we do not have available cash to satisfy our payment obligations under the Tax Receivable Agreements or if our contractual obligations limit our ability to make these payments. Any such deferred payments under the Tax Receivable Agreements generally will accrue interest.
We account for any amounts payable under the Tax Receivable Agreements in accordance with Accounting Standards Codification (“ASC”) Topic 450, Contingencies. For a discussion regarding an acceleration
of the amounts payable under the Tax Receivable Agreements if we elect to terminate the Tax Receivable Agreements
early or they are terminated early due to our failure to honor a material obligation thereunder or due to certain mergers,
asset sales, other forms of business combinations or other changes of control and the potential impact of such an acceleration and the potential impact of such acceleration, please read Part I, Item 1A. “Risk Factors – Risks Related to Our Organizational Structure. In certain cases, payments under the Tax Receivable Agreements may be accelerated and/or significantly exceed the actual benefits, if any, we realize in respect of the tax attributes subject to the Tax Receivable Agreements.
We have assessed the amount of any liability under the Tax Receivable Agreements required under the provisions of ASC 450 in connection with preparing the consolidated financial statements. As of December 31, 2023, we determined that we were in a position to reasonably estimate an amount of liability associated with the Tax Receivable Agreements and determined that future payments under the terms of the Tax Receivable Agreements were probable, and therefore recorded liabilities of $38.2 million as of December 31, 2023. Prior to this, we had determined that we were not in a position to reasonably estimate such amount and that future payments were not probable. The projection of future taxable income and utilization of tax attributes associated with the Tax Receivable Agreements involve estimates which require significant judgment. The amount of the Company’s actual taxable income, passage of future legislation, or consummation of significant transactions in the future may significantly impact the liability related to the Tax Receivable Agreements.
Realizability of Deferred Tax Assets: We establish valuation allowances when necessary to reduce deferred tax assets to the amounts more likely than not to be realized. Deferred income tax assets are evaluated quarterly to determine if valuation allowances are required or should be adjusted. The ability to realize deferred tax assets depends on the ability to generate sufficient taxable income within the carryback or carryforward periods provided for in the tax law for
80
each applicable tax jurisdiction. The assessment regarding whether a valuation allowance is required or should be adjusted is based on an evaluation of possible sources of taxable income and also considers all available positive and negative evidence factors. Our accounting for the realization of deferred tax assets incorporates, amongst other factors, our best estimate of future events. Changes in our current estimates, due to unanticipated market conditions, governmental legislative actions or events, could have a material effect on our ability to utilize deferred tax assets. As of December 31, 2023, valuation allowances against deferred tax assets were $112 million. See “Note 15—Income Taxes” for additional information.
Recent Accounting Pronouncements
Refer to “Note 2—Significant Accounting Policies” for recent accounting pronouncements.
ITEM 7A. QUANTITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE DISCLOSURES ABOUT MARKET RISK
The demand, pricing and terms for oilfield services provided by us are largely dependent upon the level of drilling and completion activity in the U.S. oil and gas industry as well as the level of oil and gas production. The level of drilling and completion activity is influenced by numerous factors over which we have no control, including, but not limited to: the supply of and demand for oil and gas; war, armed conflicts, economic sanctions and other constraints to global trade and economic growth; current price levels as well as expectations about future prices of oil and gas; the magnitude and timing of capital spending by our customers; the cost of exploring for, developing, producing and delivering oil and gas; the extent to which our E&P customers choose to drill and complete new wells to offset decline from their existing wells; the extent to which our E&P customers choose to invest to grow production; discoveries of new oil and gas reserves; available storage capacity and pipeline and other transportation capacity; weather conditions; domestic and worldwide economic conditions; political instability in oil-producing countries; environmental regulations; technical advances in alternative forms of energy (e.g. wind and solar electricity, electric vehicles) that encourage substitution for or displacement of oil and gas consumption in end-use markets; the price and availability of alternative fuels; the ability of oil and gas producers to raise equity capital and debt financing; global health events; merger and acquisition activity and consolidation in our industry, and other factors.
Any combination of these factors that results in sustained low oil and gas prices and, therefore, lower capital spending and / or reduced drilling and completion activity by our customers, would likely have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations and cash flows.
Interest Rate Risk
As of December 31, 2023, we did not have any indebtedness under our Sustainability-Linked Credit Facility. As of February 19, 2024, we had $55.0 million in outstanding indebtedness and $146.3 million of available borrowing capacity under our Sustainability-Linked Credit Facility. Interest is calculated under the terms of our Sustainability-Linked Credit Facility based on our selection, from time to time, of one of the index rates available to us plus an applicable margin that varies based on certain factors. We do not currently have or intend to enter into any derivative arrangements to protect against fluctuations in interest rates applicable to our outstanding indebtedness.
ITEM 8. FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AND SUPPLEMENTARY DATA
The report of our independent registered public accounting firm and our consolidated financial statements and supplementary data are included in this Annual Report beginning on page F-1.
ITEM 9. CHANGES IN AND DISAGREEMENTS WITH ACCOUNTANTS ON ACCOUNTING AND FINANCIAL DISCLOSURE
None.
81
ITEM 9A. CONTROLS AND PROCEDURES
Disclosure Controls and Procedures
We maintain disclosure controls and procedures that are designed to provide reasonable assurance that information required to be disclosed by us in reports that we file or submit under the Exchange Act is recorded, processed, summarized and reported within the time periods specified in the SEC's rules and forms, and that such information is accumulated and communicated to our management, including our chief executive officer ("CEO") (principal executive officer) and chief financial officer ("CFO") (principal financial officer), as appropriate, to allow for timely decisions regarding required disclosure. In designing and evaluating the disclosure controls and procedures, management recognizes that any controls and procedures, no matter how well-designed and operated, can provide only reasonable assurance of achieving the desired control objectives, and management is required to apply its judgment in evaluating the cost-benefit relationship of possible controls and procedures.
As required by SEC Rule 13a-15(b), we carried out an evaluation, under the supervision and with the participation of our management, including our CEO and CFO, of the effectiveness of our disclosure controls and procedures as of December 31, 2023. Based on their evaluation, the Company's CEO and CFO have concluded that the Company's disclosure controls and procedures were effective at a reasonable level of assurance as of December 31, 2023.
Management’s Annual Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting
Our management is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting. Internal control over financial reporting is defined in Rule 13a-15(f) and 15d-15(f) promulgated under the Exchange Act as a process designed by, or under the supervision of, our principal executive and principal financial officers, or persons performing similar functions, and effected by our board of directors, management and other personnel, to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
Under the supervision and with the participation of management, including the CEO and CFO, the Company conducted an evaluation of the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting based on the framework in “Internal Control – Integrated Framework (2013)” issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (“COSO”). Based on this assessment, our management concluded that our internal control over financial reporting was effective as of December 31, 2023. Grant Thornton LLP, an independent registered public accounting firm, audited the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2023.
Changes in Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
There were no changes in our internal control over financial reporting (as defined in Exchange Act Rule 13a-15(f)) during the quarter ended December 31, 2023 which materially affected, or are reasonably likely to materially affect, our internal control over financial reporting.
82
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
Board of Directors and Shareholders
Select Water Solutions, Inc.
Opinion on internal control over financial reporting
We have audited the internal control over financial reporting of Select Water Solutions, Inc. (formerly known as Select Energy Services, Inc.) (a Delaware corporation) and subsidiaries (the “Company”) as of December 31, 2023, based on criteria established in the 2013 Internal Control—Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (“COSO”). In our opinion, the Company maintained, in all material respects, effective internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2023, based on criteria established in the 2013 Internal Control—Integrated Framework issued by COSO.
We also have audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (“PCAOB”), the consolidated financial statements of the Company as of and for the year ended December 31, 2023, and our report dated February 21, 2024 expressed an unqualified opinion on those financial statements.
Basis for opinion
The Company’s management is responsible for maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting and for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting, included in the accompanying Management’s Annual Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company’s internal control over financial reporting based on our audit. We are a public accounting firm registered with the PCAOB and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audit in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether effective internal control over financial reporting was maintained in all material respects. Our audit included obtaining an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, assessing the risk that a material weakness exists, testing and evaluating the design and operating effectiveness of internal control based on the assessed risk, and performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe that our audit provides a reasonable basis for our opinion.
Definition and limitations of internal control over financial reporting
A company’s internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. A company’s internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (1) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company; (2) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company; and (3) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the company’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
/s/ GRANT THORNTON LLP
Dallas, Texas
February 21, 2024
83
Item 9B. |
Other Information |
Item 9C. |
Disclosure Regarding Foreign Jurisdictions that Prevent Inspections |
None.
PART III
ITEM 10.DIRECTORS, EXECUTIVE OFFICERS AND CORPORATE GOVERNANCE
The information required in response to this Item 10 will be set forth in our definitive proxy statement for the 2024 annual meeting of stockholders and is incorporated herein by reference.
ITEM 11.EXECUTIVE COMPENSATION
The information required in response to this Item 11 will be set forth in our definitive proxy statement for the 2024 annual meeting of stockholders and is incorporated herein by reference.
ITEM 12. |
SECURITY OWNERSHIP OF CERTAIN BENEFICIAL OWNERS AND MANAGEMENT AND RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS |
The information required in response to this Item 12 will be set forth in our definitive proxy statement for the 2024 annual meeting of stockholders and is incorporated herein by reference.
ITEM 13. |
CERTAIN RELATIONSHIPS AND RELATED TRANSACTIONS, AND DIRECTOR INDEPENDENCE |
The information required in response to this Item 13 will be set forth in our definitive proxy statement for the 2024 annual meeting of stockholders and is incorporated herein by reference.
ITEM 14.PRINCIPAL ACCOUNTING FEES AND SERVICES
The information required in response to this Item 14 will be set forth in our definitive proxy statement for the 2024 annual meeting of stockholders and is incorporated herein by reference.
PART IV
ITEM 15.EXHIBIT AND FINANCIAL STATEMENT SCHEDULES
(a)(1) and (a)(2) Financial Statements and Financial Statement Schedules
Our consolidated financial statements are incorporated under Part II, Item 8. “Financial Statements and Supplementary Data” of this Annual Report. For a listing of these statements and accompanying notes, see “Index to Financial Statements” on Page F-1 of this Annual Report.
(a)(3) Exhibits
The exhibits required to be filed or furnished under Item 15 of this Annual Report are set forth below in the Exhibit Index included within this Annual Report.
84
EXHIBIT INDEX
|
|
||
|
Exhibit Number |
|
Description |
3.1 |
||
3.2 |
||
4.1 |
||
4.2 |
||
*4.3 |
||
10.1 |
||
†10.2 |
||
†10.3 |
||
†10.4 |
||
†10.5 |
||
†10.6 |
||
†10.7 |
||
85
10.8 |
||
10.9 |
||
10.10 |
||
10.11 |
||
10.12 |
||
10.13 |
||
†10.14 |
||
†10.15 |
||
†10.16 |
||
†10.17 |
||
†10.18 |
||
†10.19 |
||
†10.20 |
||
86
†10.21 |
||
†10.22 |
||
†10.23 |
||
†10.24 |
||
†10.25 |
||
†10.26 |
||
†10.27 |
||
†10.28 |
||
†10.29 |
||
†10.30 |
||
†10.31 |
||
†10.32 |
||
87
†10.33 |
||
†10.34 |
||
†10.35 |
||
10.36 |
||
10.37 |
||
*21.1 |
||
*23.1 |
||
*31.1 |
Certification of the Chief Executive Officer Pursuant to Rule 13a-14(a)/15d-14(a). |
|
*31.2 |
Certification of the Chief Financial Officer Pursuant to Rule 13a-14(a)/15d-14(a). |
|
*32.1 |
||
*32.2 |
||
*97.1 |
||
*101 |
Interactive Data Files |
|
*101.INS |
iXBRL Instance Document. |
|
*101.SCH |
iXBRL Taxonomy Extension Schema Document. |
|
*101.CAL |
iXBRL Taxonomy Extension Calculation Linkbase Document. |
|
*101.DEF |
iXBRL Taxonomy Extension Definition Linkbase Document. |
|
*101.LAB |
iXBRL Taxonomy Extension Label Linkbase Document. |
|
*101.PRE |
iXBRL Taxonomy Extension Presentation Linkbase Document. |
|
*101 |
The following materials from Select Water Solutions, Inc.’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2023 formatted in iXBRL (Inline eXtensible Business Reporting Language): (i) Consolidated Balance Sheets; (ii) Consolidated Statements of Operations; (iii) Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Income (Loss); (iv) Consolidated Statements of Changes in Equity; (v) Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows; and (vi) Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements. |
|
104 |
104 Cover Page Interactive Data File (formatted as inline XBRL and contained in Exhibit 101). |
* |
Filed or furnished with this Annual Report on Form 10-K. |
† |
Management contract or compensatory plan or arrangement. |
88
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the Company has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized.
Select Water Solutions, Inc. |
|
Dated: February 21, 2024 |
/s/ JOHN D. SCHMITZ |
John D. Schmitz |
|
Chairman, President and Chief Executive Officer |
|
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the Company and in the capacities indicated on February 21, 2024.
/s/ JOHN D. SCHMITZ |
Chairman, President and Chief Executive Officer |
|
John D. Schmitz |
(Principal Executive Officer) |
|
/s/ NICK L. SWYKA |
Chief Financial Officer and Senior Vice President |
|
Nick L. Swyka |
(Principal Financial Officer) |
|
/s/ BRIAN P. SZYMANSKI |
Chief Accounting Officer |
|
Brian P. Szymanski |
(Principal Accounting Officer) |
|
/s/ TROY W. THACKER |
Director |
|
Troy W. Thacker |
||
/s/ ROBIN FIELDER |
Director |
|
Robin Fielder |
||
/s/ DOUGLAS J. WALL |
Director |
|
Douglas J. Wall |
||
/s/ RICHARD A. BURNETT |
Director |
|
Richard A. Burnett |
||
/s/ GAYLE BURLESON |
Director |
|
Gayle Burleson |
||
/s/ LUIS FERNANDEZ-MORENO |
Director |
|
Luis Fernandez-Moreno |
||
89
INDEX TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
SELECT WATER SOLUTIONS, INC.
|
|
Page(s) |
|
|
Select Water Solutions, Inc. |
|
|
|
|
Annual Financial Statements |
|
|
|
|
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm (PCAOB ID Number |
|
|
F-2 |
|
Consolidated Balance Sheets as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 |
|
|
F-4 |
|
Consolidated Statements of Operations for the Years Ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021 |
|
|
F-5 |
|
|
|
F-6 |
|
|
Consolidated Statements of Changes in Equity for the Years Ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021 |
|
|
F-7 |
|
Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows for the Years Ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021 |
|
|
F-8 |
|
|
|
F-9 |
|
|
F-1
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
Board of Directors and Shareholders
Select Water Solutions, Inc.
Opinion on the financial statements
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of Select Water Solutions, Inc. (formerly known as Select Energy Services, Inc.) (a Delaware corporation) and subsidiaries (the “Company”) as of December 31, 2023 and 2022, the related consolidated statements of operations, comprehensive income (loss), changes in equity, and cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2023, and the related notes (collectively referred to as the “financial statements”). In our opinion, the financial statements present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of the Company as of December 31, 2023 and 2022, and the results of its operations and its cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2023, in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America.
We also have audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (“PCAOB”), the Company’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2023, based on criteria established in the 2013 Internal Control—Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (“COSO”), and our report dated February 21, 2024 expressed an unqualified opinion.
Basis for opinion
These financial statements are the responsibility of the Company’s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company’s financial statements based on our audits. We are a public accounting firm registered with the PCAOB and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement, whether due to error or fraud. Our audits included performing procedures to assess the risks of material misstatement of the financial statements, whether due to error or fraud, and performing procedures that respond to those risks. Such procedures included examining, on a test basis, evidence regarding the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. Our audits also included evaluating the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall presentation of the financial statements. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
Critical audit matters
The critical audit matters communicated below are matters arising from the current period audit of the financial statements that were communicated or required to be communicated to the audit committee and that: (1) relate to accounts or disclosures that are material to the financial statements and (2) involved our especially challenging, subjective, or complex judgments. The communication of critical audit matters does not alter in any way our opinion on the financial statements, taken as a whole, and we are not, by communicating the critical audit matters below, providing separate opinions on the critical audit matters or on the accounts or disclosures to which they relate.
Realizability of deferred tax assets
As described further in Note 15 to the consolidated financial statements, deferred tax assets are reduced by a valuation allowance if, based on the evaluation of positive and negative evidence, in management’s judgment it is more likely than not that some portion, or all, of the deferred tax assets will not be realized. As of December 31, 2023, management concluded that sufficient positive evidence existed to release a portion of its valuation allowance related to its deferred tax assets, resulting in a deferred income tax benefit of $62 million for the year ended December 31, 2023. The assessment of the realizability of deferred tax assets requires management to make significant estimates and assumptions related to forecasts of future profitability. Changes in these assumptions could materially affect the assessment of the realizability of deferred tax assets and whether they are more likely than not to be realized in the future. We identified the realizability of deferred tax assets as a critical audit matter.
F-2
The principal consideration for our determination that the realizability of deferred tax assets is a critical audit matter is that management utilized significant judgment in determining that the net deferred tax assets are more likely than not to be realized in the future. In turn, auditing management’s judgments regarding the future realizability of deferred tax assets involved a high degree of subjectivity due to the estimation uncertainty of management’s significant judgments.
Our audit procedures related to the realizability of deferred tax assets included the following, among others:
| ● | We tested the design and operating effectiveness of internal controls over income taxes, including those over management’s deferred tax asset realizability assessment. |
| ● | With the assistance of individuals with specialized skills and knowledge in income taxes, we tested the completeness and accuracy of the underlying data used in management’s assessment, including the reasonableness of the method and significant assumptions used in the calculations. |
| ● | We evaluated the prospective financial information related to future profitability including consideration of: |
| - | the current and past performance of the Company |
| - | the consistency with external market and industry data |
| - | the consistency with evidence obtained in other areas of the audit. |
Measurement of the tax receivable agreement (“TRA”) liabilities
As described further in Note 14 to the consolidated financial statements, the Company has two tax receivable agreements, which are contractual commitments to pay 85% of any tax benefits (“TRA Payments”), realized or deemed to be realized by the Company, to the parties of the TRAs pursuant to certain terms and conditions described in the TRAs. The assessment of the TRA liabilities is based on the estimated amount of forecasted payments expected to be made to the parties of the TRAs that have been determined to be probable of occurring and requires management to make significant estimates and assumptions related to forecasts of future profitability. Changes in these assumptions could materially affect the assessment of the amount of TRA Payments and whether such payments are probable of occurring. As of December 31, 2023, the Company recognized TRA liabilities of $38 million. We identified measurement of the TRA liabilities as a critical audit matter.
The principal consideration for our determination that the measurement of the TRA liabilities is a critical audit matter is that management utilized significant judgment in determining the measurement of the TRA liabilities. In turn, auditing management’s judgments regarding the future profitability and amount of TRA liabilities involved a high degree of subjectivity due to the estimation uncertainty of management’s significant judgments.
Our audit procedures related to the measurement of the TRA liabilities included the following, among others:
| ● | We tested the design and operating effectiveness of internal controls over management’s determination of the TRA liabilities, including those over management’s deferred tax assets. |
| ● | With the assistance of individuals with specialized skills and knowledge in income taxes, we tested the completeness and accuracy of the underlying data used in management’s measurement of the TRA liabilities, including the reasonableness of the method and significant assumptions used in the calculations. |
| ● | We evaluated the prospective financial information related to future profitability including consideration of: |
| - | the current and past performance of the Company |
| - | the consistency with external market and industry data |
| - | the consistency with evidence obtained in other areas of the audit. |
/s/
We have served as the Company’s auditor since 2016.
February 21, 2024
F-3
SELECT WATER SOLUTIONS, INC.
CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS
(in thousands, except share data)
As of December 31, |
||||||
2023 |
|
2022 |
||||
Assets |
||||||
Current assets |
|
|
|
|||
Cash and cash equivalents |
$ |
|
$ |
|
||
Accounts receivable trade, net of allowance for credit losses of $ |
|
|
|
|
||
Accounts receivable, related parties |
|
|
|
|
||
Inventories |
|
|
|
|
||
Prepaid expenses and other current assets |
|
|
|
|
||
Total current assets |
|
|
|
|
||
Property and equipment |
|
|
|
|
||
Accumulated depreciation |
|
( |
|
( |
||
Total property and equipment, net |
|
|
|
|
||
Right-of-use assets, net |
|
|
||||
Goodwill |
|
|
|
— |
||
Other intangible assets, net |
|
|
|
|
||
Deferred tax assets, net |
|
|
|
— |
||
Other long-term assets, net |
|
|
|
|
||
Total assets |
$ |
|
$ |
|
||
Liabilities and Equity |
|
|
|
|||
Current liabilities |
|
|
|
|||
Accounts payable |
$ |
|
$ |
|
||
Accrued accounts payable |
|
|
||||
Accounts payable and accrued expenses, related parties |
|
|
|
|
||
Accrued salaries and benefits |
|
|
|
|
||
Accrued insurance |
|
|
|
|
||
Sales tax payable |
|
|
||||
Tax receivable agreements liabilities |
|
— |
||||
Accrued expenses and other current liabilities |
|
|
|
|
||
Current operating lease liabilities |
|
|
||||
Current portion of finance lease obligations |
|
|
|
|
||
Total current liabilities |
|
|
|
|
||
Tax receivable agreements liabilities |
|
|
|
— |
||
Long-term operating lease liabilities |
|
|
|
|
||
Long-term debt |
|
— |
|
|
||
Other long-term liabilities |
|
|
|
|
||
Total liabilities |
|
|
|
|
||
Commitments and contingencies (Note 11) |
|
|
|
|||
Class A common stock, $ |
|
|
|
|||
Class A-2 common stock, $ |
|
|
|
|
||
Class B common stock, $ |
|
|
|
|
||
Preferred stock, $ |
|
|
||||
Additional paid-in capital |
|
|
|
|
||
Accumulated deficit |
|
( |
|
( |
||
Total stockholders’ equity |
|
|
|
|
||
Noncontrolling interests |
|
|
|
|
||
Total equity |
|
|
|
|
||
Total liabilities and equity |
$ |
|
$ |
|
||
The accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements are an integral part of these financial statements.
F-4
SELECT WATER SOLUTIONS, INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF OPERATIONS
(in thousands, except share and per share data)
Year Ended December 31, |
|||||||||
2023 |
2022 |
2021 |
|||||||
Revenue |
|
|
|
||||||
Water Services |
$ |
|
$ |
|
$ |
|
|||
Water Infrastructure |
|
|
|
||||||
Chemical Technologies |
|
|
|
|
|||||
Total revenue |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Costs of revenue |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Water Services |
|
|
|
||||||
Water Infrastructure |
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Chemical Technologies |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Depreciation and amortization |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Total costs of revenue |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Gross profit |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Operating expenses |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Selling, general and administrative |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Depreciation and amortization |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Impairments and abandonments |
|
|
|
— |
|
— |
|||
Lease abandonment costs |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Total operating expenses |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Income (loss) from operations |
|
|
|
|
|
( |
|||
Other income (expense) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
(Loss) gain on sales of property and equipment and divestitures, net |
( |
|
( |
||||||
Interest expense, net |
|
( |
|
( |
( |
||||
Bargain purchase gain |
— |
|
|
|
|||||
Tax receivable agreements expense |
( |
|
— |
— |
|||||
Other |
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Income (loss) before income tax benefit (expense) |
|
|
|
|
|
( |
|||
Income tax benefit (expense) |
|
|
|
( |
|
( |
|||
Equity in losses of unconsolidated entities |
( |
( |
( |
||||||
Net income (loss) |
|
|
|
|
|
( |
|||
Less: net (income) loss attributable to noncontrolling interests |
|
( |
|
( |
|
|
|||
Net income (loss) attributable to Select Water Solutions, Inc. |
$ |
|
$ |
|
$ |
( |
|||
Net income (loss) per share attributable to common stockholders (Note 17): |
|||||||||
Class A—Basic |
$ |
|
$ |
|
$ |
( |
|||
Class B—Basic |
$ |
— |
$ |
— |
$ |
— |
|||
Net income (loss) per share attributable to common stockholders (Note 17): |
|||||||||
Class A—Diluted |
$ |
|
$ |
|
$ |
( |
|||
Class B—Diluted |
$ |
— |
$ |
— |
$ |
— |
|||
The accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements are an integral part of these financial statements.
F-5
SELECT WATER SOLUTIONS, INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF COMPREHENSIVE INCOME (LOSS)
(in thousands)
Year Ended December 31, |
|||||||||
2023 |
2022 |
2021 |
|||||||
Net income (loss) |
$ |
|
$ |
|
$ |
( |
|||
Comprehensive income (loss) |
|
|
|
|
|
( |
|||
Less: comprehensive (income) loss attributable to noncontrolling interests |
|
( |
|
( |
|
|
|||
Comprehensive income (loss) attributable to Select Water Solutions, Inc. |
$ |
|
$ |
|
$ |
( |
|||
The accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements are an integral part of these financial statements.
F-6
SELECT WATER SOLUTIONS, INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CHANGES IN EQUITY
(in thousands, except share data)
Class A |
Class B |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
Stockholders |
Stockholders |
Retained |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
Class A |
Class B |
Additional |
Earnings |
Total |
|||||||||||||||||||||
Common |
Common |
Paid-In |
(Accumulated |
Stockholders’ |
Noncontrolling |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
Shares |
|
Stock |
|
Shares |
|
Stock |
|
Capital |
|
Deficit) |
|
Equity |
|
Interests |
|
Total |
||||||||
Balance as of December 31, 2020 |
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
$ |
|
$ |
( |
$ |
|
$ |
|
$ |
|
|||||||
ESPP shares issued |
|
|
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
( |
|
|
|
||||||
Equity-based compensation |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
Issuance of restricted shares |
|
|
— |
— |
|
— |
|
( |
|
||||||||||||||||
Other |
|
|
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
||||||
Issuance of shares for acquisitions |
|
|
— |
— |
|
— |
|
( |
|
||||||||||||||||
Repurchase of common stock |
( |
( |
— |
— |
( |
— |
( |
|
( |
||||||||||||||||
Restricted shares forfeited |
( |
( |
— |
— |
( |
— |
( |
|
— |
||||||||||||||||
Distributions to noncontrolling interests, net |
— |
— |
— |
— |
( |
— |
( |
( |
( |
||||||||||||||||
NCI income tax adjustment |
— |
— |
— |
— |
|
— |
|
( |
— |
||||||||||||||||
Net loss |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
( |
|
( |
|
( |
|
|
( |
||||||
Balance as of December 31, 2021 |
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
$ |
|
$ |
( |
$ |
|
$ |
|
$ |
|
|||||||
ESPP shares issued |
|
|
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
Equity-based compensation |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
Issuance of restricted shares |
|
|
— |
— |
|
— |
|
( |
— |
||||||||||||||||
Stock options exercised |
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
Issuance of shares for acquisitions |
|
|
— |
— |
|
— |
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||
Repurchase of common stock |
( |
( |
— |
— |
( |
— |
( |
( |
( |
||||||||||||||||
Restricted shares forfeited |
( |
( |
— |
— |
( |
— |
( |
|
— |
||||||||||||||||
Distributions to noncontrolling interests |
— |
— |
— |
— |
( |
— |
( |
— |
( |
||||||||||||||||
Contributions from noncontrolling interests |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
|
|
||||||||||||||||
Purchase of noncontrolling interest |
— |
— |
— |
— |
|
— |
|
( |
|
||||||||||||||||
NCI income tax adjustment |
— |
— |
— |
— |
|
— |
|
( |
— |
||||||||||||||||
Dividend and distribution declared: |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
Class A common stock ($ |
— |
— |
— |
— |
( |
— |
( |
( |
( |
||||||||||||||||
Unvested restricted stock ($ |
— |
— |
— |
— |
( |
— |
( |
|
( |
||||||||||||||||
Class B common stock ($ |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
( |
( |
||||||||||||||||
Net income |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
Balance as of December 31, 2022 |
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
$ |
|
$ |
( |
$ |
|
$ |
|
$ |
|
|||||||
Equity-based compensation |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
Issuance of restricted shares |
|
|
— |
— |
|
— |
|
( |
( |
||||||||||||||||
Issuance of shares for acquisitions |
( |
— |
— |
— |
( |
— |
( |
( |
( |
||||||||||||||||
Repurchase of common stock |
( |
( |
— |
— |
( |
— |
( |
( |
( |
||||||||||||||||
Restricted shares forfeited |
( |
( |
— |
— |
( |
— |
( |
|
— |
||||||||||||||||
Distributions to noncontrolling interests |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
( |
( |
||||||||||||||||
Contributions from noncontrolling interests |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
|
|
||||||||||||||||
Dividend and distribution declared: |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
Class A common stock ($ |
— |
— |
— |
— |
( |
— |
( |
— |
( |
||||||||||||||||
Unvested restricted stock ($ |
— |
— |
— |
— |
( |
— |
( |
— |
( |
||||||||||||||||
Class B common stock ($ |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
( |
( |
||||||||||||||||
Net income |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
Balance as of December 31, 2023 |
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
$ |
|
$ |
( |
$ |
|
$ |
|
$ |
|
|||||||
The accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements are an integral part of these financial statements.
F-7
SELECT WATER SOLUTIONS, INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
(in thousands)
Year Ended December 31, |
|||||||||
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
2021 |
|||||
Cash flows from operating activities |
|
|
|
|
|||||
Net income (loss) |
$ |
|
$ |
|
$ |
( |
|||
Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash used in operating activities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Depreciation and amortization |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Deferred tax (benefit) expense |
( |
|
( |
|
|
||||
Tax receivable agreements expense |
|
|
— |
|
— |
||||
Loss (gain) on disposal of property and equipment and divestitures |
|
|
|
( |
|
|
|||
Equity in losses of unconsolidated entities |
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Bad debt expense (recovery) |
|
|
|
|
|
( |
|||
Amortization of debt issuance costs |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Inventory adjustments |
|
( |
|
||||||
Equity-based compensation |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Impairments and abandonments |
|
|
|
— |
|
— |
|||
Bargain purchase gain |
|
— |
|
( |
|
( |
|||
Unrealized loss on short-term investment |
— |
— |
|
||||||
Other operating items, net |
|
( |
|
( |
|
( |
|||
Changes in operating assets and liabilities |
|
|
|
|
|||||
Accounts receivable |
|
|
|
( |
|
( |
|||
Prepaid expenses and other assets |
|
( |
|
|
|
( |
|||
Accounts payable and accrued liabilities |
|
( |
|
|
|
|
|||
Net cash provided by (used in) operating activities |
|
|
|
|
|
( |
|||
Cash flows from investing activities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Proceeds from sale of securities |
— |
— |
|
||||||
Proceeds received from divestitures |
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|||
Purchase of property and equipment |
|
( |
|
( |
|
( |
|||
Investment in note receivable |
— |
|
— |
|
( |
||||
Purchase of equity-method investments |
( |
( |
( |
||||||
Collection of note receivable |
— |
|
|
||||||
Distribution from cost method investment |
— |
|
|
||||||
Acquisitions, net of cash and restricted cash received |
|
( |
|
( |
|
( |
|||
Proceeds received from sales of property and equipment |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Net cash used in investing activities |
|
( |
|
( |
|
( |
|||
Cash flows from financing activities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Borrowings from revolving line of credit |
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|||
Payments on revolving line of credit |
( |
( |
— |
||||||
Payments on current and long-term debt |
|
— |
|
( |
|
— |
|||
Payments of finance lease obligations |
( |
( |
( |
||||||
Payment of debt issuance costs |
|
— |
|
( |
|
— |
|||
Dividends and distributions paid |
|
( |
|
( |
|
— |
|||
Proceeds from share issuance |
— |
|
|
||||||
Distributions to noncontrolling interests |
|
( |
|
( |
|
( |
|||
Purchase of noncontrolling interests |
|
— |
|
( |
|
— |
|||
Contributions from noncontrolling interests |
|
|
|
— |
|
— |
|||
Repurchase of common stock |
|
( |
|
( |
|
( |
|||
Net cash used in financing activities |
|
( |
|
( |
|
( |
|||
Effect of exchange rate changes on cash |
|
( |
|
( |
|
|
|||
Net increase (decrease) in cash and cash equivalents |
|
|
|
( |
|
( |
|||
Cash and cash equivalents, beginning of period |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Cash and cash equivalents, end of period |
$ |
|
$ |
|
$ |
|
|||
Supplemental cash flow disclosure: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Cash paid for interest |
$ |
|
$ |
|
$ |
|
|||
Cash paid (refunds received) for income taxes, net |
$ |
|
$ |
( |
$ |
( |
|||
Supplemental disclosure of noncash operating activities: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Lease liabilities arising from obtaining right-of-use assets |
$ |
|
$ |
|
$ |
|
|||
Supplemental disclosure of noncash investing activities: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
(Recoupment) issuance of shares for acquisitions |
$ |
( |
$ |
|
$ |
|
|||
Conversion of notes receivable to equity-method investment |
$ |
— |
$ |
|
$ |
— |
|||
Capital expenditures included in accounts payable and accrued liabilities |
$ |
|
$ |
|
$ |
|
|||
Supplemental disclosure of noncash financing activities: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Accrued contributions from noncontrolling interests |
$ |
— |
$ |
|
$ |
— |
|||
Issuance of shares for NCI acquisitions |
$ |
— |
$ |
|
$ |
— |
|||
The accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements are an integral part of these financial statements.
F-8
SELECT WATER SOLUTIONS, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
NOTE 1—BUSINESS AND BASIS OF PRESENTATION
Description of the business: Select Water Solutions, Inc. (“we,” “Select Inc.,” “Select” or the “Company”), formerly Select Energy Services, Inc., was incorporated as a Delaware corporation on November 21, 2016. On May 8, 2023, Select Energy Services, Inc.’s Fifth Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation became effective upon filing with the Secretary of State of the State of Delaware which, among other things, changed the name of the company from Select Energy Services, Inc. to Select Water Solutions, Inc. to reflect its strategic focus as a water-focused company. We retained our stock ticker “WTTR” trading on the New York Stock Exchange. The Company is a holding company whose sole material asset consists of common units (“SES Holdings LLC Units”) in SES Holdings, LLC (“SES Holdings”).
We are a leading provider of sustainable water-management and chemical solutions to the energy industry in the United States (“U.S.”). As a leader in the water solutions industry, we place the utmost importance on safe, environmentally responsible management of oilfield water throughout the lifecycle of a well. Additionally, we believe that responsibly managing water resources through our operations to help conserve and protect the environment in the communities in which we operate is paramount to our continued success.
Class A and Class B common stock: As of December 31, 2023, the Company had both Class A and Class B common shares issued and outstanding. Holders of shares of our Class A common stock, par value $
Exchange rights: Under the Eighth Amended and Restated Limited Liability Company Agreement of SES Holdings (the “SES Holdings LLC Agreement”), SES Legacy Holdings LLC (“Legacy Owner Holdco”) and its permitted transferees have the right (an “Exchange Right”) to cause SES Holdings to acquire all or a portion of its SES Holdings LLC Units for, at SES Holdings’ election, (i) shares of Class A common stock at an exchange ratio of
Basis of presentation: The accompanying consolidated financial statements of the Company have been prepared in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles in the U.S. (“GAAP”) and pursuant to the rules and regulations of the SEC. The consolidated financial statements include the accounts of the Company and all of its majority-owned or controlled subsidiaries. All intercompany accounts and transactions have been eliminated in consolidation.
For investments in subsidiaries that are not wholly owned, but where the Company exercises control, the equity held by the minority owners and their portion of net income or loss are reflected as noncontrolling interests. Investments in entities in which the Company exercises significant influence over operating and financial policies are accounted for using the equity method, and investments in entities for which the Company does not have significant control or influence are accounted for using the cost-method or other appropriate basis as applicable. As of December 31, 2023, the Company had
F-9
fair value of its investment is less than its carrying value and the reduction in value is other than temporary, the reduction in value is recognized in earnings. Our investments in unconsolidated entities are summarized below and are included in the assets of our Water Services segment:
Year |
As of December 31, |
||||||||
Type of Investment |
attained |
Accounting method |
Balance Sheet Location |
2023 |
|
2022 |
|||
(in thousands) |
|||||||||
2020 |
Equity-method |
Other long-term assets, net |
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||
2021 |
Equity-method |
Other long-term assets, net |
|
|
|
||||
2021 |
Equity-method |
Other long-term assets, net |
|
|
|||||
| (1) |
Ownership percentage decreased during the year ended December 31, 2023 due to contributions from other owners. Minority interest was |
Dividends: During 2023, the Company paid $
Segment reporting: The Company has
Effective June 1, 2023, our CODM began to strategically view and manage certain water sourcing and transfer operations, previously included in our Water Infrastructure segment, as part of our Water Services segment. These changes were driven by a number of factors, including the preponderance of our water sourcing business that integrates with our water transfer operations, the continued transition of completions water demand from fresh and brackish water to recycled water, as well, we anticipate more efficient sharing and utilization of resources and to realize potential synergies. Prior periods have been recast to include the water sourcing and transfer operations within the Water Services segment and remove the results of those operations from the Water Infrastructure segment.
Concurrently, the Company also decided to rename its Oilfield Chemicals segment as Chemical Technologies. This change was based on a number of factors, including the continued success of our chemicals business in delivering customized, specialty chemicals products developed through our own research and development efforts and the de-emphasis of certain traditional commoditized chemistry products within the oil and gas industry, as well as the continued investments in time and resources we make to manufacture and sell our specialty chemical products into non-oilfield industrial-related applications. We believe these segment changes better align the business with the current and future state of the Company’s operations and capital allocation and strategic objectives. This change was a naming convention only change that did not impact any numbers for all years presented.
The Water Services segment consists of the Company’s services businesses, including water sourcing, water transfer, flowback and well testing, fluids hauling, water monitoring, water containment and water network automation, primarily serving exploration and production (“E&P”) companies. Additionally, this segment includes the operations of our accommodations and rentals business.
The Water Infrastructure segment consists of the Company’s fixed infrastructure assets, including operations associated with our water distribution pipeline infrastructure, our water recycling solutions, and our produced water gathering systems and saltwater disposal wells, as well as solids disposal facilities, primarily serving E&P companies.
The Chemical Technologies segment provides technical solutions, products and expertise related to chemical applications in the oil and gas industry. We develop, manufacture, manage logistics and provide a full suite of chemicals used in hydraulic fracturing, stimulation, cementing and well completions for customers ranging from pressure pumpers
F-10
to major integrated and independent oil and gas producers. This segment also utilizes its chemical experience and lab testing capabilities to customize tailored water treatment solutions designed to optimize the fracturing fluid system in conjunction with the quality of water used in well completions.
Reclassifications: Certain reclassifications have been made to the Company’s prior period consolidated financial information to conform to the current year presentation. These presentation changes did not impact the Company’s consolidated net income, consolidated cash flows, total assets, total liabilities or total stockholders’ equity.
NOTE 2—SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES
Use of estimates: The preparation of consolidated financial statements in conformity with GAAP requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the financial statements and the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting period. Actual results could differ from those estimates.
On an ongoing basis, the Company evaluates its estimates, including those related to the recoverability of long-lived assets and intangibles, useful lives used in depreciation and amortization, uncollectible accounts receivable, inventory reserve, income taxes, self-insurance liabilities, share-based compensation, contingent liabilities, lease-related reasonably certain option exercise assessments, and the incremental borrowing rate for leases. The Company bases its estimates on historical and other pertinent information that are believed to be reasonable under the circumstances. The accounting estimates used in the preparation of the consolidated financial statements may change as new events occur, as more experience is acquired, as additional information is obtained and as the Company’s operating environment changes.
Cash and cash equivalents: The Company considers all highly liquid investments with an original maturity of three months or less to be cash equivalents.
Allowance for credit losses: The Company’s allowance for credit losses relates to trade accounts receivable. The Company treats trade accounts receivable as one portfolio and records an initial allowance calculated as a percentage of revenue recognized based on a combination of historical information and future expectations. Additionally, the Company adjusts this allowance based on specific information in connection with aged receivables. Historically, most bad debt has been incurred when a customer’s financial condition significantly deteriorates, which in some cases leads to bankruptcy. Market volatility is highly uncertain and, as such, the impact on expected losses is subject to significant judgment and may cause variability in the Company’s allowance for credit losses in future periods.
The change in the allowance for credit losses is as follows:
For the year ended December 31, |
|||||||||
2023 |
2022 |
|
2021 |
||||||
(in thousands) |
|||||||||
Balance at beginning of year |
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|
Increase to allowance based on a percentage of revenue |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Adjustment based on aged receivable analysis |
|
( |
( |
||||||
Charge-offs |
|
( |
|
|
( |
|
|
( |
|
Recoveries |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Balance at end of year |
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|
F-11
Concentrations of credit and customer risk: Financial instruments that potentially subject the Company to concentrations of credit risk consist principally of cash and cash equivalents and trade accounts receivable. The amounts held in financial institutions periodically exceed the federally insured limit. Management believes that the financial institutions are financially sound and the risk of loss is minimal. The Company minimizes its exposure to counterparty credit risk by performing credit evaluations and ongoing monitoring of the financial stability of its customers. There were
Inventories: The Company values its inventories at lower of cost or net realizable value. Inventory costs are determined under the weighted-average method. Inventory costs primarily consist of chemicals and materials available for resale and parts and consumables used in operations.
Property and equipment: Property and equipment are stated at cost less accumulated depreciation.
Depreciation (and amortization of finance lease assets) is calculated on a straight-line basis over the estimated useful life of each asset as noted below:
Asset Classification |
|
Useful Life (years) |
Land |
|
Indefinite |
Buildings and leasehold improvements |
|
|
Vehicles and equipment |
|
|
Machinery and equipment |
|
|
Recycling facilities |
||
Pipelines |
||
Computer equipment and software |
|
|
Office furniture and equipment |
|
|
Gathering and disposal infrastructure |
|
Depreciation expense related to the Company’s property and equipment, including amortization of property under finance leases, was $
Change in depreciable lives of property and equipment: In accordance with its policy, the Company reviews the estimated useful lives and estimated salvage values of its fixed assets on an ongoing basis.
Business Combinations: The Company records business combinations using the acquisition method of accounting. Under the acquisition method of accounting, identifiable assets acquired and liabilities assumed are recorded at their acquisition-date fair values. The excess of the purchase price over the estimated fair value is recorded as goodwill and the excess of the fair value over the purchase price is recorded as a bargain purchase gain. Changes in the estimated fair values of net assets recorded for acquisitions prior to the finalization of more detailed analysis, but not to exceed one year from the date of acquisition, will adjust the amount of the purchase price allocable to goodwill. Measurement period adjustments are reflected in the period in which they occur.
Other intangible assets: Other intangible assets not subject to amortization are tested for impairment annually or more frequently if events or changes in circumstances indicate that the asset might be impaired. Intangible assets with finite useful lives are amortized either on a straight-line basis over the asset’s estimated useful life or on a basis that reflects the pattern in which the economic benefits of the intangible assets are realized.
Impairment of long-lived assets and intangible assets: Long-lived assets, such as property and equipment and finite-lived intangible assets, are evaluated for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that its carrying value may not be recoverable. Recoverability is measured by a comparison of its carrying amount to the estimated undiscounted cash flows to be generated by those assets. If the undiscounted cash flows are less than the
F-12
carrying amount, the Company records impairment losses for the excess of its carrying value over the estimated fair value. The development of future cash flows and the estimate of fair value represent its best estimates based on industry trends and reference to market transactions and are subject to variability. The Company considers the factors within the fair value analysis to be Level 3 inputs within the fair value hierarchy. See “Note 4—Abandonments and Other Costs” for further discussion.
Asset retirement obligations: The asset retirement obligation (“ARO”) liability reflects the present value of estimated costs of plugging, site reclamation and similar activities associated with the Company’s saltwater disposal wells. The Company utilizes current retirement costs to estimate the expected cash outflows for retirement obligations. The Company also estimates the productive life of the disposal wells, a credit-adjusted risk-free discount rate and an inflation factor in order to determine the current present value of this obligation. The Company’s ARO liabilities are included in accrued expenses and other current liabilities and other long-term liabilities as of December 31, 2023, and 2022.
The change in asset retirement obligations is as follows:
For the year ended December 31, |
||||||
2023 |
|
2022 |
||||
(in thousands) |
||||||
Balance as of December 31, 2022 |
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|
Accretion expense, included in depreciation and amortization expense |
|
|
|
|||
Acquired AROs |
|
|
|
|||
Divested |
( |
( |
||||
Payments |
( |
( |
||||
Balance as of December 31, 2023 |
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|
Short-term ARO liability |
|
|
||||
Long-term ARO liability |
|
|
||||
Balance as of December 31, 2023 |
$ |
|
$ |
|
||
In addition to the obligations described above, the Company may be obligated to remove facilities or perform other remediation upon retirement of certain other assets. However, the fair value of the asset retirement obligation cannot currently be reasonably estimated because the settlement dates are indeterminable. If applicable, the Company will record an asset retirement obligation for these assets in the periods in which settlement dates are reasonably determinable.
Retentions: The Company assumes risk of loss through deductibles and self-insured retentions, up to certain levels for losses related to general liability, workers’ compensation and employer’s liability, vehicle liability and health insurance. The Company’s exposure (i.e., the self-insured retention or deductible) per occurrence is $
Defined Contribution Plan: The Company sponsors a defined contribution 401(k) Profit Sharing Plan (the “401(k) Plan”) for the benefit of substantially all employees of the Company. The 401(k) Plan allows eligible employees to make tax-deferred contributions, not to exceed annual limits established by the Internal Revenue Service. The vesting
F-13
schedule for new hires is
Effective July 1, 2021, the Company matched contributions of
Revenue recognition: The Company follows ASU 2014-09, Revenue from Contracts with Customers (Topic 606). See “Note 5—Revenue” for further detail on applying this standard. The Company uses the five step process to recognize revenue which entails (i) identifying contracts with customers; (ii) identifying the performance obligations in each contract; (iii) determining the transaction price; (iv) allocating the transaction price to the performance obligations; and (v) recognizing revenue as we satisfy performance obligations. The Company only applies the five-step model to contracts when it is probable that the Company will collect the consideration it is entitled to in exchange for the goods or services transferred to the customer. Revenue from the Company’s Water Services and Water Infrastructure segments is typically recognized over the course of time, whereas revenue from the Company’s Chemical Technologies segment is typically recognized upon change in control. Revenue generated by each of the Company’s revenue streams are outlined as follows:
Water Services and Water Infrastructure—The Company provides water-related services to customers, including the sourcing and transfer of water, produced water gathering, treatment and reuse, the containment of fluids, measuring and monitoring of water, the filtering and treatment of fluids, well testing and handling, transportation and recycling or disposal of fluids. The Company recognizes revenue as services are performed.
The Company’s agreements with its customers are often referred to as “price sheets” and sometimes provide pricing for multiple services. However, these agreements generally do not authorize the performance of specific services or provide for guaranteed throughput amounts. As customers are free to choose which services, if any, to use based on the Company’s price sheet, the Company prices its separate services on the basis of their standalone selling prices. Customer agreements generally do not provide for performance-, cancellation-, termination-, or refund-type provisions. Services based on price sheets with customers are generally performed under separately-issued “work orders” or “field tickets” as services are requested. Multiple service lines of the Company’s Water Services and Water Infrastructure segments are sometimes part of the same arrangement. In these instances, revenue for the applicable service lines are recognized concurrently when delivered. Additionally, asset rentals are recognized on a straight-line basis.
Chemical Technologies Product Sales—The Company develops, manufactures and markets a full suite of chemicals utilized in hydraulic fracturing, stimulation, cementing and well completions, including polymers that create viscosity, crosslinkers, friction reducers, surfactants, buffers, breakers and other chemical technologies, to leading pressure pumping service companies in the U.S. The Company also provides production chemicals solutions, which are applied to underperforming wells in order to enhance well performance and reduce production costs through the use of production treating chemicals, corrosion and scale monitoring, chemical inventory management, well failure analysis and lab services.
Chemical Technologies products are generally sold under sales agreements based upon purchase orders or contracts with customers that do not include right of return provisions or other significant post-delivery obligations. The Company’s products are produced in a standard manufacturing operation, even if produced to the customer’s specifications. The prices of products are fixed and determinable and are established in price lists or customer purchase orders. The Company recognizes revenue from product sales when title passes to the customer, the customer assumes risks and rewards of ownership, collectability is reasonably assured and delivery occurs as directed by the customer.
Equity-based compensation: The Company accounts for equity-based awards for restricted stock awards, restricted stock units, and stock-settled appreciation awards by measuring the awards at the date of grant and recognizing the grant-date fair value as an expense using either straight-line or accelerated attribution, depending on the specific
F-14
terms of the award agreements over the requisite service period, which is usually equivalent to the vesting period. The Company expenses awards with graded-vesting service conditions on a straight-line basis and accounts for forfeitures as they occur. The Company accounts for performance share units by remeasuring the awards at the end of each reporting period based on the period-end closing share price, factoring in the percentage expected to vest, and the percentage of the service period completed.
Fair value measurements: The Company measures certain assets and liabilities pursuant to accounting guidance, which establishes a three-tier fair value hierarchy and prioritizes the inputs used in measuring fair value. Level 1 inputs are unadjusted quoted prices in active markets for identical assets or liabilities. Level 2 inputs are quoted prices or other market data for similar assets and liabilities in active markets, or inputs that are observable for the asset or liability, either directly or indirectly through market corroboration, for substantially the full term of the asset or liability. Level 3 inputs are unobservable inputs based upon the Company’s own judgment and assumptions used to measure assets and liabilities at fair value. See “Note 13—Fair Value Measurement” for further discussion.
Income taxes: Select Inc. is subject to U.S. federal, foreign and state income taxes as a corporation. SES Holdings and its subsidiaries, with the exception of certain corporate subsidiaries, are treated as flow-through entities for U.S. federal income tax purposes and as such, are generally not subject to U.S. federal income tax at the entity level. Rather, the tax liability with respect to their taxable income is passed through to their members or partners. Select Inc. recognizes a tax liability on its allocable share of SES Holdings’ taxable income. The state of Texas includes in its tax system a franchise tax applicable to the Company and an accrual for franchise taxes is included in the financial statements when appropriate.
The Company and its subsidiaries account for income taxes under the asset and liability method. Under this method, deferred tax assets and liabilities are recognized for the estimated future tax consequences attributable to differences between the financial statement carrying amounts of existing assets and liabilities and their respective tax basis. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are measured using enacted tax rates in effect for the year in which those temporary differences are expected to be recovered or settled pursuant to the provisions of Accounting Standards Codification (“ASC”) 740, Income Taxes. The effect on deferred tax assets and liabilities of a change in tax rate is recognized in earnings in the period that includes the enactment date. Valuation allowances are established when necessary to reduce deferred tax assets to the amounts more likely than not to be realized.
The determination of the provision for income taxes requires significant judgment, use of estimates and the interpretation and application of complex tax laws. Significant judgment is required in assessing the timing and amounts of deductible and taxable items and the probability of sustaining uncertain tax positions. The benefits of uncertain tax positions are recorded in the Company’s financial statements only after determining a more likely than not probability that the uncertain tax positions will withstand challenge, if any, from taxing authorities. When facts and circumstances change, the Company reassesses these probabilities and records any changes through the provision for income taxes. The Company recognizes interest and penalties relating to uncertain tax provisions as a component of tax expense. The Company identified no material uncertain tax positions as of December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021. See “Note 15—Income Taxes” for further discussion.
Tax Receivable Agreements: In connection with the Select 144A Offering, the Company entered into two tax receivable agreements (the “Tax Receivable Agreements”) with Legacy Owner Holdco and certain other affiliates of the then holders of SES Holdings LLC Units (each such person and any permitted transferee thereof, a “TRA Holder,” and together, the “TRA Holders”). The 144A Offering represented a reorganization transaction between entities under common control and was recorded based on the historical carrying amounts of affected assets and liabilities in accordance with ASC 805-50, Business Combinations – Related Issues. Accordingly, the Tax Receivable Agreements liabilities are accounted for in accordance with ASC 450, Contingencies, on a gross undiscounted basis, for amounts payable under the provisions of the Tax Receivable Agreements that have been determined to be probable of occurring for amounts that are reasonably estimable. Changes in estimated Tax Receivable Agreements liabilities are recognized as tax receivable agreements expense on the consolidated statements of operations. Additionally, following the Company’s acquisition (or deemed acquisition for U.S. federal income tax purposes) of all or a portion of a TRA Holder’s SES Holdings LLC Units pursuant to the exercise of the Exchange Right or the Company’s Call Right, the Company records obligations under the Tax Receivable Agreements at the gross undiscounted amount as an increase to the liability with
F-15
an offset to additional paid-in capital for the amount of expected future payments that are determined to be probable of occurring for amounts that are reasonably estimable.
The first of the Tax Receivable Agreements, which the Company entered into with Legacy Owner Holdco and Crestview Partners II GP, L.P. (“Crestview GP”), generally provides for the payment by the Company to such TRA Holders of
The second of the Tax Receivable Agreements, which the Company entered into with an affiliate of Legacy Owner Holdco and Crestview GP, generally provides for the payment by the Company to such TRA Holders of
The Company will retain the benefit of the remaining
Realizability of Deferred Tax Assets: We establish valuation allowances when necessary to reduce deferred tax assets to the amounts more likely than not to be realized. Deferred income tax assets are evaluated quarterly to determine if valuation allowances are required or should be adjusted. The ability to realize deferred tax assets depends on the ability to generate sufficient taxable income within the carryback or carryforward periods provided for in the tax law for each applicable tax jurisdiction. The assessment regarding whether a valuation allowance is required or should be adjusted is based on an evaluation of possible sources of taxable income and also considers all available positive and negative evidence factors. Our accounting for the realization of deferred tax assets incorporates, amongst other factors, our best estimate of future events. Changes in our current estimates, due to unanticipated market conditions, governmental legislative actions or events, could have a material effect on our ability to utilize deferred tax assets. As of December 31, 2023, valuation allowances against deferred tax assets were $
Recent accounting pronouncements: In March 2020, the Financial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”) issued Accounting Standards Update ("ASU") 2020-04, Facilitation of the Effects of Reference Rate Reform on Financial Reporting. As the London Interbank Offered Rate ("LIBOR") was no longer available beginning July 2023, this standard update provided practical expedients for contract modifications made as part of the transition from LIBOR to alternative reference rates. The guidance was effective upon issuance and at present can generally be applied through December 31, 2024. The Company adopted this ASU in the Current Period, and it had no impact on the consolidated financial statements.
F-16
In November 2023, the FASB issued ASU No. 2023-07, “Segment Reporting (Topic 280): Improvements to Reportable Segment Disclosures” (“ASU 2023-07”). ASU 2023-07 requires disclosure of significant segment expenses that are regularly provided to the chief operating decision maker (“CODM”) and included within each reported measure of segment profit or loss, an amount and description of its composition for other segment items to reconcile to segment profit or loss, and the title and position of the entity’s CODM. The amendments in this update also expand the interim segment disclosure requirements. ASU 2023-07 will be effective for our fiscal year ending December 31, 2024, and for interim periods starting in our first quarter of 2025. Early adoption is permitted and the amendments in this update are required to be applied on a retrospective basis. We are currently reviewing the impact that the adoption of ASU 2023-07 may have on our consolidated financial statements and disclosures.
In December 2023, the FASB issued ASU 2023-09, Income Taxes (Topic 740): Improvements to Income Tax Disclosures, which includes amendments that further enhance income tax disclosures, primarily through standardization and disaggregation of rate reconciliation categories and income taxes paid by jurisdiction. ASU 2023-09 will be effective for our fiscal year ending December 31, 2025 with early adoption permitted, and should be applied either prospectively or retrospectively. The Company is currently evaluating the ASU to determine its impact on the Company’s disclosures.
NOTE 3—ACQUISITIONS
The following table presents key information connected with our 2023, 2022 and 2021 acquisitions (dollars in thousands, except share amounts):
Assets and Operations Acquired |
Acquisition Date |
Shares Issued |
Cash Consideration |
Acquisition related costs for Asset Acquisition |
Contingent Consideration |
Value of Shares Issued |
Total Consideration |
Segments |
||||||||
Four Smaller Asset Acquisitions |
Multiple 2023 Dates |
— |
|
- |
— |
— |
|
Water Infrastructure |
||||||||
Asset Acquisition |
April 3, 2023 |
— |
|
- |
— |
— |
|
Water Services |
||||||||
Asset Acquisition |
January 31, 2023 |
— |
|
|
— |
— |
|
Water Infrastructure |
||||||||
Asset Acquisition |
December 2, 2022 |
— |
|
|
— |
— |
|
Water Infrastructure |
||||||||
Noncontrolling Interests in Big Spring Recycling System |
December 2, 2022 |
|
|
— |
— |
|
|
Water Infrastructure |
||||||||
Breakwater |
November 1, 2022 |
|
|
— |
— |
|
|
Water Services & Water Infrastructure |
||||||||
Cypress |
November 1, 2022 |
|
— |
— |
— |
|
|
Water Infrastructure |
||||||||
Nuverra |
February 23, 2022 |
|
— |
— |
— |
|
|
Water Services & Water Infrastructure |
||||||||
HB Rentals |
December 3, 2021 |
|
|
— |
— |
|
|
Water Services |
||||||||
Agua Libre and Basic |
October 1, 2021 |
|
|
— |
— |
|
|
Water Services & Water Infrastructure |
||||||||
UltRecovery |
August 2, 2021 |
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
Chemical Technologies |
||||||||
Complete |
July 9, 2021 |
|
|
— |
— |
|
|
Water Services & Water Infrastructure |
||||||||
Total |
|
$ |
|
$ |
|
$ |
|
$ |
|
$ |
|
2023 Asset Acquisitions
During the year ended December 31, 2023, Select acquired certain assets, revenue-producing contracts and associated liabilities, primarily in the Permian Basin, from multiple entities for $
F-17
Breakwater Acquisition
On November 1, 2022, the Company completed the acquisition of Breakwater Energy Services, LLC. (“Breakwater”) in a stock-for-stock transaction for total consideration of $
The Breakwater Acquisition was accounted for as a business combination under the acquisition method of accounting. When determining the fair values of assets acquired and liabilities assumed, management made estimates, judgments and assumptions. The Company engaged third-party valuation experts to assist in the purchase price allocation. These estimates, judgments and assumptions and valuation of the property and equipment acquired, intangible assets, current assets, current liabilities and long-term liabilities were finalized as of September 30, 2023. The total consideration paid exceeded the fair value of the net assets acquired by $
The following table summarizes the consideration transferred and the estimated fair value of identified assets acquired and liabilities assumed as of the date of acquisition:
Purchase price allocation |
As Reported as of December 31, 2022 |
Current Year Adjustment |
Amount |
||||||
Consideration transferred |
(in thousands) |
||||||||
Class A common stock ( |
$ |
|
$ |
( |
$ |
|
|||
Cash paid |
|
— |
|
||||||
Total consideration transferred |
|
|
( |
|
|||||
Less: identifiable assets acquired and liabilities assumed |
|
||||||||
Working capital |
|
|
( |
|
|||||
Property and equipment |
|
|
( |
|
|||||
Right-of-use assets |
|
|
— |
|
|||||
Customer relationships |
|
|
|
||||||
Other long-term assets |
|
— |
|
||||||
Long-term debt |
( |
— |
( |
||||||
Long-term lease liabilities |
( |
— |
( |
||||||
Noncontrolling interest(2) |
( |
— |
( |
||||||
Total identifiable net assets acquired |
|
( |
|
||||||
Goodwill |
|
— |
|
|
|||||
Fair value allocated to net assets acquired |
|
$ |
|
$ |
( |
$ |
|
||
| (1) |
During the year ended December 31, 2023, the parties agreed that |
| (2) |
The noncontrolling interests acquired on November 1, 2022 were subsequently purchased on December 2, 2022, thereby giving the Company |
F-18
Big Spring Recycling System Noncontrolling Interests
In connection with Select’s acquisition of Breakwater on November 1, 2022, Select acquired all noncontrolling interests in the Big Spring Recycling System (“BSRS”) on December 2, 2022. BSRS includes significant pipeline, storage, recycling and disposal infrastructure assets in the Midland Basin. The consideration paid included $
2022 Asset Acquisition
On December 2, 2022, Select acquired certain assets and revenue-producing contracts in the Midland Basin from an entity for $
Cypress Acquisition
On November 1, 2022, the Company completed the acquisition of certain saltwater disposal assets from Cypress Environmental Solutions, LLC (“Cypress”) for total consideration of $
The Cypress Acquisition was accounted for as a business combination under the acquisition method of accounting. When determining the fair values of assets acquired and liabilities assumed, management made estimates, judgments and assumptions. These estimates, judgments and assumptions and valuation of the property and equipment acquired, current assets, current liabilities and long-term liabilities were finalized as of March 31, 2023. The assets acquired and liabilities assumed are included in the Company’s Water Infrastructure segment. The Company incurred less than $
The following table summarizes the consideration transferred and the estimated fair value of identified assets acquired and liabilities assumed as of the date of acquisition:
Purchase price allocation |
Amount |
||
Consideration transferred |
(in thousands) |
||
Class A common stock ( |
$ |
|
|
Total consideration transferred |
|
|
|
Less: identifiable assets acquired and liabilities assumed |
|
||
Working capital |
|
( |
|
Property and equipment |
|
|
|
Customer relationships |
|
||
Long-term ARO |
( |
||
Total identifiable net assets acquired |
|
||
Fair value allocated to net assets acquired |
|
$ |
|
F-19
Nuverra Acquisition
On February 23, 2022, the Company completed the acquisition of Nuverra Environmental Solutions, Inc. (“Nuverra”) for total consideration of $
The Nuverra Acquisition was accounted for as a business combination under the acquisition method of accounting. When determining the fair values of assets acquired and liabilities assumed, management made estimates, judgments and assumptions. The Company engaged third-party valuation experts to assist in the purchase price allocation. These estimates, judgments and assumptions and valuation of the property and equipment acquired, current assets, current liabilities and long-term liabilities have been finalized as of December 31, 2022. The Nuverra debt, including accrued interest, totaled $
The Company assumed $
The following table summarizes the consideration transferred and the estimated fair value of identified assets acquired and liabilities assumed as of the date of acquisition:
Purchase price allocation |
Amount |
||
Consideration transferred |
(in thousands) |
||
Class A common stock ( |
$ |
|
|
Total consideration transferred |
|
|
|
Less: identifiable assets acquired and liabilities assumed |
|
||
Working capital |
|
|
|
Property and equipment |
|
|
|
Right-of-use assets |
|
|
|
Other long-term assets |
|
||
Long-term debt |
( |
||
Long-term ARO |
( |
||
Other long-term liabilities |
( |
||
Total identifiable net assets acquired |
|
||
|
( |
||
Fair value allocated to net assets acquired, net of bargain purchase gain |
|
$ |
|
F-20
HB Rentals Acquisition
On December 3, 2021, the Company, through its subsidiary Peak Oilfield Services, LLC, completed the acquisition of certain assets of H.B. Rentals, L.C. (“HB Rentals”), an operating subsidiary of Superior Energy Services, Inc. (“Superior”) for total initial consideration of $
The HB Rentals Acquisition was accounted for as a business combination under the acquisition method of accounting. When determining the fair values of assets acquired and liabilities assumed, management made estimates, judgments and assumptions. These estimates, judgments and assumptions and valuation of the property and equipment acquired, current assets, current liabilities and long-term liabilities were finalized as of June 30, 2022. The assets acquired and liabilities assumed are included in the Company’s Water Services segment. The Company incurred $
The following table summarizes the consideration transferred and the estimated fair value of identified assets acquired and liabilities assumed as of the date of acquisition:
Purchase price allocation |
Amount |
||
Consideration transferred |
(in thousands) |
||
Class A common stock ( |
$ |
|
|
Cash paid |
|
||
Final working capital settlement |
|
||
Total consideration transferred |
|
||
Less: identifiable assets acquired and liabilities assumed |
|
||
Working capital |
|
||
Property and equipment |
|
||
Right-of-use assets |
|
||
Long-term lease liabilities |
( |
||
Total identifiable net assets acquired |
|
||
Bargain Purchase Gain |
( |
||
Fair value allocated to net assets acquired, net of bargain purchase gain |
$ |
|
|
Agua Libre Midstream and water-related assets from Basic Energy Services Acquisition
On October 1, 2021, the Company completed the acquisition of certain assets of Agua Libre Midstream, LLC (“Agua Libre”) and other water-related assets, operations and assumed liabilities from Basic Energy Services, Inc. (“Basic”) for total initial consideration of $
F-21
The Agua Libre and Basic Acquisition was accounted for as a business combination under the acquisition method of accounting. When determining the fair values of assets acquired and liabilities assumed, management made estimates, judgments and assumptions. The Company also engaged third-party valuation experts to assist in the purchase price allocation. These estimates, judgments and assumptions and valuation of the property and equipment acquired, current assets, current liabilities and long-term liabilities were finalized as of September 30, 2022. The assets acquired and liabilities assumed are included in the Company’s Water Services and Water Infrastructure segments. The Company incurred $
The following table summarizes the consideration transferred and the estimated fair value of identified assets acquired and liabilities assumed as of the date of acquisition:
Purchase price allocation |
Amount |
||
Consideration transferred |
(in thousands) |
||
Class A common stock ( |
$ |
|
|
Cash paid |
|
||
Total consideration transferred |
|
||
Less: identifiable assets acquired and liabilities assumed |
|||
Working capital |
( |
||
Property and equipment |
|
||
Right-of-use assets |
|
||
Long-term ARO |
( |
||
Long-term lease liabilities |
( |
||
Total identifiable net assets acquired |
|
||
Bargain Purchase Gain |
( |
||
Fair value allocated to net assets acquired, net of bargain purchase gain |
$ |
|
|
UltRecovery Acquisition
On August 2, 2021, the Company acquired substantially all of the assets of UltRecovery Corporation (“UltRecovery”), a provider of sustainable production enhancement applications focused on existing conventional and unconventional oil and gas wells (the “UltRecovery Acquisition”). The Company paid consideration of $
The UltRecovery Acquisition was accounted for as a business combination under the acquisition method of accounting. When determining the fair values of assets acquired, management made estimates, judgments and assumptions. These estimates, judgments and assumptions and valuation of the inventory, property and equipment and intellectual property acquired were finalized as of December 31, 2021. The assets acquired are included in the Company’s Chemical Technologies segment.
F-22
The following table summarizes the consideration transferred and the estimated fair value of identified assets acquired as of the date of acquisition:
Purchase price allocation |
|
Amount |
|
Consideration transferred and estimated earn-out liability |
|
(in thousands) |
|
Cash paid |
$ |
|
|
Estimated earn-out liability assumed |
|
||
Total purchase price |
|
|
|
Less: identifiable assets acquired |
|
|
|
Inventory |
|
|
|
Property and equipment |
|
|
|
Patents and other intellectual property |
|
|
|
Total identifiable net assets acquired |
|
|
|
Fair value allocated to net assets acquired |
$ |
|
|
Complete Energy Services Acquisition
On July 9, 2021, the Company completed the acquisition (the “Complete Acquisition”) of Complete Energy Services, Inc. (“Complete”), an operating subsidiary of Superior Energy Services, Inc. (“Superior”) for initial consideration of $
The Complete Acquisition was accounted for as a business combination under the acquisition method of accounting. When determining the fair values of assets acquired and liabilities assumed, management made estimates, judgments and assumptions. The Company also engaged third-party valuation experts to assist in the purchase price allocation. These estimates, judgments and assumptions and valuation of the property and equipment acquired, current assets, current liabilities and long-term liabilities were finalized as of June 30, 2022. The assets acquired and liabilities assumed are included in the Company’s Water Services and Water Infrastructure segments. The Company incurred $
F-23
The following table summarizes the consideration transferred and the estimated fair value of identified assets acquired and liabilities assumed as of the date of acquisition:
Purchase price allocation |
Amount |
||
Consideration transferred |
(in thousands) |
||
Class A common stock ( |
$ |
|
|
Cash paid |
|
||
Total consideration transferred |
|
|
|
Less: identifiable assets acquired and liabilities assumed |
|
||
Working capital |
|
|
|
Property and equipment |
|
|
|
Right-of-use assets |
|
|
|
Other long-term assets |
|
||
Long-term ARO |
( |
||
Long-term lease liabilities |
( |
||
Total identifiable net assets acquired |
|
||
Bargain Purchase Gain |
|
( |
|
Fair value allocated to net assets acquired, net of bargain purchase gain |
|
$ |
|
NOTE 4—ABANDONMENTS AND OTHER COSTS
On February 21, 2023, the Company announced a rebranding initiative that occurred during the first half of 2023. As a result of this initiative, our existing trademarks are no longer considered indefinite-lived and will be measured for abandonment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that its carrying value may not be recoverable. The rebranding announcement qualified as a triggering event, and the Company tested the existing trademarks for abandonment. This evaluation included significant judgment, including discount rates based on our weighted-average cost of capital and the royalty rate. This resulted in $
A summary of impairments to and abandonment of property and equipment for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021 is as follows:
Year ended December 31, |
|||||||||
|
2023 |
2022 |
|
2021 |
|||||
(in thousands) |
|||||||||
Abandonment of property and equipment |
|||||||||
Water Services |
$ |
|
$ |
— |
$ |
— |
|||
Water Infrastructure |
|
— |
— |
||||||
Total abandonment of property and equipment |
$ |
|
$ |
— |
$ |
— |
|||
F-24
A summary of severance and lease abandonment costs for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021 is as follows:
Year ended December 31, |
|||||||||
|
2023 |
2022 |
|
2021 |
|||||
(in thousands) |
|||||||||
Severance |
|||||||||
Selling, general and administrative |
— |
— |
|
||||||
Total severance expense |
$ |
— |
$ |
— |
$ |
|
|||
Lease abandonment costs |
|||||||||
Water Services |
$ |
|
$ |
|
$ |
|
|||
Water Infrastructure |
|
( |
|
||||||
Chemical Technologies |
|
|
— |
||||||
Other |
— |
|
|
||||||
Total lease abandonment costs |
$ |
|
$ |
|
$ |
|
|||
During the year ended December 31, 2021, the Company incurred $
NOTE 5—REVENUE
The Company follows ASU 2014-09, Revenue from Contracts with Customers (Topic 606), for most revenue recognition, which provides a five-step model for determining revenue recognition for arrangements that are within the scope of the standard: (i) identify the contract(s) with a customer; (ii) identify the performance obligations in the contract; (iii) determine the transaction price; (iv) allocate the transaction price to the performance obligations in the contract; and (v) recognize revenue when (or as) the entity satisfies a performance obligation. The Company applies the five-step model only to contracts when it is probable that we will collect the consideration the Company is entitled to in exchange for the goods or services the Company transfers to the customer. The accommodations and rentals revenue continues to be guided by ASC 842 – Leases, which is discussed further below.
The following factors are applicable to all
| ● | The vast majority of Water Services and Chemical Technologies customer agreements are short-term, lasting less than one year. Water Infrastructure contains both short-term and long-term agreements. |
| ● | Contracts are seldom combined together as virtually all of our customer agreements constitute separate performance obligations. Each job is typically distinct, thereby not interdependent or interrelated with other customer agreements. |
| ● | Most contracts allow either party to terminate at any time without substantive penalties. If the customer terminates the contract, the Company is unconditionally entitled to the payments for the services rendered and products delivered to date. |
| ● | Contract terminations before the end of the agreement are rare. |
| ● | Sales returns are rare and no sales return assets have been recognized on the balance sheet. |
| ● | There are minimal volume discounts. |
F-25
| ● | There are no service-type warranties. |
| ● | There is no long-term customer financing. |
| ● | Taxes assessed by government authorities included on customer invoices are excluded from revenue. |
In the Water Services and Water Infrastructure segments, performance obligations arise in connection with services provided to customers in accordance with contractual terms, in an amount the Company expects to collect. Services are generally sold based upon customer orders or contracts with customers that include fixed or determinable prices. Revenues are generated by services rendered and measured based on the output generated, which is usually simultaneously received and consumed by customers at their job sites. As a multi-job site organization, contract terms, including the pricing for the Company’s services, are negotiated on a job site level on a per-job basis. Most jobs are completed in a short period of time, usually between one day and one month. Revenue is recognized as performance obligations are completed on a daily, hourly or per unit basis with unconditional rights to consideration for services rendered reflected as accounts receivable trade, net of allowance for credit losses. In cases where a prepayment is received before the Company satisfies its performance obligations, a contract liability is recorded in accrued expenses and other current liabilities. Final billings generally occur once all of the proper approvals are obtained. Mobilization and demobilization are factored into the pricing for services. Billings and costs related to mobilization and demobilization are not material for customer agreements that start in one period and end in another. As of December 31, 2023, the Company had
Accommodations and rentals revenue is included in the Water Services segment and the Company accounts for accommodations and rentals agreements as an operating lease. The Company recognizes revenue from renting equipment on a straight-line basis. Accommodations and rental contract periods are generally daily, weekly or monthly. The average lease term is less than three months and as of December 31, 2023, there were no material rental agreements in effect lasting more than one year. During 2023, 2022 and 2021, approximately $
In the Chemical Technologies segment, the typical performance obligation is to provide a specific quantity of chemicals to customers in accordance with the customer agreement in an amount the Company expects to collect. Products and services are generally sold based upon customer orders or contracts with customers that include fixed or determinable prices. Revenue is recognized as the customer takes title to chemical products in accordance with the agreement. Products may be provided to customers in packaging or delivered to the customers’ containers through a hose. In some cases, the customer takes title to the chemicals upon consumption from storage containers on their property, where the chemicals are considered inventory until customer usage. In cases where the Company delivers products and recognizes revenue before collecting payment, the Company usually has an unconditional right to payment reflected in accounts receivable trade, net of allowance for credit losses. Customer returns are rare and immaterial, and there were no material in-process customer agreements for this segment as of December 31, 2023 lasting greater than one year.
F-26
The following table sets forth certain financial information with respect to the Company’s disaggregation of revenues by geographic location:
Year ended December 31, |
|||||||||
|
2023 |
2022 |
|
2021 |
|||||
(in thousands) |
|||||||||
Geographic Region |
|||||||||
Permian Basin |
$ |
|
$ |
|
$ |
|
|||
Rockies |
|
|
|
||||||
Eagle Ford |
|
|
|
||||||
Marcellus/Utica |
|
|
|
||||||
Mid-Continent |
|
|
|
||||||
Bakken |
|
|
|
||||||
Haynesville/E. Texas |
|
|
|
||||||
Eliminations and other regions |
( |
( |
( |
||||||
Total |
$ |
|
$ |
|
$ |
|
|||
In the Water Services segment, the most recent top
NOTE 6—LEASES
As of December 31, 2023, the Company was the lessee for
The Company’s operating leases are primarily for (i) housing personnel for operations, (ii) operational yards for storing and staging equipment, (iii) vehicles and equipment used in operations, (iv) facilities used for back-office functions and (v) equipment used for back-office functions. The majority of the Company’s long-term lease expenses are at fixed prices.
Leases with an initial term of 12 months or less are not recorded on the consolidated balance sheets and the Company recognizes lease expense for these leases on a straight-line basis over the lease term. The Company has a significant number of short-term leases, including month-to-month agreements, some of which continue in perpetuity until the lessor or the Company terminates the lease agreement. The majority of the Company’s lease expenses are in connection with short-term agreements, including expenses incurred hourly, daily, monthly and for other durations of time of one year or less. Due to the volatility of the price of a barrel of oil and the short-term nature of the vast majority of customer agreements, the Company must have flexibility to continuously scale operations at multiple locations. Consequently, the Company avoids committing to long-term agreements with numerous equipment rentals, vehicle fleet agreements and man-camp agreements, unless a business case supports a longer term agreement. Consequently, the Company’s future lease commitments as of December 31, 2023 do not reflect all of the Company’s short-term lease commitments.
Certain short-term and month-to-month vehicle and equipment leases have residual value guarantees if the Company decides to turn in vehicles and equipment before the end of the lease term. Vehicles and equipment turned in early result in sale proceeds, which have historically been equal to or greater than the residual value guarantees. There are no residual value guarantees if the vehicles or equipment is fully paid off.
F-27
When available, the Company uses the rate implicit in the lease to discount lease payments to present value; however, most of the Company’s leases do not provide a readily determinable implicit rate. Therefore, the Company estimates the incremental borrowing rate based on what it would pay to borrow on a collateralized basis, over a similar term based on information available at lease commencement.
The Company’s lease arrangements may contain both lease and non-lease components. The Company has elected to combine and account for lease and non-lease components as a single lease component for its leases.
The Company’s variable lease costs are comprised of variable royalties, variable common area maintenance, and variable reimbursement of lessor insurance and property taxes. Variable lease costs were $
The lease disclosures in this “Note 6—Leases” exclude revenue governed by the lease standard associated with the Company’s accommodations and rentals business, as all customer agreements are short-term. See “Note 5—Revenue” for a comprehensive discussion on revenue recognition.
The financial impact of leases is listed in the tables below:
As of December 31, |
||||||||
Balance Sheet |
|
Classification |
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
||
(in thousands) |
||||||||
Assets |
||||||||
Right-of-use assets(1) |
$ |
|
$ |
|
||||
Finance lease assets |
|
|
||||||
Liabilities |
||||||||
Operating lease liabilities ― ST |
$ |
|
$ |
|
||||
Operating lease liabilities ― LT |
|
|
||||||
Finance lease liabilities ― ST |
|
|
||||||
Finance lease liabilities ― LT |
|
|
||||||
| (1) |
Right-of-use asset impairment of |
F-28
Year ended December 31, |
|||||||||||
Statements of Operations and Cash Flows |
|
Classification |
|
2023 |
2022 |
2021 |
|||||
(in thousands) |
|||||||||||
Operating lease cost: |
|||||||||||
Operating lease cost ― fixed |
Cost of revenue and selling, general and administrative |
$ |
|
$ |
|
$ |
|
||||
Lease abandonment costs |
Lease abandonment costs |
|
|
|
|||||||
Short-term agreements: |
Cost of revenue |
$ |
|
$ |
|
$ |
|
||||
Finance lease cost: |
|||||||||||
Amortization of leased assets |
Depreciation and amortization |
$ |
|
$ |
|
$ |
|
||||
Interest on lease liabilities |
Interest expense, net |
|
|
|
|||||||
Lessor income: |
|||||||||||
Sublease income |
Cost of revenue, selling, general and administrative and lease abandonment costs |
$ |
|
$ |
|
$ |
|
||||
Lessor income |
Cost of revenue |
|
|
|
|||||||
Statement of cash flows |
|||||||||||
Cash paid for operating leases |
Operating cash flows |
$ |
|
$ |
|
$ |
|
||||
Cash paid for finance leases lease interest |
Operating cash flows |
|
|
|
|||||||
Cash paid for finance leases |
Financing cash flows |
|
|
|
|||||||
As of December 31, |
||||||
Lease Term and Discount Rate |
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
||
Weighted-average remaining lease term (years) |
||||||
Operating leases |
||||||
Finance leases |
||||||
Weighted-average discount rate |
||||||
Operating leases |
|
% |
|
% |
||
Finance leases |
|
% |
|
% |
||
F-29
The Company has the following operating and finance lease commitments as of December 31, 2023:
Period |
|
Operating Leases(1) |
|
Finance Leases |
|
Total |
|||
(in thousands) |
|||||||||
2024 |
$ |
|
$ |
|
$ |
|
|||
2025 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
2026 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
2027 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
2028 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|||
Thereafter |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|||
Total minimum lease payments |
$ |
|
$ |
|
$ |
|
|||
Less reconciling items to reconcile undiscounted cash flows to lease liabilities: |
|
||||||||
Lease-extension commencing in the future |
|
— |
|
||||||
Short-term leases excluded from balance sheet |
|
— |
|
||||||
Imputed interest |
|
|
|
||||||
Total reconciling items |
|
|
|
||||||
$ |
|
$ |
|
$ |
|
||||
| (1) |
The table above excludes sublease and lessor income of $ |
NOTE 7—INVENTORIES
Inventories, which are comprised of chemicals and raw materials available for resale and parts and consumables used in operations, are valued at the lower of cost and net realizable value, with cost determined under the weighted-average method. The significant components of inventory are as follows:
As of December 31, |
||||||
2023 |
|
2022 |
||||
(in thousands) |
||||||
Raw materials |
$ |
|
$ |
|
||
Finished goods |
|
|
|
|
||
Total |
$ |
|
$ |
|
||
During the year ended December 31, 2023, the Company recorded charges to the reserve for excess and obsolete inventory of $
F-30
NOTE 8—PROPERTY AND EQUIPMENT
Property and equipment consists of the following as of December 31, 2023 and 2022:
As of December 31, |
||||||
2023 |
|
2022 |
||||
(in thousands) |
||||||
Machinery and equipment |
$ |
|
$ |
|
||
Buildings and leasehold improvements |
|
|
|
|
||
Gathering and disposal infrastructure |
|
|
|
|
||
Recycling facilities |
|
|
||||
Pipelines |
|
|
||||
Vehicles and equipment |
|
|
|
|
||
Land |
|
|
||||
Computer equipment and software |
|
|
||||
Office furniture and equipment |
|
|
|
|
||
Machinery and equipment - finance lease |
|
|
|
|
||
Vehicles and equipment - finance lease |
|
|
|
|
||
Computer equipment and software - finance lease |
|
|
|
|
||
Construction in progress |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|||
Less accumulated depreciation(1) |
|
( |
|
( |
||
Total property and equipment, net |
$ |
|
$ |
|
||
| (1) |
Includes $ |
Total depreciation and amortization expense related to property and equipment and finance leases presented in the table above, as well as amortization of intangible assets presented in “Note 9—Goodwill and Other Intangible Assets” is as follows:
Year ended December 31, |
|||||||||
|
2023 |
2022 |
|
2021 |
|||||
(in thousands) |
|||||||||
Category |
|||||||||
Depreciation expense from property and equipment |
$ |
|
$ |
|
$ |
|
|||
Amortization expense from finance leases |
|
|
|
||||||
Amortization expense from intangible assets |
|
|
|
||||||
Accretion expense from asset retirement obligations |
|
|
|
||||||
Total depreciation and amortization |
$ |
|
$ |
|
$ |
|
|||
Long-lived assets are evaluated for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying amount of an asset may not be recoverable. See “Note 4—Abandonments and Other Costs” for impairment and abandonment of property and equipment during the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021.
NOTE 9—GOODWILL AND OTHER INTANGIBLE ASSETS
The Company recorded $
F-31
The changes in the carrying amounts of goodwill by reportable segment for the year ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 is as follows:
Water |
Water |
||||||||
|
Services |
|
Infrastructure |
|
Total |
||||
(in thousands) |
|||||||||
Balance as of December 31, 2022 |
$ |
— |
$ |
— |
$ |
— |
|||
Additions |
|
|
|
||||||
Balance as of December 31, 2023 |
$ |
|
$ |
|
$ |
|
|||
The components of other intangible assets as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
As of December 31, 2023 |
As of December 31, 2022 |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
Gross |
|
|
Accumulated |
|
Net |
|
Gross |
|
Accumulated |
|
Net |
|||||||||
Value |
Abandonment |
Amortization |
Value |
Value |
Amortization |
Value |
|||||||||||||||
(in thousands) |
(in thousands) |
||||||||||||||||||||
Definite-lived |
|||||||||||||||||||||
Customer relationships |
$ |
|
$ |
— |
$ |
( |
$ |
|
$ |
|
$ |
( |
$ |
|
|||||||
Patents and other intellectual property |
|
— |
( |
|
|
( |
|
||||||||||||||
Trademarks |
|
( |
( |
— |
— |
— |
— |
||||||||||||||
Other |
|
— |
( |
|
|
|
|
( |
|
|
|||||||||||
Total definite-lived |
|
( |
( |
|
|
( |
|
||||||||||||||
Indefinite-lived |
|||||||||||||||||||||
Water rights |
|
— |
— |
|
|
— |
|
||||||||||||||
Trademarks |
— |
— |
— |
— |
|
— |
|
||||||||||||||
Total indefinite-lived |
|
— |
— |
|
|
— |
|
||||||||||||||
Total other intangible assets, net |
$ |
|
$ |
( |
$ |
( |
$ |
|
$ |
|
$ |
( |
$ |
|
|||||||
For a discussion of the abandonment of the trademark, See “Note 4—Abandonments and Other Costs.”
During the year ended December 31, 2023, the Company added $
The indefinite-lived rights and are generally subject to renewal every to
F-32
Amortization expense of $
Year Ending December 31, |
|
Amount |
|
(in thousands) |
|||
2024 |
$ |
|
|
2025 |
|
|
|
2026 |
|
|
|
2027 |
|
|
|
2028 |
|
|
|
Thereafter |
|
||
Total |
$ |
|
|
NOTE 10—DEBT
Sustainability-linked credit facility and revolving line of credit
On March 17, 2022 (the “Restatement Date”), SES Holdings and Select Water Solutions, LLC (“Select LLC”), formerly Select Energy Services, LLC and a wholly-owned subsidiary of SES Holdings, entered into a $
The Sustainability-Linked Credit Facility permits extensions of credit up to the lesser of $
Borrowings under the Sustainability-Linked Credit Facility bear interest, at Select LLC’s election, at either the (a) one- or three-month Term SOFR (as defined in the Sustainability-Linked Credit Facility) or (b) greatest of (i) the federal funds rate plus
F-33
otherwise applicable interest rate. The Sustainability-Linked Credit Facility is scheduled to mature on the fifth anniversary of the Restatement Date.
Level |
Average Excess Availability |
Base Rate Margin |
SOFR Margin |
|||
I |
< 33.33% of the commitments |
|||||
II |
< 66.67% of the commitments and ≥ 33.33% of the commitments |
|||||
III |
≥ 66.67% of the commitments |
Level |
Average Revolver Usage |
Unused Line Fee Percentage |
||
I |
≥ 50% of the commitments |
|||
II |
< 50% of the commitments |
Under the Sustainability-Linked Credit Facility, the interest rate margin and the facility fee rates are also subject to adjustments based on Select LLC’s performance of specified sustainability target thresholds with respect to (i) total recordable incident rate, as the Employee Health and Safety Metric and (ii) barrels of produced water recycled at permanent or semi-permanent water treatment and recycling facilities owned or operated, as the Water Stewardship Metric, in each case, subject to limited assurance verification by a qualified independent external reviewer. The adjustment for the interest rate margin is a range of plus and minus
The obligations under the Sustainability-Linked Credit Facility are guaranteed by SES Holdings and certain subsidiaries of SES Holdings and Select LLC and secured by a security interest in substantially all of the personal property assets of SES Holdings, Select LLC and their domestic subsidiaries.
The Sustainability-Linked Credit Facility contains certain customary representations and warranties, affirmative and negative covenants and events of default. If an event of default occurs and is continuing, the lenders may declare all amounts outstanding under the Sustainability-Linked Credit Facility to be immediately due and payable.
In addition, the Sustainability-Linked Credit Facility restricts SES Holdings’ and Select LLC’s ability to make distributions on, or redeem or repurchase, its equity interests, except for certain distributions, including distributions of cash so long as, both at the time of the distribution and after giving effect to the distribution, no default exists under the Sustainability-Linked Credit Facility and either (a) excess availability at all times during the preceding
The Sustainability-Linked Credit Facility also requires SES Holdings to maintain a fixed charge coverage ratio of at least
Certain lenders party to the Sustainability-Linked Credit Facility and their respective affiliates have from time to time performed, and may in the future perform, various financial advisory, commercial banking and investment banking services for the Company and its affiliates in the ordinary course of business for which they have received and
F-34
would receive customary compensation. In addition, in the ordinary course of their various business activities, such parties and their respective affiliates may make or hold a broad array of investments and actively trade debt and equity securities (or related derivative securities) and financial instruments (including bank loans) for their own account and for the accounts of their customers, and such investments and securities activities may involve the Company’s securities and/or instruments.
The Company had
In connection with the entry into the Sustainability-Linked Credit Facility, the Company incurred $
The Company was in compliance with all debt covenants as of December 31, 2023.
NOTE 11—COMMITMENTS AND CONTINGENCIES
Litigation
The Company is subject to a number of lawsuits and claims arising out of the normal conduct of its business. The ability to predict the ultimate outcome of such matters involves judgments, estimates and inherent uncertainties. Based on a consideration of all relevant facts and circumstances, including applicable insurance coverage, it is not expected that the ultimate outcome of any currently pending lawsuits or claims against the Company will have a material adverse effect on its consolidated financial position, results of operations or cash flows; however, there can be no assurance as to the ultimate outcome of these matters.
Retentions
We are self-insured up to certain retention limits with respect to workers’ compensation, general liability and vehicle liability matters, and health insurance. We maintain accruals for self-insurance retentions that we estimate using third-party data and claims history.
NOTE 12—EQUITY-BASED COMPENSATION
The SES Holdings 2011 Equity Incentive Plan (the “2011 Plan”) was approved by the board of managers of SES Holdings in April 2011. In conjunction with the private placement of
F-35
includes share recycling provisions that allow shares subject to an award that are withheld or surrendered to the Company in payment of any exercise price or taxes or an award that expires or is cancelled, forfeited or otherwise terminated without actual delivery of the underlying shares of Class A common stock to be considered not delivered and thus available to be granted as new awards under the 2016 Plan.
Currently, the maximum number of shares reserved for issuance under the 2016 Plan is approximately
On February 23, 2022, the Company assumed the Nuverra Environmental Solutions, Inc. 2017 Long Term Incentive Plan (the “2017 Plan”), and the Nuverra Environmental Solutions, Inc. 2018 Restricted Stock Plan for Directors (the “2018 Plan” and, together with the 2017 Plan, the “Assumed Plans”) and certain equity awards outstanding under the Assumed Plans in connection with the Nuverra Acquisition. Under the 2017 Plan, the Company may grant to certain eligible participants who were employees, directors or other service providers of Nuverra prior to the Nuverra Acquisition options, stock appreciation rights, restricted stock, restricted stock units, stock awards, dividend equivalents, other stock-based awards, cash awards, substitute awards, performance awards, or any combination of the foregoing, with respect to up to
The aggregate number of shares of the Company’s Class A common stock available for issuance under the Assumed Plans will be reduced by
Stock Option Awards
The Company has outstanding stock option awards as of December 31, 2023 but there have been
F-36
A summary of the Company’s stock option activity and related information as of and for the year ended December 31, 2023 is as follows:
For the year ended December 31, 2023 |
|||||||||||||
|
Weighted-average |
||||||||||||
Weighted-average |
Weighted-average |
Grant Date Value |
Aggregate Intrinsic |
||||||||||
|
Stock Options |
|
Grant Date Value |
Exercise Price |
|
Term (Years) |
|
Value (in thousands) (a) |
|||||
Beginning balance, outstanding |
|
|
$ |
|
$ |
|
$ |
|
|||||
Expired |
( |
|
|
||||||||||
Ending balance, outstanding |
|
|
$ |
|
$ |
|
$ |
— |
|||||
Ending balance, exercisable |
|
$ |
— |
$ |
|
$ |
— |
||||||
Nonvested as of December 31, 2023 |
— |
N/A |
$ |
— |
|||||||||
| (a) |
Aggregate intrinsic value for stock options is based on the difference between the exercise price of the stock options and the quoted closing Class A common stock price of $ |
The Company recognized $
Restricted Stock Awards
The value of the restricted stock awards granted was established by the market price of the Class A common stock on the date of grant and is recorded as compensation expense ratably over the vesting term, which is generally to
A summary of the Company’s restricted stock awards activity and related information for the year ended December 31, 2023 is as follows:
For the year ended December 31, 2023 |
|||||
Weighted-average |
|||||
|
Restricted Stock Awards |
|
Grant Date Fair Value |
||
Nonvested as of December 31, 2022 |
|
$ |
|
||
Granted |
|
|
|||
Vested |
( |
|
|||
Forfeited |
( |
|
|||
Nonvested as of December 31, 2023 |
|
$ |
|
||
Performance Share Units (“PSUs”)
During 2021, 2022 and 2023, the Company approved grants of PSUs that are subject to both performance-based and service-based vesting provisions related to (i) return on asset performance (“ROA”) in comparison to thirteen peer companies and (ii) Adjusted Free Cash Flow (“FCF”) performance percentage. The number of shares of Class A common stock issued to a recipient upon vesting of the PSUs will be calculated based on ROA and FCF performance over the applicable period from either January 1, 2021 through December 31, 2023, January 1, 2022 through December 31, 2024 or January 1, 2023 through December 31, 2025.
The target number of shares of Class A common stock subject to each remaining PSU granted in 2021, 2022 and 2023 is
F-37
stock that may be received in settlement of each PSU can range from
The target PSUs granted in 2021, 2022 and 2023 that become earned connected with the ROA in comparison to other companies will be determined based on the Company’s Average Return on Assets (as defined in the applicable PSU agreement) relative to the Average Return on Assets of the peer companies (as defined in the applicable PSU agreement) in accordance with the following table, but the Company must have a positive Total Shareholder Return (as defined in the applicable PSU agreement) over the performance period. As a result of this market condition, the 2021 2022 and 2023 PSUs will be valued each reporting period utilizing a Black-Scholes model.
Ranking Among Peer Group |
Percentage of Target Amount Earned |
|
Outside of Top 10 |
||
Top 10 |
||
Top 7 |
||
Top 3 |
The target PSUs that become earned in connection with the adjusted FCF performance percentage will be determined (as defined in the applicable PSU agreement) in accordance with the following table:
Adjusted FCF Performance Percentage |
Percentage of Target Amount Earned |
|
Less than 70% |
||
70% |
||
100% |
||
130% |
The fair value on the date the PSUs were granted during 2023, 2022 and 2021 was $
As of December 31, 2023, the unrecognized compensation cost related to our unvested PSUs is estimated to be $
The following table summarizes the information about the PSUs outstanding as of December 31, 2023:
|
PSUs |
|
Nonvested as of December 31, 2022 |
|
|
Target shares granted |
|
|
Target shares forfeited |
( |
|
Target shares outstanding as of December 31, 2023 |
|
F-38
Employee Stock Purchase Plan (ESPP)
The Company formerly had an Employee Stock Purchase Plan (“ESPP”) under which employees that have been continuously employed for at least may purchase shares of Class A common stock at a discount. On November 3, 2022, our board of directors approved an amendment to the ESPP, which suspended all offerings on or after December 1, 2022. Our board of directors reserves the right to recommence offerings pursuant to its discretion and the terms of the ESPP.
Share-repurchases
During the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022, the Company repurchased
The Inflation Reduction Act of 2022 (“IRA 2022”) provides for, among other things, the imposition of a new 1% U.S. federal excise tax on certain repurchases of stock by publicly traded U.S. corporations such as us after December 31, 2022. Accordingly, this excise tax applied to our share repurchase program in 2023 and will apply in subsequent taxable years. The Biden administration has proposed increasing the amount of the excise tax from 1% to 4%; however, it is unclear whether such a change in the amount of the excise tax will be enacted and, if enacted, how soon any such change could take effect.
NOTE 13—FAIR VALUE MEASUREMENT
The Company utilizes fair value measurements to measure assets and liabilities in a business combination or assess impairment and abandonment of property and equipment, intangible assets and goodwill or to measure the value of securities marked to market. Fair value is defined as the amount at which an asset (or liability) could be bought (or incurred) or sold (or settled) in an orderly transaction between market participants at the measurement date. Further, ASC 820, Fair Value Measurements, establishes a framework for measuring fair value, establishes a fair value hierarchy based on the quality of inputs used to measure fair value, and includes certain disclosure requirements. Fair value estimates are based on either (i) actual market data or (ii) assumptions that other market participants would use in pricing an asset or liability, including estimates of risk.
ASC 820 establishes a three-level valuation hierarchy for the disclosure of fair value measurements. The valuation hierarchy categorizes assets and liabilities measured at fair value into one of three different levels depending on the observability of the inputs employed in the measurement. The three levels are defined as follows:
Level 1—Unadjusted quoted prices for identical assets or liabilities in active markets.
Level 2—Quoted prices for similar assets or liabilities in non-active markets, and inputs that are observable for the asset or liability, either directly or indirectly, for substantially the full term of the financial instrument.
Level 3—Inputs that are unobservable and significant to the fair value measurement (including the Company’s own assumptions in determining fair value).
A financial instrument’s categorization within the valuation hierarchy is based upon the lowest level of input that is significant to the fair value measurement. The Company’s assessment of the significance of a particular input to the fair value measurement in its entirety requires judgment and considers factors specific to the asset or liability. There were
F-39
Assets and liabilities measured at fair value on a recurring and non-recurring basis
Nonfinancial assets and liabilities measured at fair value on a non-recurring basis include certain nonfinancial assets and liabilities as may be acquired in a business combination or asset acquisition and measurements of goodwill and intangible impairment. As there is no corroborating market activity to support the assumptions used, the Company has designated these measurements as Level 3.
Long-lived assets, such as property and equipment and finite-lived intangible assets, are evaluated for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that its carrying value may not be recoverable. The development of future cash flows and the estimate of fair value represent the Company’s best estimates based on industry trends and reference to market transactions and are subject to variability.
The Company’s estimates of fair value have been determined at discrete points in time based on relevant information. These estimates involve uncertainty and cannot be determined with precision. There were no significant changes in valuation techniques or related inputs for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021.
The following table presents information about the Company’s assets measured at fair value on a recurring and non-recurring basis for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021.
Fair Value |
|||||||||||||||||||
Measurements Using |
Carrying |
||||||||||||||||||
Level 1 |
Level 2 |
Level 3 |
Value(1) |
Abandonment(2) |
|||||||||||||||
(in thousands) |
|||||||||||||||||||
Year Ended December 31, 2023 |
|||||||||||||||||||
Trademark |
Non-recurring |
March 31 |
$ |
— |
$ |
— |
$ |
|
$ |
|
$ |
|
|||||||
Year Ended December 31, 2022 |
|||||||||||||||||||
Investments |
Recurring |
March 31 |
$ |
|
$ |
— |
$ |
— |
$ |
|
$ |
— |
|||||||
Investments |
Recurring |
June 30 |
|
— |
— |
|
— |
||||||||||||
Year Ended December 31, 2021 |
|||||||||||||||||||
Investments |
Recurring |
March 31 |
$ |
|
$ |
— |
$ |
— |
$ |
|
$ |
— |
|||||||
Investments |
Recurring |
June 30 |
|
— |
— |
|
— |
||||||||||||
Investments |
Recurring |
September 30 |
|
— |
— |
|
— |
||||||||||||
Investments |
Recurring |
December 31 |
|
— |
— |
|
— |
||||||||||||
| (1) | Amount represents carrying value at the date of assessment. |
| (2) | See “Note 4—Abandonments and Other Costs for more information on the abandonments reflected above and incurred during the year ended December 31, 2023. |
Nonmonetary transaction: During the year ended December 31, 2020, the Company had a nonmonetary exchange with a customer whereby the customer settled a $
F-40
The Company sold most of these securities during 2021 for $
Other fair value considerations
Also, see “Note 3—Acquisitions” for a discussion of the fair value incorporated into the purchase price allocation for acquisitions occurring during the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021.
The carrying values of the Company’s current financial instruments, which include cash and cash equivalents, accounts receivable trade and accounts payable, approximate their fair value as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 due to the short-term nature of these instruments. The Company had
NOTE 14—RELATED PARTY TRANSACTIONS
The Company considers its related parties to be those stockholders who are beneficial owners of more than
During the year ended December 31, 2023, sales to related parties were $
During the year ended December 31, 2022, sales to related parties were $
During the year ended December 31, 2021, sales to related parties were $
Tax Receivable Agreements
In connection with the Select 144A Offering, the Company entered into the Tax Receivable Agreements with certain then-affiliates of the then-holders of SES Holdings LLC Units. As of December 31, 2023, certain of the TRA Holders were employed by the Company, on the Company’s board of directors and/or owned shares of the Company’s Class A and/or Class B common stock.
F-41
The first of the Tax Receivable Agreements, which the Company entered into with Legacy Owner Holdco and Crestview GP, generally provides for the payment by the Company to such TRA Holders of
The second of the Tax Receivable Agreements, which the Company entered into with an affiliate of Legacy Owner Holdco and Crestview GP, generally provides for the payment by the Company to such TRA Holders of
On June 23, 2023, the Tax Receivable Agreements were amended to replace references to one year LIBOR with references to the 12-month term SOFR published by CME Group Benchmark Administration Limited plus
The Company has recognized a liability associated with the Tax Receivable Agreements as of December 31, 2023 of $
NOTE 15—INCOME TAXES
Select Inc. is subject to U.S. federal and state income taxes as a corporation. SES Holdings and its subsidiaries, with the exception of certain corporate subsidiaries, are treated as flow-through entities for U.S. federal income tax purposes and as such, are generally not subject to U.S. federal income tax at the entity level. Rather, the tax liability with respect to their taxable income is passed through to their members or partners. Select Inc. recognizes a tax liability on its allocable share of SES Holdings’ taxable income.
The Company’s effective tax rates for the years ended
F-42
The components of the federal and state income tax (benefit) expense are summarized as follows:
For the year ended |
|||||||||
December 31, |
|||||||||
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
2021 |
||||
(in thousands) |
|||||||||
Current tax expense (benefit) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Federal income tax expense |
$ |
|
$ |
|
$ |
|
|||
State and local income tax expense (benefit) |
|
|
|
|
|
( |
|||
Total current expense (benefit) |
|
|
|
|
|
( |
|||
Deferred tax (benefit) expense |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Federal income tax (benefit) expense |
|
( |
|
— |
|
|
|||
State and local income tax (benefit) expense |
|
( |
|
( |
|
|
|||
Total deferred (benefit) expense |
|
( |
|
( |
|
|
|||
Total income tax (benefit) expense |
$ |
( |
$ |
|
$ |
|
|||
Tax (benefit) expense attributable to controlling interests |
$ |
( |
$ |
|
$ |
|
|||
Tax expense attributable to noncontrolling interests |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Total income tax (benefit) expense |
$ |
( |
$ |
|
$ |
|
|||
A reconciliation of the Company’s provision for income taxes as reported and the amount computed by multiplying income before taxes, less noncontrolling interest, by the U.S. federal statutory rate of
|
For the year ended December 31, |
|||||||||||
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
2021 |
||||||||
(in thousands) |
||||||||||||
Provision calculated at federal statutory income tax rate: |
|
|
|
|
||||||||
Income (loss) before equity in losses of unconsolidated entities and taxes |
$ |
|
$ |
|
$ |
( |
||||||
Equity in losses of unconsolidated entities |
( |
( |
( |
|||||||||
Income (loss) before taxes |
|
|
( |
|||||||||
Statutory rate |
|
|
% |
|
|
% |
|
|
% |
|||
Income tax expense (benefit) computed at statutory rate |
|
|
|
|
|
( |
||||||
Less: noncontrolling interests |
|
( |
|
( |
|
|
||||||
Income tax expense (benefit) attributable to controlling interests |
|
|
|
|
|
( |
||||||
State and local income taxes, net of federal benefit |
|
|
|
|
|
( |
||||||
State rate change |
|
|
|
|
|
( |
||||||
Change in subsidiary tax status |
— |
— |
|
|||||||||
Deferred tax adjustments |
|
|
|
|||||||||
Change in valuation allowance |
|
( |
|
( |
|
|
||||||
Nondeductible items |
|
|
|
|||||||||
Income tax (benefit) expense attributable to controlling interests |
|
( |
|
|
|
|
||||||
Income tax expense attributable to noncontrolling interests |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
Total income tax (benefit) expense |
$ |
( |
$ |
|
$ |
|
||||||
F-43
Deferred taxes result from the temporary differences between financial reporting carrying amounts and the tax basis of existing assets and liabilities. As of December 31, 2023, and 2022, the Company had net deferred tax assets of $
For the year ended |
||||||
December 31, |
||||||
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|||
(in thousands) |
||||||
Deferred tax assets |
|
|
|
|
||
Outside basis difference in SES Holdings |
$ |
|
$ |
|
||
Net operating losses |
|
|
|
|
||
Credits and other carryforwards |
|
|
|
|
||
Other |
|
|
||||
Total deferred tax assets before valuation allowance |
|
|
|
|
||
Valuation allowance |
( |
( |
||||
Total deferred tax assets |
|
|
||||
Deferred tax liabilities |
|
|
|
|
||
Property and equipment |
|
|
|
|
||
Other |
|
|
|
|
||
Total deferred tax liabilities |
|
|
|
|
||
Net deferred tax assets |
$ |
|
$ |
( |
||
For the year ended December 31, 2023, the Company recorded a net decrease in valuation allowance of $
We regularly review our deferred tax assets for realization and establish a valuation allowance if it is more likely than not that some portion or all of a deferred tax asset will not be realized. Historically, we have maintained a full valuation allowance against our deferred tax assets. The Company considers all available positive and negative evidence in determining whether realization of the tax benefit is more likely than not. This evidence includes historical income / loss, projected future income, the expected timing of the reversal of existing temporary differences and the implementation of tax planning strategies. During the fourth quarter of 2023, the Company evaluated all available positive and negative evidence and determined that $
As of December 31, 2023, the Company and certain of its corporate subsidiaries had approximately $
Accounting for uncertainty in income taxes prescribes a recognition threshold and measurement methodology for the financial statement recognition and measurement of a tax position taken or expected to be taken in a tax return.
F-44
As of December 31, 2023 and 2022 there was
Separate U.S. federal and state income tax returns are filed for Select Inc., SES Holdings and certain consolidated affiliates. The tax years 2019 through 2022 remain open to examination by the major taxing jurisdictions in which the Company is subject to income tax. During 2021, the Louisiana Department of Revenue completed its audits of the corporate income and franchise tax returns of Select Inc. and Select Western, a corporate subsidiary of SES Holdings, for the years ended 2016 through 2018. The audits did not result in a material assessment.
NOTE 16—NONCONTROLLING INTERESTS
The Company’s noncontrolling interests fall into two categories as follows:
| ● | Noncontrolling interests attributable to joint ventures formed for water-related services. |
| ● | Noncontrolling interests attributable to holders of Class B common stock. |
As of December 31, |
||||||
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|||
(in thousands) |
||||||
Noncontrolling interests attributable to joint ventures formed for water-related services |
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|
Noncontrolling interests attributable to holders of Class B common stock |
|
|
|
|
||
Total noncontrolling interests |
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|
During the year ended December 31, 2023, the Company received $
During the year ended December 31, 2022, the Company acquired $
F-45
During the year ended December 31, 2021, the Company initiated the dissolution of one of its water-related services joint ventures and increased its ownership in another joint venture, which combined, eliminated $
For the year ended December 31, |
||||||||||
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
2021 |
|||||
(in thousands) |
||||||||||
Net income (loss) attributable to Select Water Solutions, Inc. |
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
( |
||
Transfers from (to) noncontrolling interests: |
|
|
|
|
||||||
Increase in additional paid-in capital due to purchase of noncontrolling interest |
— |
|
— |
|||||||
Increase (decrease) in additional paid-in capital as a result of issuing shares for business combinations |
|
( |
|
|||||||
Decrease in additional paid-in capital as a result of stock option exercises |
|
— |
|
|
( |
|
|
— |
||
Increase in additional paid-in capital as a result of restricted stock issuance, net of forfeitures |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Increase (decrease) in additional paid-in capital as a result of the repurchase of SES Holdings LLC Units |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
( |
||
(Decrease) increase in additional paid-in capital as a result of the Employee Stock Purchase Plan shares issued |
— |
( |
|
|||||||
Change to equity from net income (loss) attributable to Select Water Solutions, Inc. and transfers from noncontrolling interests |
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
( |
||
NOTE 17— INCOME (LOSS) PER SHARE
Income (loss) per share is based on the amount of income (loss) allocated to the stockholders and the weighted-average number of shares outstanding during the period for each class of common stock. Outstanding options to purchase
The following tables present the Company’s calculation of basic and diluted earnings per share for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021 (dollars in thousands, except share and per share amounts):
Year ended December 31, 2023 |
|||||||||
|
Select Water Solutions, Inc. |
|
Class A |
|
Class B |
||||
Numerator: |
|||||||||
Net income |
$ |
|
|||||||
Net income attributable to noncontrolling interests |
( |
||||||||
Net income attributable to Select Water Solutions, Inc. — basic |
$ |
|
$ |
|
$ |
— |
|||
Add: Reallocation of net income attributable to noncontrolling interests for the dilutive effect of restricted stock |
|
|
— |
||||||
Add: Reallocation of net income attributable to noncontrolling interests for the dilutive effect of performance units |
|
|
— |
||||||
Net income attributable to Select Water Solutions, Inc. — diluted |
$ |
|
$ |
|
$ |
— |
|||
Denominator: |
|||||||||
Weighted-average shares of common stock outstanding — basic |
|
|
|||||||
Dilutive effect of restricted stock |
|
— |
|||||||
Dilutive effect of performance share units |
|
— |
|||||||
Weighted-average shares of common stock outstanding — diluted |
|
|
|||||||
Income per share: |
|||||||||
Basic |
$ |
|
$ |
— |
|||||
Diluted |
$ |
|
$ |
— |
|||||
F-46
Year ended December 31, 2022 |
|||||||||
Select Water Solutions, Inc. |
Class A |
Class B |
|||||||
Numerator: |
|||||||||
Net income |
$ |
|
|||||||
Net income attributable to noncontrolling interests |
( |
||||||||
Net income attributable to Select Water Solutions, Inc. — basic |
$ |
|
$ |
|
$ |
— |
|||
Add: Reallocation of net income attributable to noncontrolling interests for the dilutive effect of restricted stock |
|
|
— |
||||||
Add: Reallocation of net income attributable to noncontrolling interests for the dilutive effect of performance units |
|
|
— |
||||||
Net income attributable to Select Water Solutions, Inc. — diluted |
$ |
|
$ |
|
$ |
— |
|||
Denominator: |
|||||||||
Weighted-average shares of common stock outstanding — basic |
|
|
|||||||
Dilutive effect of restricted stock |
|
— |
|||||||
Dilutive effect of performance share units |
|
— |
|||||||
Dilutive effect of ESPP |
|
— |
|||||||
Weighted-average shares of common stock outstanding — diluted |
|
|
|||||||
Income per share: |
|||||||||
Basic |
$ |
|
$ |
— |
|||||
Diluted |
$ |
|
$ |
— |
|||||
Year ended December 31, 2021 |
|||||||||
Select Water Solutions, Inc. |
Class A |
Class B |
|||||||
Numerator: |
|||||||||
Net loss |
$ |
( |
|||||||
Net loss attributable to noncontrolling interests |
|
||||||||
Net loss attributable to Select Water Solutions, Inc. — basic |
$ |
( |
$ |
( |
$ |
— |
|||
Net loss attributable to Select Water Solutions, Inc. — diluted |
$ |
( |
$ |
( |
$ |
— |
|||
Denominator: |
|||||||||
Weighted-average shares of common stock outstanding — basic |
|
|
|||||||
Weighted-average shares of common stock outstanding — diluted |
|
|
|||||||
Loss per share: |
|||||||||
Basic |
$ |
( |
$ |
— |
|||||
Diluted |
$ |
( |
$ |
— |
|||||
NOTE 18—SEGMENT INFORMATION
Select Inc. is a leading provider of sustainable water-management and chemical solutions to the oil and gas industry in the U.S. The Company’s services are offered through
The Company’s CODM assesses performance and allocates resources on the basis of the following
Water Services — The Water Services segment consists of the Company’s services businesses, including water sourcing, water transfer, flowback and well testing, fluids hauling, water monitoring, water containment and water network automation, primarily serving E&P companies. Additionally, this segment includes the operations of our accommodations and rentals business.
Water Infrastructure — The Water Infrastructure segment consists of the Company’s fixed infrastructure assets, including operations associated with our water distribution pipeline infrastructure, our water recycling solutions, and our produced water gathering systems and saltwater disposal wells, as well as solids disposal facilities, primarily serving E&P companies.
F-47
Chemical Technologies — The Chemical Technologies segment provides technical solutions, products and expertise related to chemical applications in the oil and gas industry. We develop, manufacture, manage logistics and provide a full suite of chemicals used in hydraulic fracturing, stimulation, cementing and well completions for customers ranging from pressure pumpers to major integrated and independent oil and gas producers. This segment also utilizes its chemical experience and lab testing capabilities to customize tailored water treatment solutions designed to optimize the fracturing fluid system in conjunction with the quality of water used in well completions.
Financial information by segment for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021 is as follows:
For the year ended December 31, 2023 |
|||||||||||||||
|
Impairments and |
|
Income |
|
Depreciation and |
|
Capital |
||||||||
Revenue |
abandonments |
before taxes |
Amortization |
Expenditures |
|||||||||||
(in thousands) |
|||||||||||||||
Water Services |
$ |
|
$ |
|
$ |
|
$ |
|
$ |
|
|||||
Water Infrastructure |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
Chemical Technologies |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
Other |
— |
— |
( |
— |
— |
||||||||||
Eliminations |
|
( |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|||||
Income from operations |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
Corporate |
|
— |
|
— |
|
( |
|
|
|
|
|||||
Interest expense, net |
|
— |
|
— |
|
( |
|
— |
|
— |
|||||
Tax receivable agreements expense |
— |
— |
( |
— |
— |
||||||||||
Other income, net |
|
— |
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
— |
|||||
$ |
|
$ |
|
$ |
|
$ |
|
$ |
|
||||||
For the year ended December 31, 2022 |
||||||||||||
|
Income |
|
Depreciation and |
|
Capital |
|||||||
Revenue |
before taxes |
Amortization |
Expenditures |
|||||||||
(in thousands) |
||||||||||||
Water Services |
$ |
|
$ |
|
$ |
|
$ |
|
||||
Water Infrastructure |
|
|
|
|
||||||||
Chemical Technologies |
|
|
|
|
||||||||
Other |
— |
( |
— |
— |
||||||||
Eliminations |
|
( |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
||||
Income from operations |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Corporate |
|
— |
|
( |
|
|
|
|
||||
Interest expense, net |
|
— |
|
( |
|
— |
|
— |
||||
Bargain purchase gain |
— |
|
— |
— |
||||||||
Other income, net |
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
— |
||||
$ |
|
$ |
|
$ |
|
$ |
|
|||||
F-48
For the year ended December 31, 2021 |
||||||||||||
|
Loss |
|
Depreciation and |
|
Capital |
|||||||
Revenue |
before taxes |
Amortization |
Expenditures |
|||||||||
(in thousands) |
||||||||||||
Water Services |
$ |
|
$ |
( |
$ |
|
$ |
|
||||
Water Infrastructure |
|
( |
|
|
||||||||
Chemical Technologies |
|
|
|
|
||||||||
Other |
— |
( |
— |
— |
||||||||
Eliminations |
|
( |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
||||
Loss from operations |
|
|
|
( |
|
|
|
|
||||
Corporate |
|
— |
|
( |
|
|
|
|
||||
Interest expense, net |
|
— |
|
( |
|
— |
|
— |
||||
Bargain purchase gain |
— |
|
— |
— |
||||||||
Other expense, net |
|
— |
|
( |
|
— |
|
— |
||||
$ |
|
$ |
( |
$ |
|
$ |
|
|||||
Total assets by segment as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
As of December 31, |
||||||
2023 |
2022 |
|||||
(in thousands) |
||||||
Water Services |
$ |
|
$ |
|
||
Water Infrastructure |
|
|
|
|||
Chemical Technologies |
|
|
|
|||
Other |
|
|
||||
$ |
|
$ |
|
|||
Revenue by groups of similar products and services is as follows:
For the year ended December 31, |
|||||||||
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
2021 |
|||||
(in thousands) |
|||||||||
Water transfer and monitoring |
$ |
|
$ |
|
$ |
|
|||
Chemical technologies |
|
|
|
||||||
Fluids hauling |
|
|
|
||||||
Flowback and well testing |
|
|
|
||||||
Water recycling and reuse |
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Disposals |
|
|
|
||||||
Accommodations and rentals |
|
|
|
|
|||||
Water containment |
|
|
|
||||||
Water sourcing |
|
|
|
||||||
Pipelines and logistics |
|
|
|
||||||
Eliminations and other service lines |
|
( |
|
( |
( |
||||
$ |
|
$ |
|
$ |
|
||||
NOTE 19—SUBSEQUENT EVENT
On January 29, 2024, we announced the acquisition of strategic water infrastructure assets in the Haynesville Shale and Rockies regions for approximately $
F-49
significant portfolio of interconnected gathering pipelines, strategic surface acreage and right-of-way, and multiple long-term pipeline gathering and dedication contracts.
F-50